Part of these ruins lies by the Litani River in the Bekaa Valley of Lebanon from the Roman period, but most of these remains are believed to originate from an even older civilization.
When we think of ancient civilizations, we often envision the pyramids of Egypt, the Parthenon in Greece, the Colosseum in Rome, and so on.
These are masterpieces in human history, showcasing the intellect and artistry of various cultures and eras. However, there is a mysterious site that may challenge our understanding of human civilization.
This site also serves as evidence of a previous generation of civilization. The Temple of the Sun at Baalbek, also known as the largest Temple of Jupiter in Rome, is most commonly referred to as Baalbek Temple.
Today, it is often considered a site of ancient Rome, but in reality, it may be a product of a fusion between Phoenicia and Rome. Archaeologists also refer to it as the last civilization site, because there are inexplicable artifacts found here.
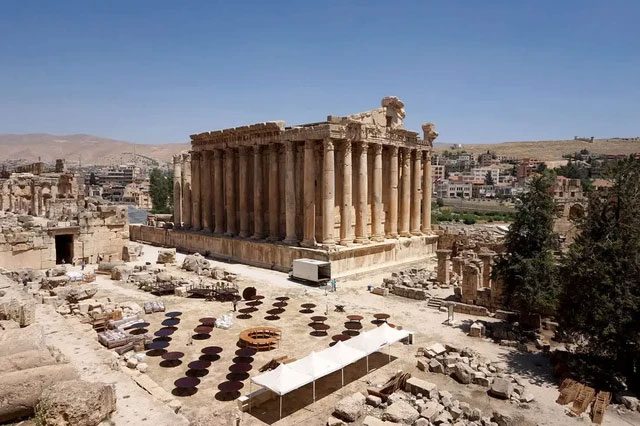

The Temple of the Sun at Baalbek, known as the largest Temple of Jupiter in Rome, is commonly referred to as Baalbek Temple. (Image: CNN).
The Baalbek Sun Temple is located in Lebanon and is a true megalithic city. The scale of the megaliths here is much larger than that of the ancient Egyptian pyramids. The most notable features inside the temple are three enormous stone bases. On these stone bases, there are numerous stone columns, statues, stone steps, and gates in various sizes and shapes, all embodying the wisdom and craftsmanship of ancient peoples.
However, what is truly impressive are the three platforms of the Baalbek Temple. These stones measure 21 meters in length, 4 meters in height, and 3 meters in width, meticulously cut into rectangular shapes and placed so tightly that not even a needle can fit in between. Importantly, these three stones are raised 4 meters off the ground, with the heaviest stone weighing over 1,400 tons, and the smallest weighing around 1,200 tons. The stone slabs beneath the stones also weigh 350 tons each. Standing before these stones, one seems incredibly small.

These retaining walls are formed from various sized megaliths. (Image: CNN).
Along the walkway of this temple, pre-cut stones are placed, each weighing over 800 tons. There are artificial holes on the surfaces of these stones, showcasing the remarkable craftsmanship of ancient peoples.
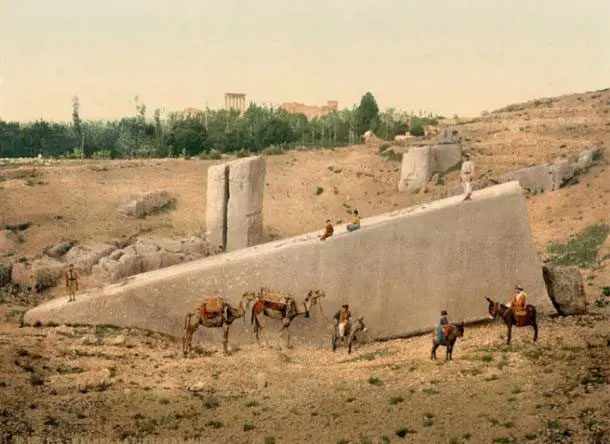
Outside the temple lies a stone that is unmovable, measuring 19.6 meters in length, 6 meters in height, 5.5 meters in width, and weighing approximately 1,650 tons. This stone is partially buried in the ground, with some traces of cutting and drilling on its surface. The purpose of this stone remains a mystery. Some believe it was brought by the Romans or an earlier civilization to construct a building or monolithic statue, but for some reason, it was never completed. However, what perplexes many is how they could transport it here?

What perplexes scientists is how ancient people could transport such large monolithic stones to the exact construction site of the temple. (Image: Ancient-origins)
Archaeologists speculate that the pyramid stones were built and transported by the Egyptians based on river principles or rolling logs. However, this theory does not apply to the case of Baalbek.
Firstly, Baalbek lacks canals, so it would be impossible to float the stones on rafts. Secondly, these stones weigh over 1,000 tons; if transported with rolling logs, the logs would be crushed beneath them. Even if they could be transported to the designated location using rolling logs, how were they lifted and placed four meters off the ground?
Transporting and elevating the megaliths are entirely different techniques. Some suggest that ancient peoples may have used simple machines like levers, pulleys, and ropes to achieve this feat. However, the operational principles and effectiveness of these machines are limited, requiring a vast amount of manpower and time to haul and lift these stones.
Furthermore, the materials used for these machines must be durable and sturdy; otherwise, they risk breaking or failing easily. Some scholars have conducted experiments where they lifted a one-ton stone using logs and found that 16 people took 22 hours to move it 500 to 700 meters. If scaled, moving a 1,000-ton stone would require 16,000 people and 22,000 hours. This is clearly impractical.

These giant stones have left archaeologists with many unanswered questions. With today’s technology, it would require 24 heavy cranes just to lift it, but moving it is a different story. (Image: Ancient-origins).
If the incredible trio of megaliths does not astound you, then beneath the Baalbek temple lies some ancient and more mysterious structures. These buildings may be traces of the Phoenicians or an earlier civilization, or they may serve as evidence of a previous generation of civilization.
According to archaeological studies, the foundations of the Baalbek Sun Temple and the buildings above were not constructed simultaneously. In other words, it is unknown who built the foundational stones below, while the later Phoenicians or Romans built the Baalbek temple above these foundational stones.
It is speculated that the construction of this monument may date back approximately 9,000 years, while the temple above was built around 3,000 BC.
It is commonly believed that the temple was built by the Phoenicians. They referred to this place as Baalbek, where “Beck” means city, while “Baal” is the name of the sun god of the Phoenicians and Canaanites. The Phoenicians who later lived here mysteriously disappeared, and the Romans took over the area, turning it into a Roman site.
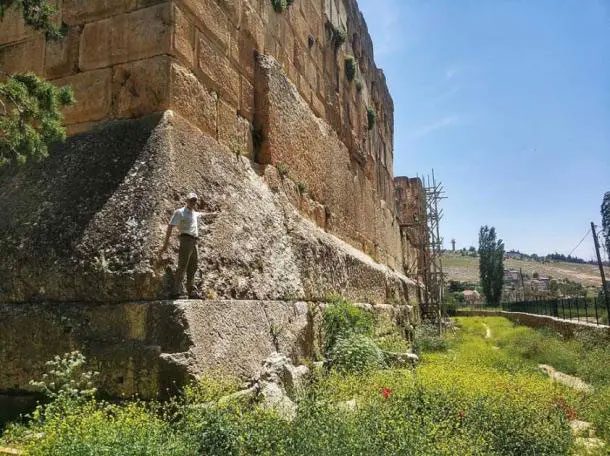

The Trilithon is a group of three megaliths used in the foundation of the Baalbek Temple. (Image: Ancient-origins).
The construction process of the Baalbek Temple remains a mystery. One hypothesis suggests that the Baalbek Temple was built by the Romans or earlier civilizations, employing some advanced technologies and methods that were not beyond human capabilities.
According to this theory, the Baalbek Temple was originally a Phoenician worship center dedicated to the sun god and the moon goddess Astarte. Another hypothesis posits that the Baalbek Temple was constructed by an ancient civilization, using techniques and methods that surpass the understanding of modern humanity. This argument suggests that the Baalbek Temple predates the Phoenicians or Romans and may have been built by extraterrestrials or ancient supercivilizations to serve as an energy station or communication hub.
Many also believe that the Baalbek Temple is not just an ordinary temple but also an astronomical observatory. The stones here are not placed randomly but arranged according to specific rules and orientations.
These stones may have been used to observe the movements of the sun, moon, stars, and planets, even predicting the occurrences of solar eclipses, lunar eclipses, and comets.
Both assertions have some basis and reasoning but also contain certain flaws and controversies. As of now, there are still no definite answers. For many, the Baalbek Temple is not merely an ancient architectural complex but also a repository of ancient knowledge. It records not only the history and culture of ancient civilizations but also conveys the beliefs and wisdom of these civilizations. It allows us to ponder and imagine more about the origins of human civilization, while also offering us more hope and optimism for the future of human civilization.