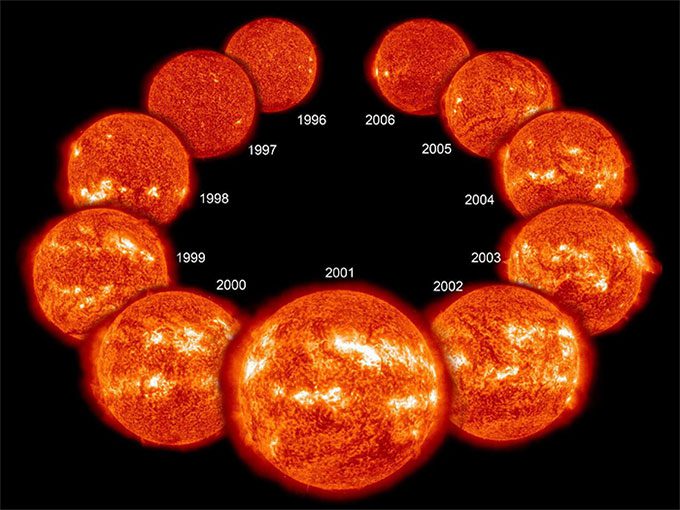
By observing changes in the number of sunspots, scientists have discovered that solar activity shows periodic changes.
In the vast universe, the Sun seems to be the most reliable ally of Earth. However, intriguingly, recent scientific studies suggest that the Sun is entering a state of inactivity, with its activity significantly decreasing. This shocking discovery raises an intriguing question: Are we heading towards a new Ice Age?
The Inactive Sun and Its Effects: Will Earth’s Temperature Decrease?
With advancements in technology and human space exploration, our understanding of the Sun has deepened. The Sun is the source of life for all things on Earth, and its energy maintains Earth’s temperature and climate. However, recent research indicates that the Sun may enter a dormant state, which will have profound consequences for Earth.

The Sun is one of the essential conditions for the existence of life on Earth. Its light and heat provide energy for Earth and maintain the climate and environment. (Photo: ZME).
By observing changes in the number of sunspots, scientists have discovered that solar activity shows periodic changes. Each cycle lasts about 11 years or longer and is referred to as a solar cycle. During active periods, the number of sunspots is high, and the intensity of solar radiation is also elevated. In inactive periods, the number of sunspots gradually decreases, along with a corresponding weakening of solar radiation intensity.
After the Sun enters an inactive state, the decrease in solar radiation intensity will lead to a drop in Earth’s temperature. Solar radiation is the primary source of heat in the atmosphere and on Earth’s surface. When solar radiation decreases, the heat provided to Earth’s surface diminishes, resulting in lower temperatures. This cooling could have irreversible effects on ecosystems, climate, and melting glaciers on Earth.
The global climate system is a complex network of interactions, where solar radiation is a key factor. A reduction in solar radiation can alter atmospheric circulation patterns, thereby affecting global climate patterns. For instance, some regions may experience colder winters with increased snowfall, while others may become drier.
Many plant and animal species grow and reproduce under the conditions of solar radiation and temperature. A decrease in solar radiation could hinder plant growth, affecting the balance of food chains and biodiversity. Additionally, the Sun’s dormant period could disrupt the migration and breeding habits of some animal species, adversely affecting their survival and reproduction capabilities.
According to scientists’ research, the Sun could also enter a prolonged dormant state, negatively impacting agriculture and the ecological environment. (Photo: NPR)
The Sun’s dormancy could exacerbate global warming issues. While the weakening solar activity may lead to lower Earth temperatures, this does not mean that the trend of global warming will be reversed. Human-induced greenhouse gas emissions remain the primary cause, and the Sun’s inactivity will only provide a temporary respite from global warming trends. However, the temperature drop following the Sun’s inactivity could worsen issues related to climate change, such as rising sea levels and increasing extreme weather events.
Prolonged Cold Weather
The principle of the Sun’s periodic dormancy and the discovery that the Sun has a cycle of activity changes approximately every 11 years, including the number of sunspots, coronal activity, and solar flares, is a topic that scientists have not yet fully clarified. However, there is increasing observational data and simulation experiments supporting this hypothesis.
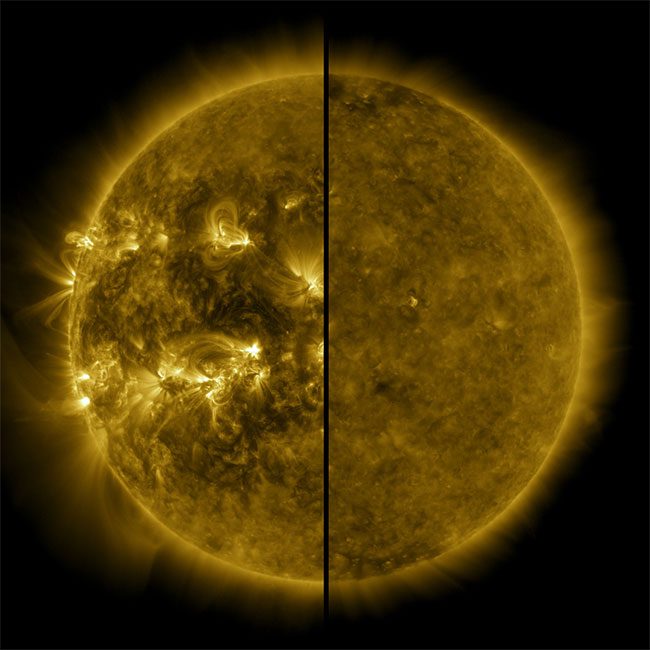

After the Sun enters an inactive state, the decrease in solar radiation intensity will lead to a drop in Earth’s temperature. (Photo: Zhihu)
Research shows that when the Sun is inactive, it emits less energy, causing temperatures on Earth to drop. A decrease in solar radiation could lead Earth into a cold climate phase, similar to the Little Ice Age experienced previously. The Little Ice Age refers to the period from the 14th to the 19th century when Earth’s temperatures were relatively low. This could significantly impact life on Earth and the environment.
The growth cycle of plants may shorten, and vegetation cover could decrease, affecting the food supply for herbivores. Colder climates may also lead to changes in animal migration patterns, putting some species at risk of extinction.
Restricted agriculture could lead to food shortages, increasing the risk of famine and social instability. Cold climatic conditions could also facilitate the spread of infectious diseases, as pathogens spread more easily at lower temperatures. Meanwhile, the energy demand of human society would rise, as people require more energy for heating.

Restricted agriculture could lead to food shortages, increasing the risk of famine and social instability. (Photo: Zhihu).
Negative Impacts on Agriculture and Ecology
The Sun’s inactive state will lead to unusual climate changes. Solar activity is closely linked to climate change. The temperature and radiation from the Sun’s flames impact Earth’s climate system.
When the Sun is inactive, solar radiation decreases. This will lead to a drop in average temperatures on Earth and a colder climate. A colder climate will negatively affect the growth and development of crops, reducing agricultural yields. Additionally, a colder climate may also impact the supply and distribution of water resources, further affecting the stability of agricultural production.
A reduction in solar activity means a decrease in solar radiation, which will impact the photosynthesis process in plants. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants synthesize nutrients by absorbing sunlight and carbon dioxide. It not only provides energy for plants but also produces oxygen.
However, if solar radiation decreases, the photosynthesis process in plants will be inhibited, significantly affecting the balance of the ecosystem. The restricted growth of plants will also impact other organisms in the food chain, leading to ecosystem instability and reduced biodiversity.


















































