Just a handful of soil can be valued at up to 9 billion USD, making it difficult even for the super-rich to afford due to its rarity. So, what kind of soil is this?
The most expensive soil in the world is actually Mars dust. According to experts, a handful of Mars dust could potentially be auctioned for as much as 9 billion USD. This can be considered the most expensive dust in the Milky Way.
Mars dust holds immense value because it would take up to a decade, billions of dollars, and three space missions to bring it to Earth.
Specifically, on July 30, 2020, an Atlas V rocket was launched from the Earth’s surface to Mars. The cost of a single rocket launch is approximately 109 million USD. Moreover, the rocket was carrying the Perseverance rover and the Ingenuity helicopter. This journey lasted about seven months.

Simulation of the Perseverance rover on Mars. (Photo: Reuters).
By February 18, 2021, the Atlas V rocket finally reached its destination. The landing module carrying the rover and the small helicopter entered Mars’ atmosphere. According to experts, this assembly was moving faster than the speed of sound and was protected by a heat shield to prevent the valuable robots inside from burning due to high temperatures.
After successfully landing on the surface of Mars, the Perseverance rover began the sample collection process, officially embarking on a mission to bring back the most expensive dust particles known to humanity in history.

Simulation of the Ingenuity helicopter on Mars. (Photo: NASA).
Bringing Mars dust back to Earth is not an easy task
In fact, this phase has been underway for a long time on Earth. The Perseverance rover carries 43 titanium tubes. Each tube can hold a soil sample about the size of a pinky finger.
Notably, while preparing these tubes in a laboratory on Earth, scientists blew some air through them and then immersed them in a container filled with acetone and other chemicals. This was done to ensure that no bacteria remained inside. The tubes were then placed in a furnace heated to 300 degrees Fahrenheit for 29 hours.
When the Perseverance rover collects samples in these tubes, they can be stored there for at least 10 years. Meanwhile, lunar soil samples stored in sealed boxes can only be preserved for 10 days. Scientists hope to find traces of living organisms in these soil samples.
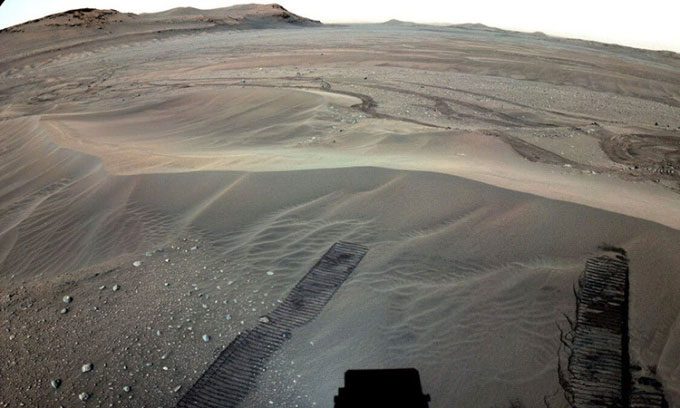

In a photo from the Perseverance rover, NASA reveals the location of the first extraterrestrial sample storage facility on Mars. (Photo: NASA).
Additionally, another goal of the Perseverance rover is to test technology that can produce oxygen right on Mars. To achieve this, the MOXIE experiment, which stands for Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resources Utilization Experiment, was initiated.
This small tool on Perseverance, NASA’s Mars exploration rover, is managed by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and is designed to convert CO2, which makes up about 96% of the Martian atmosphere, into breathable oxygen. This is extremely crucial for the mission to send humans to Mars.
If this technology succeeds, it will be scaled up by 200 times. In this way, scientists will generate enough oxygen for astronauts to breathe and enough fuel for the rocket to be launched back to Earth.
Thus, NASA’s 2.7 billion USD rover (including design, construction, and maintenance costs) will collect soil and rock samples until 2023. However, this rover will leave the sealed tubes containing samples right on the Martian surface.

Collecting soil on Mars is not easy. It requires a lot of time and money. Therefore, a handful of Mars dust could be valued at up to 9 billion USD. (Photo: BS).
Nearly a decade later, these samples will be collected. By the time of sampling, NASA will need another rover. Naturally, a new mission will require several billion USD for development. After that, the rover will take up to seven months to reach Mars and will have another complex landing.
The entire sample collection mission is expected to last about five years. Once the new samples are collected and brought back to Earth, they will be ready for study, and humanity will finally discover whether there is life on Mars.
Furthermore, studying soil and rock samples from Mars could help scientists uncover or decode numerous mysteries related to this planet. This is also why Mars dust samples are valued at up to 9 billion USD.