Regarding the origin of life, different people in different eras have various perspectives. Although we know that there are many doubts about Darwin’s theory of evolution, to date, evolution remains the best theory concerning the origin of humanity.
In 2012, the American scientific journal Frontiers launched a survey on “the most beautiful scientific theories.” They invited researchers and humanities scholars to nominate their favorite theories. Approximately several hundred people participated in the survey, where “the theory of evolution” and “the theory of relativity” received significant support.
Dawkins, an Emeritus Professor at the University of Oxford, believes that Darwin’s theory of evolution is one of the best theories. He asserts: “In the history of humanity, no theory can explain so many facts with such simple assumptions.” In fact, the theory of evolution has been praised since its inception, but it has also faced skepticism from that time to the present day.

If evolution was accepted by the scientific community and the public during Darwin’s era, then his theory of selection in the 1930s was seen as the primary explanation for this process, and today it has become the foundation for modern evolutionary theory. (Image: CNN).
In 1859, Darwin published “On the Origin of Species,” sparking widespread controversy and skepticism. For the next hundred years, doubts about the theory of evolution persisted. Especially in recent decades, the phrase “Darwin’s theory of evolution has been disproven” occasionally appeared in newspapers and books. In 2006, a statement signed by over 500 scientists created a stir and quickly spread worldwide, claiming that “500 scientists have questioned Darwin’s theory of evolution.” This left many people bewildered: “Is the theory of evolution truly flawed?”

One of the most notable aspects of Charles Darwin’s “On the Origin of Species” released in 1859 is that he proposed the hypothesis of evolution at a time when scientists were still unaware of how the genetic mechanisms of animal species worked. It wasn’t until 1950, with Watson and Crick’s discovery of DNA, that we gained accurate answers about evolution. (Image: ZME)
Let us revisit the emergence of the theory of evolution and the issues it has addressed. Throughout history, humans have always possessed curiosity and a desire to explore the natural world. People want to answer questions like “What is in the world,” “Where does it come from,” and “Why does it happen?”
At the beginning of the 18th century, with advancements in geographical exploration and biological classification, particularly with Linnaeus’s creation of the “binomial method” for naming organisms, the first question was relatively well answered. However, regarding the second question, the prevailing view at the time was that God created all things. This perspective, however, lacked scientific basis and could not explain the similarities and differences among living beings.
After decades of observation and research, Darwin proposed the hypothesis that species originated from a common ancestor and gradually evolved through natural selection. His theory certainly challenged the creationist view of the world, sparking intense debates about religion and philosophy at the time, while also inspiring scientists to explore the mechanisms of biological evolution.

The development of gene technology is perhaps the most significant contribution to research related to evolutionary biology since Darwin’s hypothesis emerged. DNA exists in all living organisms, implying that all species on Earth may have evolved from a common ancestor. (Image: CNN).
Regarding the third question, Darwin proposed the theory of natural selection, which states that the driving force of evolution arises from the survival of the fittest through natural selection. However, at that time, due to the relative lack of evidence from transitional fossils and the absence of molecular biology theory, Darwin lacked sufficient evidence to support his answer to this question.
Nevertheless, with the richness and development of subsequent scientific research, the theory of evolution has been further reinforced. As more evidence has been discovered, subsequent scholars have incorporated the importance of mutation into the theory of evolution and introduced Mendelian genetic mechanisms to explain inheritance and variation.
This allowed for the development of the theory of evolution based on Darwin’s ideas and the formation of a comprehensive theoretical system of evolution. These developments have made the theory of evolution more complex, and increasingly more people have begun to believe in it. The process of enriching and developing the theory of evolution aligns with the rules of our understanding of phenomena and demonstrates that science is an open and continuously evolving system.
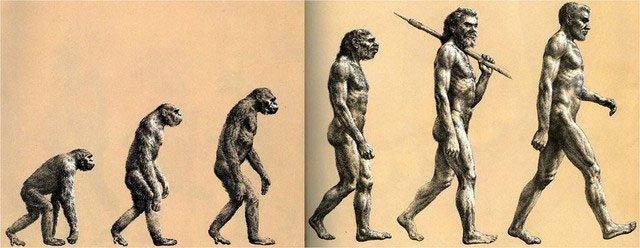
Typically, evolutionary researchers tend to point out the differences between current species and their ancestors while simultaneously searching for similar traits that exist to this day. This enables us to clearly observe the process of evolution and reflects the intricacy involved in species formation. (Image: Zhihu).
Research on biological evolution holds significant meaning for our worldview. Humanity’s understanding of the origins of species will directly impact our perceptions and views of the world.
The theory of evolution has been controversial since its inception, and the debate has never ceased. In fact, fundamentally, the theory of evolution is based on a wealth of scientific foundations and can withstand thorough scrutiny over millions of years. After all, it is merely a hypothesis, and this theory will continue to be improved and refined in the years to come.


















































