The 7.8-meter height of the Great Wall of China is considered low and ineffective in stopping enemy troops. What is the true purpose of this monumental structure built by the emperors?
When thinking of the Great Wall of China, the first name that likely comes to mind is Qin Shi Huang, as he invested significant manpower and resources over a long period to construct the Great Wall.
Most of the Great Wall was built using unremarkable materials such as earth and stones. However, glutinous rice was included in the mortar mix due to its superior adhesive properties. Many studies indicate that the amylopectin compound (a binding agent) found in glutinous rice helps to make the walls more solid and durable.
According to Travel China Guide, “The Great Wall of China is a network of fortifications consisting of numerous walls and fortresses built during different historical periods, with some segments scattered while others run parallel. In some areas, the wall can be twice or even three times as high as in others.”
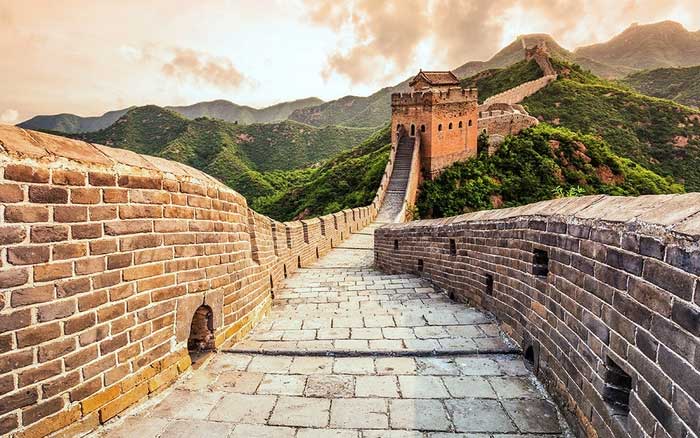

The Great Wall of China is a network of fortifications, consisting of numerous walls and fortresses.
In fact, Qin Shi Huang was not the first to build the Great Wall. During the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods, continuous warfare among the states prompted rulers to order their soldiers to construct segments of walls to defend against invasions from other states.
After Qin Shi Huang unified the six states, these segments were connected to form the winding wall that we recognize today as the Great Wall. The primary purpose of Qin Shi Huang’s construction of the Great Wall was to prevent invasions by nomadic tribes such as the Xiongnu and Donghu.
After many years of construction, the serpentine shape of the Great Wall was formed. However, during the Ming Dynasty, the Great Wall continued to be repaired, reaching a total length of 21,196.18 kilometers and an average height of 7.8 meters, as we see it today.
Nevertheless, in terms of military defense, the height of the walls is considered relatively low, making them less effective in stopping soldiers. So, what was the main purpose of building the Great Wall?
Military Purpose
According to Sohu, the segments of the Great Wall built during the Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods were constructed in rugged and desolate terrains, primarily using local materials such as rammed earth and rubble. However, the low wall height allows a determined army to easily set up ladders and climb over.
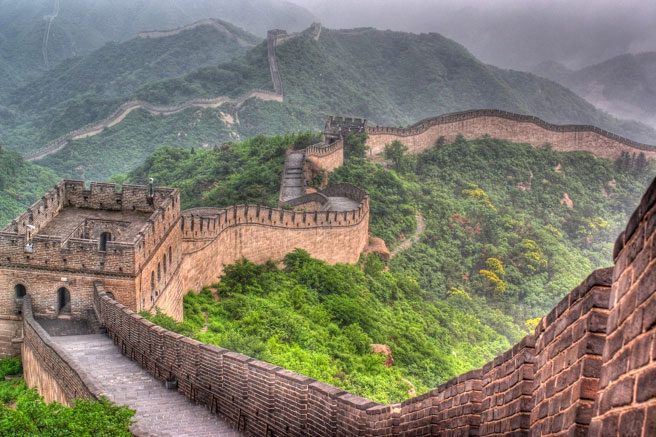

The wall serves as a barrier to prevent cavalry from invading from afar.
Thus, the primary purpose of constructing the Great Wall was to defend against the cavalry of northern nomadic troops. In other words, the wall was not intended to block people but to serve as a barrier to prevent cavalry from thousands of miles away from invading.
The nomadic peoples had an advantage on the battlefield due to their swift and powerful horses. Once deprived of their horses, the combat capabilities of the soldiers would significantly diminish.
Trade Purpose
Besides its military function, the Great Wall also served to economically blockade the nomadic tribes. The natural conditions of the grasslands were primarily favorable for raising livestock such as cattle, sheep, and horses but lacked daily necessities like salt, alcohol, iron, and textiles…

The Great Wall can also economically blockade the nomadic tribes.
After the Great Wall was completed, the nomads could no longer cross the barrier and were forced to rely on traders from the Central Plains for commerce. In addition to selling salt, iron, tea, and other daily necessities to the nomads, traders could also acquire livestock and even rare horses for military use. Additionally, through this trade, people in the Central Plains could collect high taxes from the merchants, enriching the national treasury.