An invisible, mysterious force is pulling our Milky Way at a staggering speed of 12 million miles per hour. This discovery has compelled scientists to face new complex cosmic challenges.
Currently, astrophysicists are grappling with a perplexing issue:
An unseen force is pulling the entire Milky Way, despite the Big Bang theory suggesting that the universe is expanding and objects within it are moving away from each other. However, this mysterious pull is not merely a result of cosmic expansion!
Moreover, some other galaxies are moving at astonishing speeds of up to 22 million miles per hour. So, what is this mysterious force?
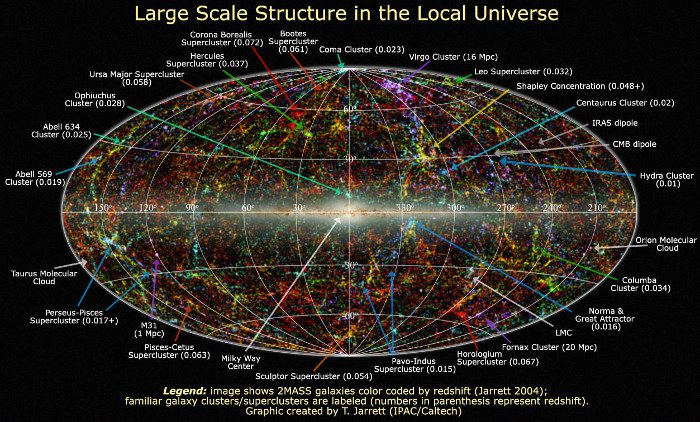
A comprehensive map of the universe projected onto a plane.
Just as the movement of tectonic plates allows researchers to explore what is happening beneath the Earth’s surface, the movement of galaxies provides crucial information about the structure of the universe.
Dark Matter and Dark Energy

Dark matter and dark energy remain a mystery.
Many scientists and astrophysicists have proposed theories regarding dark matter and dark energy – the most enigmatic forms of matter and energy in the universe.
In astrophysics, the term dark matter refers to a hypothetical type of matter in the universe whose composition is not yet understood.
Dark matter neither emits nor reflects enough electromagnetic radiation to be observed using telescopes or current measurement devices.
However, it can be detected through its gravitational effects on solid matter and/or other objects, as well as on the universe as a whole.
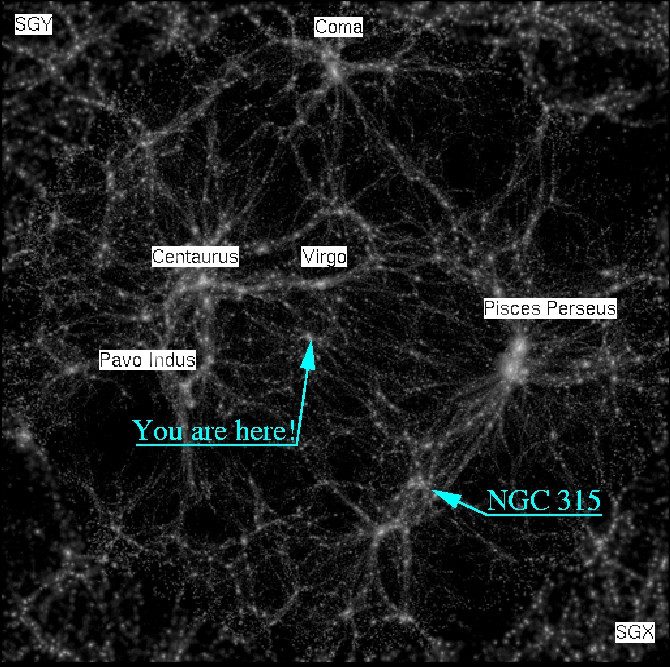
“The Great Attractor.”
Based on our current understanding of larger cosmic structures, as well as widely accepted theories about the Big Bang, scientists believe that:
Dark matter constitutes about 70% of the total matter (dark matter + ordinary matter) in the universe.
Dark energy is a poorly understood form of energy that makes up most of the universe and is thought to accelerate the expansion of the universe.
The dark energy theory has been the most accepted since the 1990s, indicating that the universe is expanding at an increasing rate.
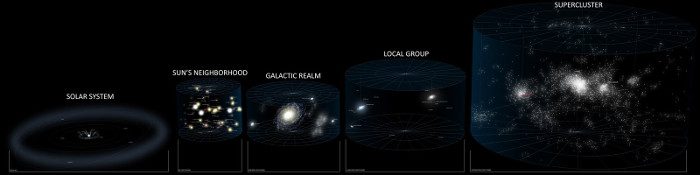
The solar system is just a speck of dust in the universe.
According to the Planck research team and based on the standard model of cosmology, the relative proportions of matter and energy are as follows:
The visible universe contains 26.8% dark matter, 63.8% dark energy, while ordinary matter only accounts for 4.9%.
Once again, according to the relative matter-energy ratio, the density of dark energy (6.91 x 10-27 kg/m3) is extremely low, even lower than the density of ordinary matter and dark matter in galaxies.
Despite this, it dominates the matter-energy composition of the universe because it is spread throughout space.
However, there are other equally compelling hypotheses.

Is our universe not unique?
Interestingly, many researchers have proposed the “multiverse” hypothesis, which suggests the existence of parallel universes (including our own), encompassing everything that exists and can exist:
Space, time, matter, energy, and the laws of physics.
The term “multiverse” was coined in 1895 by American psychologist and philosopher William James. The universes existing within the multiverse are referred to as parallel worlds.
These universes may exert gravitational forces and influence the galaxies within our universe, and researchers believe they are closer to us than we might think.

Many surrounding universes have an impact on us.
If this is true, it would provide compelling evidence for the existence of other universes, and we would need to reevaluate our understanding of the entire cosmos:
Are we alone in the universe, and what mysteries of life might other universes conceal?
Researchers suggest that these surrounding universes influence our universe through gravitational forces, infiltrating our cosmic space.
Some scientists even explain that these forces are the reasons behind the production of dark energy and dark matter.
This invisible force is known as the “Great Attractor”, drawing all galaxies and everything within our universe toward a specific destination in space—about 250 million light-years away.
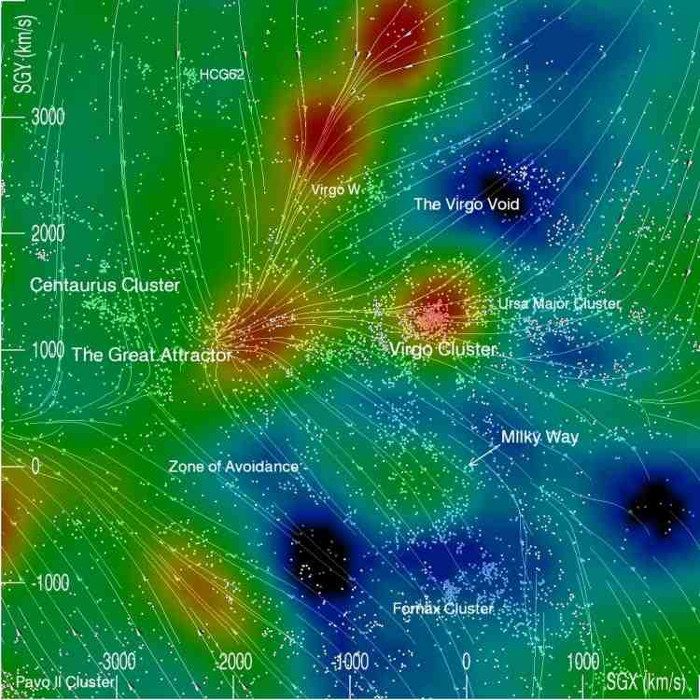
These forces are the reasons behind the production of dark energy and dark matter.
Researchers view this invisible force as an unusual gravitational force located near the Hydra-Centaurus Supercluster and within the center of the Laniakea Supercluster (of which our Milky Way is just a small part).
However, due to the extreme distance and the presence of dust and gas, we cannot accurately pinpoint its location.


















































