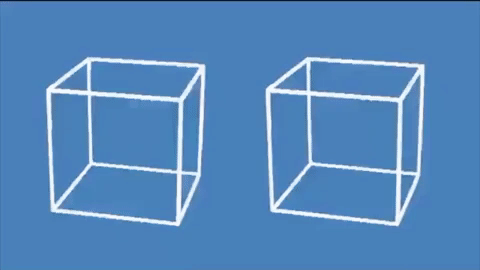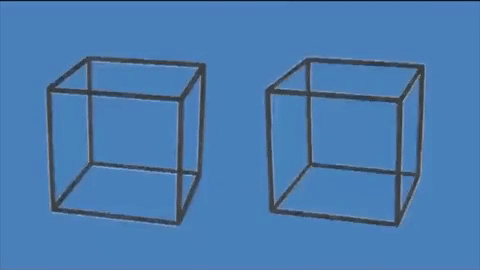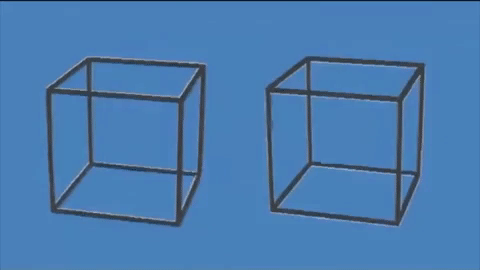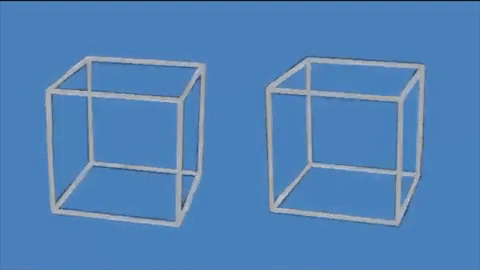
This incredible optical illusion appears to show two 3D cubes moving on a flat surface, but in reality, they remain completely still.
Humans are adept at determining the speed and direction of a moving object just by looking at it. This ability allows us to catch a ball, judge depth, or decide whether it is safe to cross the street. This is achieved by processing changing light patterns into “motion perception”, although many aspects of how this occurs remain poorly understood. Scientists believe it is challenging to directly assess what happens inside the human brain when perceiving motion, and even the best medical technology cannot display the entire system at work.
This animation, shared by various accounts on Twitter such as jagarikin, Science Girl, and non aesthetic things, has garnered significant attention.
The lines of the cubes transitioning between black and white create the illusion that the cubes are moving up and down, rotating, and increasing in size.
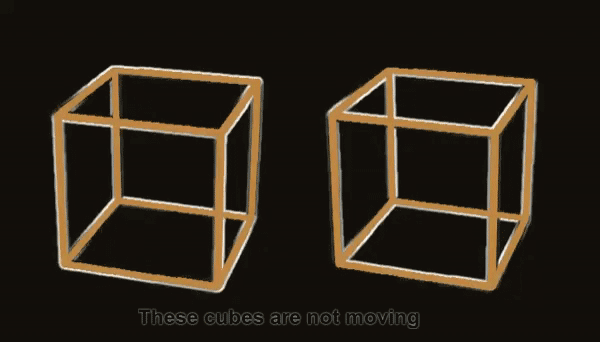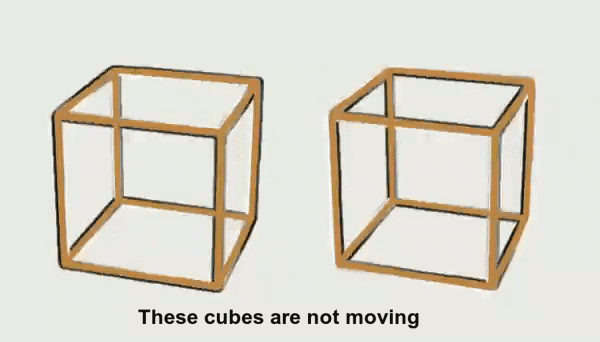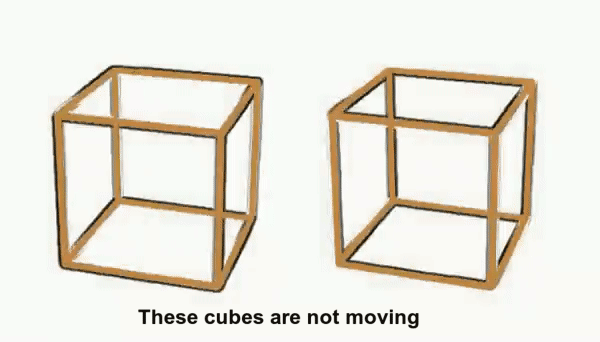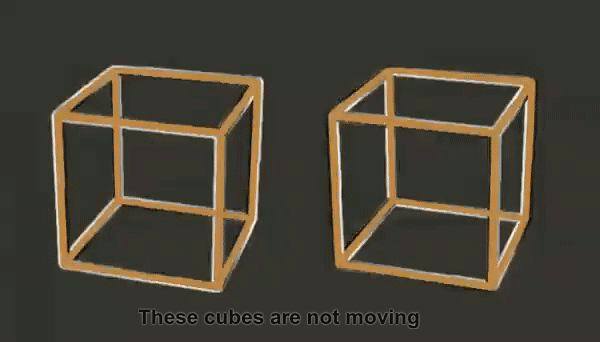
Because our human brains perceive changes in light (such as a cube flickering from light to dark) as motion, it appears that the cubes are moving when in fact they are completely static.
In reality, this visual phenomenon is known as Reverse Phi (Reverse Phi Illusion), and researchers at Stanford University explained how the Reverse Phi Illusion works in 2011.
“If a bright point appears in one position and then reappears in a position shifted to the right, we tend to perceive an object moving from left to right.”
Scientists explain: “It is a fundamental effect and forms the basis for the apparent and fluid motions we see in film and animation.”
Simply put, when our brains notice things transitioning from light to dark, they interpret it as motion. As the edges of the cubes shift from white to gray to black, our brains believe they are rotating.
The brain can be easily tricked. For example, if there is a black dot on the left side of the screen that disappears while another dot appears on the right, the dot seems to move from left to right. Such motion is referred to as ‘Phi’ motion. However, if the dot appearing on the right is white against a dark background, it will appear to move from right to left. This motion is known as “Reverse Phi” motion.
The Reverse Phi Illusion is a type of Phi phenomenon that fades or dissipates from a positive direction to a negative direction that is displaced, thus the apparent motion perceived by humans is opposite to the actual physical displacement. The Reverse Phi Illusion is often demonstrated by black and white patterns.
It is believed that the Reverse Phi Illusion is actually a brightness effect, occurring when an inverted brightness image moves across our retina. It can be explained by the mechanism of the receptive field model of vision, where visual stimuli are synthesized spatially (a process contrary to spatial differentiation).
This spatial synthesis slightly blurs the outlines and thus alters the perceived brightness.