From carbon capture utilizing phytoplankton to 3D reconstruction scanners, scientists are exploring advanced technologies that they believe can reshape humanity for the better. Below are some of the standout technologies of 2023 that have the potential to change the world in the future.
1. Real-Time Monitoring for Disaster Prediction
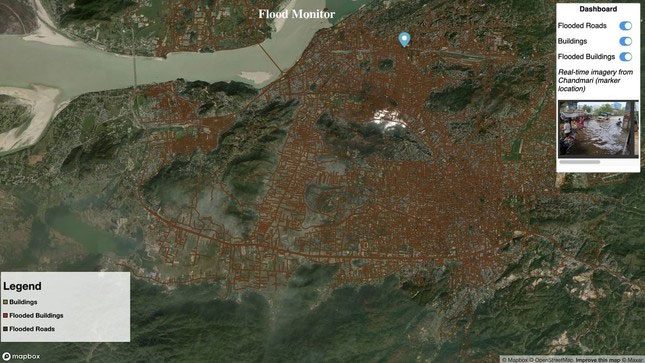
NatCat aims to utilize satellite imagery, remote sensing, and machine learning to assess disaster risks. (Image: Najah Pokkiri/NatCat).
NatCat aims to leverage satellite imagery, remote sensing, and machine learning to evaluate disaster risks in various locations, potentially helping to reduce the threat to the local populations. It may also utilize climate change data to forecast the frequency and intensity of certain natural hazards in the future.
2. Converting Air Moisture into Electrical Energy

Electric Skin – Converting air moisture into electricity using advanced biodegradable materials. (Image: Nada Raafat Elkharashi, Paige Perillat Piratoine, Sequoia Fischer & Catherine Euale).
This project, called Electric Skin, creates self-powered biological materials for electronic devices by harnessing the conductive properties of bacteria found in mud known as Geobacter sulfurrenducens. Specifically, the bacteria’s protein nanowires can generate electricity from the moisture in the air. Scientists have extracted the DNA from the bacteria and infused it into E. coli for production.
To generate energy, the research team embedded the nanowires obtained from E. coli into biodegradable materials to create a textured and flexible membrane that can power electronic devices using air and water.
3. Recycled Bricks for Temperature and Humidity Control

Recycled brick roofing. (Image: Angela Piazza).
Driven by the excessive production of non-recyclable plastics along with the impacts of climate change in southern India, Wastly Roof Tiles will replace conventional roofing tiles with tiles made from recycled materials that can reduce indoor temperatures.
These tiles are created by shredding and melting multilayer plastics, making them lightweight, waterproof, and capable of reflecting heat.
4. Bioplastics

PhytoMat – A nature-based carbon absorption solution utilizing phytoplankton. (Image: Gabriele Troisi & Alberto Perro)
Phytoplankton convert 40% of the carbon dioxide in the atmosphere into the ocean through photosynthesis. With PhytoMat, scientists now aim to harness this natural process on an industrial scale.
PhytoMat is a flexible technology, similar to a mat, installed horizontally and vertically on surfaces, containing recycled materials infused with phytoplankton. As they grow, they absorb carbon dioxide from the surrounding environment and transform it into biomass – organic material that can be reused – before being harvested and sent to recycling plants. This material can then be converted into new products, such as bioplastics.
5. Electric-Free Medical Injection Device for Disaster Areas

Golden Capsule – A medication delivery device optimized for emergency disaster situations. (Image: Yujin Chae).
Using only air pressure and the elasticity of a balloon, Golden Capsule is a device capable of delivering medication intravenously without the need for another person to hold the medication package.
This project differs from other devices as it does not require electricity – making it ideal for use in areas affected by natural disasters.
6. Biodegradable Foam

Carbon Cell will replace harmful polystyrene with new biodegradable foam (Image: Eden Harrison).
Carbon Cell is a biodegradable expandable foam made from biochar – a secret combination of biological components derived from food waste – mixed and expanded using a patented manufacturing process.
This process is similar to injection molding and allows for the rapid production of various shapes and sizes when packaging. Scientists ultimately aim to replace polystyrene, which they consider toxic and harmful to the environment, with the new biodegradable foam.
7. Ultra-Dense Chip
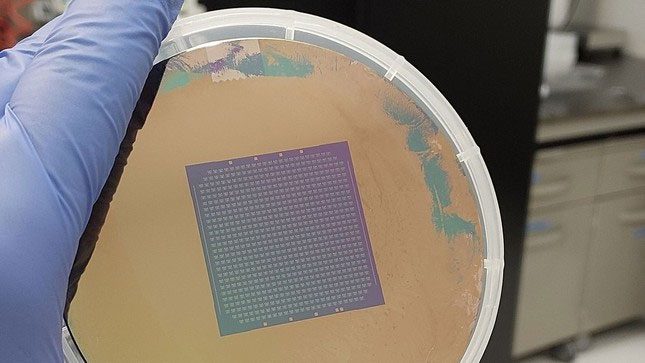
Tasawwur D310 – A new GPU that significantly reduces carbon emissions for AI training operations. (Image: Saravanan Yuvaraja)
Generative AI models require training in large data centers, typically utilizing the power of dedicated graphics cards (GPUs). This means that Generative AI has a substantial carbon footprint. However, Tasawwur D310 is a much more energy-efficient GPU compared to today’s leading GPUs.
This ultra-dense chip – with electronic components packed more closely together and stacked across 10 layers (compared to two layers in one of the leading competitor’s chips, Nvidia) – allows for much faster data exchange, energy savings, and accelerated training processes.
8. Programmable Soft Robots

FlowIO Platform – An advanced platform for soft robots, streamlining the prototyping process with integrated tools (Image: Ali Shtarbanov & Hye Jun Youn)
FlowIO Platform is the world’s first versatile approach for creating prototypes of soft robot components. This tiny device includes integrated pumps and batteries, as well as five programmable ports that users can manipulate through a web browser via Bluetooth connection.
The device also features an integrated battery and ten different sensors. It will allow robotics experts to turn their ideas into reality much faster than before.
9. Drones

FlyVision – A drone-based inspection system for monitoring building safety (Image: Peisen Xu).
FlyVision combines mixed reality with drones to help humans inspect buildings and other spaces more efficiently. Using Microsoft’s HoloLens 2 augmented reality headset, the system provides drone operators with the tools to instantly scan the surrounding environment and create a 3D digital twin in the system. They can then map a path within the space and use that path to guide the drone through its environment.
10. AI-Powered Renewable Energy

Streamlining renewable energy assessments using AI, saving time and money. (Image: Sarah Sausan & Arkanu Andaru).
This software platform, called “Renescout”, utilizes data mining, remote sensing, and AI to better evaluate renewable energy projects, a process that typically takes 18 months.
11. Real-Time Air Pollution Monitoring

Data2Action employs AI algorithms to monitor air pollution in real-time – even in areas lacking air sensors. Manufacturers state that machine learning models also predict potential health outcomes based on exposure to air pollution.




















































