Antioxidants, beta-carotene, folate, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids are food groups recommended for individuals with psoriasis.
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is characterized by patches of skin that flake and form scales. The affected areas may appear pink or red, and can even take on purple or dark brown hues; the scales themselves may be gray, white, or silver. These patches can occur anywhere on the body, but are commonly found on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back.
Psoriasis is a chronic (long-lasting) non-contagious condition that can affect individuals of all ages, but it typically manifests in adults aged 20-30 years and 50-60 years, with the incidence being roughly equal between men and women. Most individuals with psoriasis are only affected by small patches on the skin, but in some cases, the patches can be itchy or painful.
According to Dr. Vu Thi Phuong Thao, Head of the General Planning Department at Ho Chi Minh City Dermatology Hospital, there is currently no specific diet exclusively for psoriasis patients as most studies have not yet established a clear link between diet and this condition.
However, many patients report that certain foods can exacerbate their symptoms, while others can help reduce inflammation caused by psoriasis.
Therefore, experts recommend that the diet of psoriasis patients should include the following five food groups:
Antioxidants
Antioxidants are found in fruits such as grapes, grapefruit, legumes, nuts, apricots, raisins, plums, grains, cloves, and cinnamon. These substances are essential for preventing the formation of leukotrienes, which are one of the culprits that worsen psoriasis.
Beta-Carotene
This group of substances is commonly found in carrots, dark leafy greens, apricots, and mangoes. Beta-carotene aids in the conversion of vitamin A in the body, which is vital for healthy skin.
Folate
Folate is present in grains, lentils, wheat, peas, broccoli, cabbage, and bean sprouts. Folate is important for the division of skin cells, contributing to healthy skin.
Zinc
Zinc is commonly found in shellfish and various grain products. Zinc deficiency is frequently observed in individuals with psoriasis. Therefore, including zinc-rich foods in the diet is advisable.
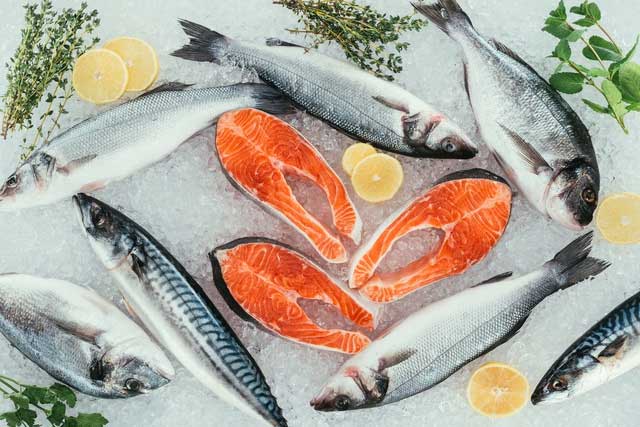

Omega-3 fatty acids are commonly found in fish such as sardines, mackerel, and salmon…
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids, also known as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), are typically found in fish such as sardines, mackerel, and salmon; as well as in flaxseeds, sunflower seeds, and sesame seeds. This group of substances helps psoriasis patients reduce their need for topical corticosteroid treatments without worsening their condition.
Additionally, experts recommend that psoriasis patients limit their intake of foods high in sugar, fried and processed foods, spicy foods, pepper, chocolate, eggs, red meat, and alcoholic beverages to avoid triggering flare-ups.
Moreover, certain foods may increase or decrease the effectiveness of some psoriasis treatments. Therefore, patients should consult their doctors about which foods to avoid while undergoing treatment for optimal results.
Simultaneously, psoriasis patients should maintain a healthy diet along with regular exercise to achieve a moderate weight, which can help reduce the severity of psoriasis and lower the risk of related health issues.