Fast food has become a staple in modern life. It is not only a favorite among children but is also popular with adults, especially office workers. Have you ever considered the negative effects of fast food? Let’s take a closer look at how it can “erode” 8 parts of the body and reconsider this habit.
If you are wondering whether eating fast food every day is harmful or if it leads to significant weight gain, here are the answers related to the dangers of fast food and the body parts affected by this unhealthy habit, according to Healthline.
The term fast food refers to foods that are pre-cooked for sale or served quickly within minutes using common cooking methods such as frying and grilling. While these foods are convenient for consumption when you don’t have much time for meals, excessive intake can indeed lead to negative health effects. Fast food is typically high in fat, salt, calories, added sugars, and low or devoid of fiber. This includes items like French fries, pastries, sausages, and fried chicken.
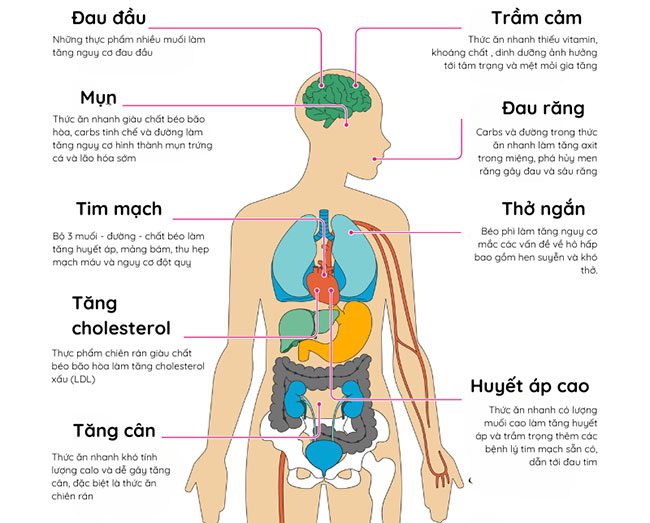
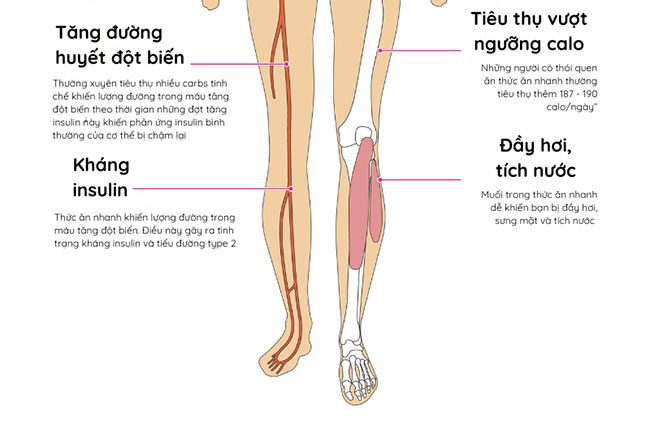
Image: Kim Phung SKHN
1. Digestive and Cardiovascular System
Most fast food, including beverages and side dishes, contains little to no fiber. When your digestive system breaks down these foods, carbohydrates are released as glucose into the bloodstream, resulting in increased blood sugar levels.
The pancreas responds to the rise in glucose by releasing insulin. Insulin transports sugar throughout the body to cells that need it for energy. As your body uses or stores sugar, your blood sugar levels return to normal. This process is tightly regulated by the body. As long as you are healthy, your organs can handle these spikes in blood sugar.
However, regularly consuming high amounts of carbs can lead to spikes in blood sugar over time, and these insulin surges can slow down the body’s normal insulin response, increasing the risk of insulin resistance, which can lead to weight gain and type 2 diabetes.
Many fast-food meals also contain added sugars—meaning extra calories without nutrition. These are often found in donuts, pastries, pizza dough, cookies, and more. Additionally, deep-fried foods contain high levels of fat—including saturated fats—which increase the risk of raising bad cholesterol, lowering good cholesterol, and increasing the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Moreover, the combination of fats, sugars, and salt can enhance flavor and stimulate the eater’s taste buds. However, too much salt can lead to facial swelling, bloating, and this is particularly dangerous for those with high blood pressure while putting stress on your heart. In other words, a high-salt diet over time increases the risk of high blood pressure, which can harden or narrow your blood vessels, becoming a major risk factor for heart attacks, strokes, and heart failure.
Additionally, a lack of fiber (the average adult needs 25-35 grams of fiber daily) can lead to digestive difficulties, increasing the risk of diverticulitis, constipation, hemorrhoids, and more. Furthermore, because they are highly processed, fast foods—especially fried or creamy types—can be difficult to digest, entering the colon as fatty acids that cause diarrhea.

Most fast food, including beverages and side dishes, contains little to no fiber. (Image: Internet).
2. Impact on the Respiratory System
Excess calories from fast food can lead to weight gain and obesity. Obesity increases the risk of respiratory issues including asthma and shortness of breath. Extra weight can also put additional pressure on your lungs and heart—symptoms may even occur with minimal exertion. For instance, you might find it harder to breathe when walking, climbing stairs, or exercising.
More research is needed to determine the exact reasons, but initial studies suggest that increased fat tissue leading to inflammation may affect your lungs.
3. Central Nervous System
The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. These areas of your body can also be affected by fast food.
According to Healthline, a 2020 study found that eating a lot of fast food is linked to poorer short-term memory. Although many studies show conflicting results, this is something worth noting.
4. Impact on Reproductive Organs
Components in fast food and snacks can affect your reproductive health. One study found that processed foods containing phthalates disrupt hormone activity in the body, particularly when consumed at high levels, leading to reproductive issues, including problems with fetal development.

There are many harms from fast food if consumed excessively. (Image: Internet).
5. Skin, Hair, and Nails (Integumentary System)
The types of food you choose to consume can affect the appearance of your skin. A 2021 study on NCBI found that milk, chocolate, saturated fat-rich foods, and high glycemic index foods (carbohydrates and sugars) are linked to increased acne development. In contrast, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids found in fish and olive oil can help protect against and combat acne.
Additionally, sugars in beverages can reduce collagen levels, leading to early signs of aging such as wrinkle formation. Salt strips moisture from your skin but can also cause water retention, leading to puffiness.
However, this study requires further research with more data.
6. Impact on Bones and Teeth
Carbs and sugars in fast food and processed foods can increase acidity in your mouth. These acids can erode tooth enamel—once enamel wears down, bacteria can easily invade and settle deeper into the teeth, leading to cavities and other oral diseases.
As mentioned earlier, fast food can cause obesity and lead to complications related to bone density and muscle mass. Numerous studies have shown that obese individuals may have reduced bone density, increasing their risk of fractures, especially in older adults. Excess weight and obesity from fast food also place additional stress on joints, particularly the hips and knees, making you more prone to fractures around these joints.

Carbs and sugars in fast food and processed foods can increase acidity in your mouth. (Image: Internet).
It is important to maintain an exercise routine to build muscle, support healthy bones, and follow a scientific diet to minimize bone loss instead of frequently consuming fast food or processed foods.
7. Mental Health
Many people tend to eat more fried foods or fast food when they are feeling down. However, this habit of consuming a diet high in saturated fats, salt, sugars, and refined carbs does not only lead to weight gain but also increases mental health issues such as depression rather than improving one’s mood. In other words, fast food lacks the vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients your body needs to enhance your mood.
Additionally, when you consume a large amount of processed carbs, blood sugar levels spike and then drop quickly, which can make you feel fatigued sooner.
Instead, consider eating fruits and vegetables (beyond just lettuce and a slice of tomato in a sandwich) to boost your intake of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that provide healthy energy and improve your mood.

Many people have a habit of eating more fried foods or fast food when they are feeling down. (Image: Internet).
Moreover, according to WebMD, saturated fats and trans fats can cause your body to produce plaques in the brain. These lead to memory loss and triple the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease compared to those who do not eat fast food.
8. Energy
Quickly consuming refined carbohydrates and sugars causes a spike in blood sugar levels, prompting your body to produce a surge of insulin to rapidly lower blood glucose. This spike-and-drop cycle can leave you feeling fatigued and irritable.
In contrast, a balanced meal containing protein, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbohydrates allows your body to digest and absorb nutrients more slowly. This gradual release of sugar into the bloodstream provides you with sustainable energy without the crash.


















































