The video below captures the assembly process of a giant wind turbine, from the foundation construction, assembly in the engineering workshop, to the completion and commissioning of the turbines.
What is a Wind Turbine?
A wind turbine is a device used to convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical energy and subsequently convert it into electrical energy.
Wind power generates a high amount of electricity while still protecting the environment, making it one of the most attractive forms of sustainable energy.
Components of a Typical Wind Turbine Motor
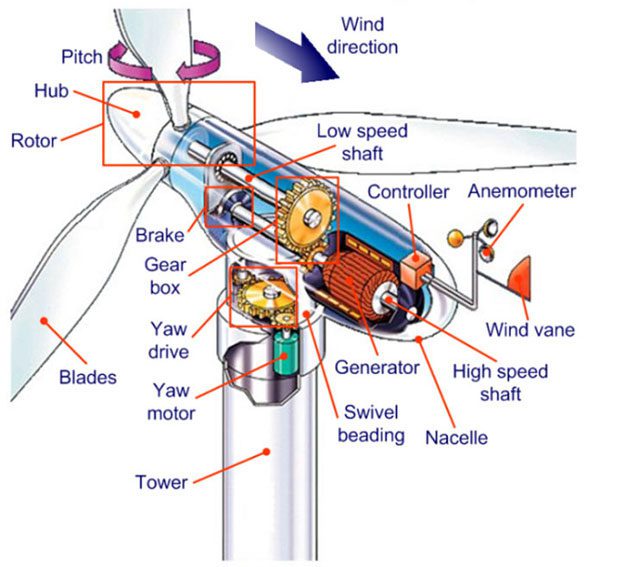
The components of a wind turbine motor include:
- Anemometer: A device that measures wind speed and transmits the data to the control unit.
- Blades: The rotor blades. When the wind blows, it creates force on the blades, causing them to spin and turn the turbine motor shaft. This leads to the continuous motion of the wind turbine system.
- Brake: The braking system (also known as the brake) is responsible for stopping the motor in case of emergency.
- Rotor: Comprising the blades and the shaft.
- Controller: The control unit.
- Gearbox: The gearbox consists of gears connected to both the high-speed and low-speed shafts.
- Generator: The generator unit that produces electrical power.
- High-speed shaft: The high-speed motion shaft of a generator.
- Low-speed shaft: The low-speed motion shaft.
- Nacelle: The housing of the motor, which includes the outer shell and rotor housing, designed to protect the internal components of the motor.
- Pitch: This component ensures that the rotor can generate electricity when it spins in the wind.
Above is the process of constructing a wind turbine, quite elaborate, isn’t it?


















































