What is a cyclone’s circulation, its causes, and its level of destruction in nature? Let’s explore in detail the impact of cyclone circulation.
Essential Information About Cyclone Circulation
Many people have certainly heard of “cyclone circulation.” However, not everyone is familiar with this phenomenon.
Essential Information About Cyclone Circulation
To gain a deeper understanding of cyclone circulation, one must first understand cyclones. Cyclones are a factor that creates disturbances in the atmosphere. When a cyclone occurs, it is often accompanied by adverse phenomena, leading to significant human and material losses.
In tropical or subtropical waters, cyclones typically generate strong whirlpools. The intensity of cyclones is not fixed and is associated with specific circulation phenomena.
Cyclone circulation is characterized by heavy rainfall in bursts. These rains often persist and occur after the cyclone has passed. Cyclone circulation can cause damage to property and loss of life. Sometimes, cyclone circulation can lead to human complacency, making it difficult to avoid risks.
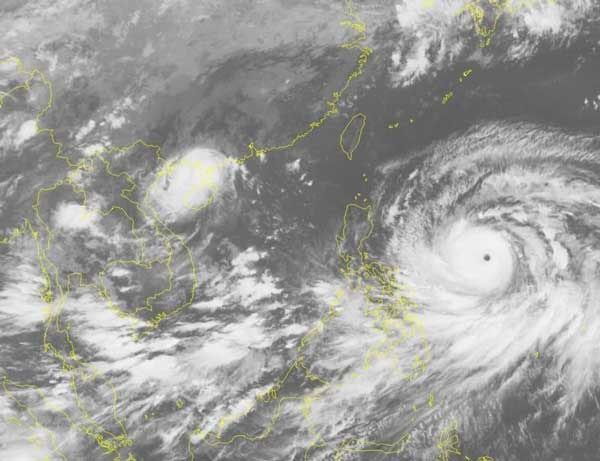
Cyclone circulation caused by sea surface temperature.
How Does Cyclone Circulation Occur?
There are many causes of cyclone circulation, but primarily it stems from the aftermath of a cyclone.
Sea Surface Temperature
The instability of sea surface temperature leads to the formation of cyclones. Cyclones typically occur in waters deeper than 50 meters. Generally, cyclones form when sea surface temperatures rise to between 26°C and 27°C.
Wind Shear
Tropical cyclones arise when there is wind shear between the surface and the upper levels of the atmosphere. At this time, wind speeds below 10 m/s create favorable conditions for cyclone development. The weaker the wind shear, the stronger the cyclone and the more destructive the subsequent cyclone circulation.
Atmospheric Balance
During hot weather, high temperatures shining down on the sea warm the water and cause evaporation. In areas of low pressure, this allows water vapor to rise into a column of moist air.
The process of evaporation, combined with warm sea water and disrupted air pressure in the area, leads to cyclone formation when weather factors, pressure differences, and humidity combine.
Additionally, human impacts on nature contribute to greenhouse effects and climate change. The average temperature of the Earth is rising, causing the air and sea water to warm as well. The ozone layer has holes, making sunlight more intense, which increases the occurrences and irregularities of cyclones.

Cyclone circulation leaves serious consequences for humans.
Consequences of Cyclone Circulation
Cyclone circulation leaves serious consequences for humans. Heavy rains accompanied by strong winds, lightning, and gusts can cause significant damage. In Vietnam, large cyclones often lead to severe destruction. When cyclone circulation becomes complex, it is very difficult to control.
In many cases, cyclone circulation, combined with cold air masses, results in heavy rains causing widespread flooding. This not only impacts the lives of residents but also devastates material wealth.
In mountainous areas, the rain produced by cyclone circulation can cause soil saturation, leading to landslides, which pose a serious risk. Households living around these areas often face high-risk situations.
During transit, roads may sink and rocks may slide, obstructing traffic. Many vehicles and lives are endangered.
Public infrastructure in cyclone-affected areas suffers greatly. Many structures are washed away and lost.

Public infrastructure in cyclone-affected areas is heavily impacted.
After being affected by cyclone circulation, many localities experience environmental pollution. Water sources in the area become contaminated with dirt and parasites. If these areas are not cleaned and maintained, they will suffer significant impacts. Especially, residents relying on these water sources are at high risk of disease outbreaks.
Mitigation of Cyclone Circulation
Mitigating cyclone circulation depends on the consequences it leaves behind. However, residents can take preemptive or post-cyclone measures to avoid significant risks.
Prevention Measures
First, we need to identify the occurrence and direction of storm movement. Local authorities must ensure that accurate information reaches residents so they can prepare and evacuate in a timely manner.
The drainage system must be constructed robustly and tightly to ensure proper flow. In addition, this system will also help minimize the risk of flooding in areas affected by cyclone circulation.
Post-Cyclone Measures
After the storms pass, authorities and residents must work together to mitigate the damage. Understanding what cyclone circulation is can help determine clear causes, facilitating timely search and rescue efforts.
Above are details about cyclone circulation. We hope this information helps you prepare for and mitigate the impact of cyclone circulation in the future.