Vietnam and the world are both aiming for a Net Zero target by 2050. This term is frequently mentioned but may still be unfamiliar to many people. Let’s explore the meaning behind Net Zero.
Science has proven that greenhouse gases emitted by humans are the primary cause of global warming, which has led to numerous consequences for humanity and future generations. Recognizing the dangers of greenhouse gas emissions, the United Nations has set a global Net Zero target.

Net Zero is the common goal of humanity today.
Understanding the Concept of Net Zero
Net Zero is understood as reducing greenhouse gas emissions to as close to zero as possible, with any remaining emissions being reabsorbed from the atmosphere by forests and oceans.
Currently, the Earth has warmed by 1.1 degrees Celsius compared to the late 1800s. To meet the target of limiting the temperature increase to just 1.5 degrees as stipulated in the Paris Agreement on climate change (COP 21) in 2015, the world must reduce emissions by 45% by 2030 and achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. Since then, the Net Zero target – net emissions of zero has been established.
What Are the Consequences of Not Achieving Net Zero?
At the time the Paris Agreement was signed in 2015, many giants in the fossil fuel industry opposed the 1.5°C target, as fossil fuels were a lucrative source of revenue at the time. However, reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) have indicated that if emission levels continue to rise unchecked, the Earth could warm by more than 2°C, potentially reaching 4 to 5°C. This is an extremely dangerous scenario for the survival of humanity.
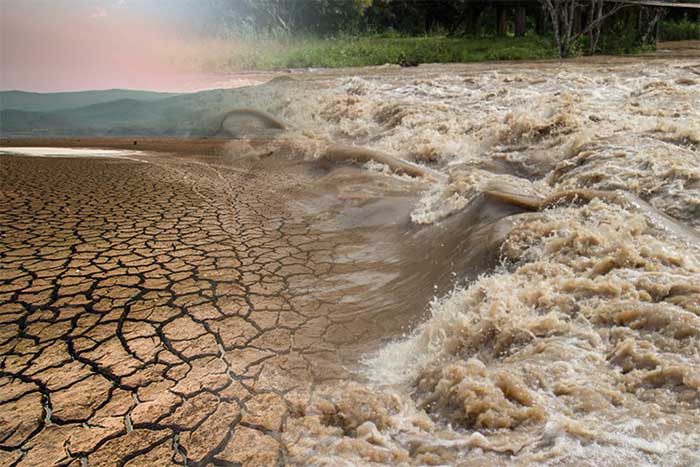

Natural disasters may occur more violently.
Global warming will lead to climate change, affecting air, water, ice, soil, and ecosystems. Rising temperatures in the atmosphere create conditions for increased humidity, resulting in heavy rains, storms, and floods. Meanwhile, prolonged heat will exacerbate drought and water shortages. In general, climate change intensifies the severity and frequency of natural disasters.
Prolonged heat is considered a health threat to humanity, especially for children, the elderly, outdoor workers, and the poor. This group is at risk of heatstroke, heat exhaustion, or cardiovascular diseases, which can be fatal. Statistics show that during severe heatwaves, there are often cases of death due to heatstroke.
Additionally, air quality deteriorates as the Earth’s temperature rises. At this point, the ozone layer thickens, smog becomes denser, and the air becomes more polluted due to emissions from human activities.
Melting ice is also a significant issue as global temperatures rise. Currently, temperatures in the Arctic are increasing at twice the global rate, causing ice to melt faster. Melting ice raises sea levels and can lead to seawater encroaching inland, putting many islands and low-lying areas at risk of sinking.
As emissions continue to rise, the oceans will become more acidic due to direct absorption of pollutants. Increased acidity will put marine life at high risk of extinction, such as crustaceans like crabs and shrimp, and coral reefs. Furthermore, as global temperatures rise, terrestrial animals must change their behaviors to avoid heat; otherwise, they risk extinction if they cannot adapt in time.
It is clear that the Earth’s temperature has a significant impact on human survival. To achieve a moderate temperature, the world must control net emissions to zero. This underscores the importance of the Net Zero target.

The two opposing states of a warming Earth and a temperate Earth. Your choice of planet is your action starting now.
How Can We Achieve Net Zero?
Transitioning to a net-zero emissions world is one of the greatest challenges humanity faces. It requires nothing less than a complete transformation in how we produce, consume, and move. The energy sector is responsible for about 3/4 of current greenhouse gas emissions, thus playing a crucial role in preventing the worst impacts of climate change. Replacing coal, gas, and oil-fired power plants with renewable energy sources, such as wind or solar, will significantly reduce carbon emissions.