VLAN stands for Virtual Local Area Network, which is also known as a virtual LAN. A VLAN is defined as a logical grouping of network devices, established based on factors such as function, department, application, etc., within a company.
Currently, VLAN plays a crucial role in LAN technology. To illustrate the benefits of VLAN, let’s consider the following scenario:
Assume a company has three departments: Engineering, Marketing, and Accounting, each department spanning three floors. To connect computers within a department, we could install a switch on each floor. This means that each floor would require three switches for the three departments, resulting in a need for nine switches to connect all three floors of the company. Clearly, this approach is very costly and does not fully utilize the available ports on each switch. For this reason, the VLAN solution was developed to address this issue simply and efficiently, conserving resources.
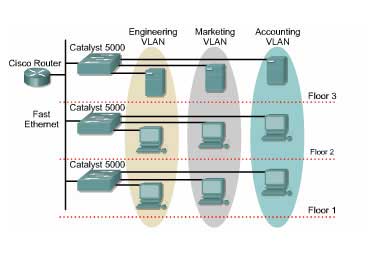
As illustrated above, each floor of the company only needs one switch, which is divided into VLANs. Computers in the Engineering department are assigned to the VLAN for Engineering, while PCs in other departments are assigned to their corresponding VLANs for Marketing and Accounting. This method maximizes the number of switches used and fully utilizes the available ports on each switch.
Types of VLAN
-
Port-based VLAN: This is a simple and commonly used VLAN configuration method. Each port on the switch is associated with a specific VLAN (default is VLAN 1), so any host device connected to that port belongs to that VLAN.
-
MAC address based VLAN: This configuration method is less commonly used due to management inconveniences. Each MAC address is tagged with a specific VLAN.
-
Protocol-based VLAN: This configuration is similar to MAC address-based VLANs but uses a logical address or IP address instead of a MAC address. This configuration method is becoming less common due to the use of DHCP protocols.
Benefits of VLAN
-
Bandwidth conservation:
VLAN segments a LAN into smaller segments, each of which is a broadcast domain. When a broadcast packet is sent, it is only transmitted within the corresponding VLAN. Therefore, dividing into VLANs helps to save bandwidth in the network system. -
Enhanced security:
Devices in different VLANs cannot access each other (unless a router is used to connect the VLANs). As in the example above, computers in the Accounting VLAN can only communicate with each other. Machines in the Accounting VLAN cannot connect to computers in the Engineering VLAN. -
Easy addition or removal of computers in VLAN:
Adding a computer to a VLAN is very straightforward; you only need to configure the port for that machine to the desired VLAN. -
High network flexibility:
VLAN allows for easy relocation of devices. For instance, in the previous example, if the company decides to place each department on a separate floor after some time, with VLAN, we simply need to reconfigure the switch ports and assign them to the required VLANs.
VLAN can be configured statically or dynamically. In static configuration, the network administrator must configure each port on each switch. Then, assign it to a specific VLAN. In dynamic configuration, each switch port can automatically configure its VLAN based on the MAC address of the connected device.