This article will share some ways to easily track the current location of the International Space Station (ISS) in the sky.
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large modular spacecraft that orbits Earth at a low altitude. It began as a space program called “Freedom” during the presidency of Ronald Reagan in the United States.

It took about two years before the ISS was inhabited.
However, in 1993, this program merged into a joint multinational effort between the United States and Russia. The project quickly received additional support from the European Space Agency (ESA) and Japan, thus becoming a truly “international” space station. The ISS started with a single module called “Zarya”, launched by Russia into space on November 20, 1998, followed a few weeks later by a U.S. module named “Unity.”
It took about two years before the ISS was inhabited. The first crew arrived to live on the ISS on November 2, 2000. The construction of the ISS was officially completed in 2011.
Today, the ISS has an internal volume equivalent to that of a large house with five bedrooms or two Boeing 747 jets, and it can accommodate six crew members. The station weighs approximately 453 tons, and its shadow covers an area on Earth the size of a football field. It is also large enough to be seen with the naked eye when it is dark.
The ISS orbits Earth at an average altitude of about 402 kilometers above sea level. Traveling at a speed of 28,100 kilometers per hour, it circles the planet every 90 minutes. The best way to find out where the ISS is currently located is by using the following websites.
Live Space Station Tracking Map on NASA’s website is your first option.
This site features a single flight path map that shows the exact location of the ISS as it moves across the planet in real-time.
![]()
It also shows where the station was 90 minutes ago and where it is projected to be 90 minutes in the future. The map even features dark overlays indicating where it is nighttime in various regions around the world. Real-time remote sensing data provided by the European Space Agency includes the latitude, longitude, altitude, and speed of the ISS in either metric or imperial units.
Your second option is the ISS Astro Viewer.
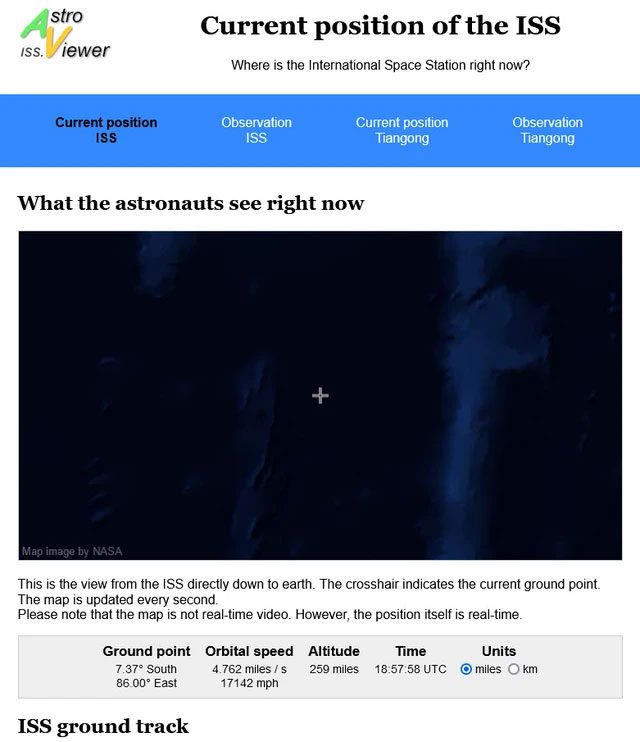
This tool is developed by German software developer Dirk Matussek. This page is interesting because it provides real-time ground tracking images and remote sensing data similar to NASA’s website.
Additionally, it shows what astronauts see when they look down at Earth. If you are interested in China’s Tiangong space station, you can view similar data for that station.
The third option for tracking the ISS is a tool called ISS Position.
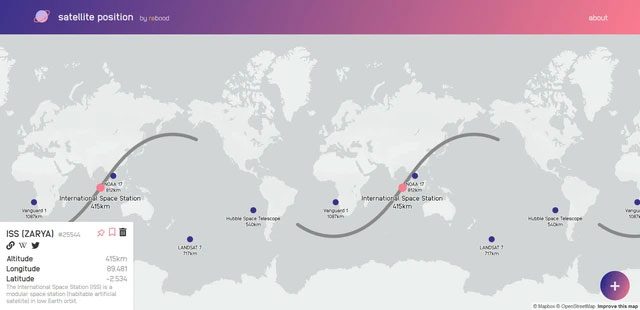
This tool is created by a private group of space enthusiasts. It is the simplest website, providing a real-time image of the ISS as it moves across a global map. It can also track the Hubble Space Telescope, Vanguard 1 (the oldest satellite still in orbit), NOAA weather satellites, and the Landsat 7 world imaging satellite.
Moreover, you can watch live streaming images from the ISS in real-time through the Space channel’s YouTube link below:
Space scientists are planning for the ISS to be retired and gradually replaced by another version by 2031. Therefore, the time to observe the movement of the ISS is limited.


















































