You’ve probably seen players from your favorite football club chewing gum while playing. You might think it’s just a personal habit. You may even believe that chewing gum while running on the field poses significant risks, such as choking. So why do these players take such risks?
Very few people consider that chewing gum can affect cognitive function, yet numerous studies have found a connection between chewing and brain function. When we chew something, receptors in the mouth detect flavor, and the pressure from jaw movement sends signals to the brain. These signals from the nervous system to the brain help keep the mind alert. That’s why concentration improves.
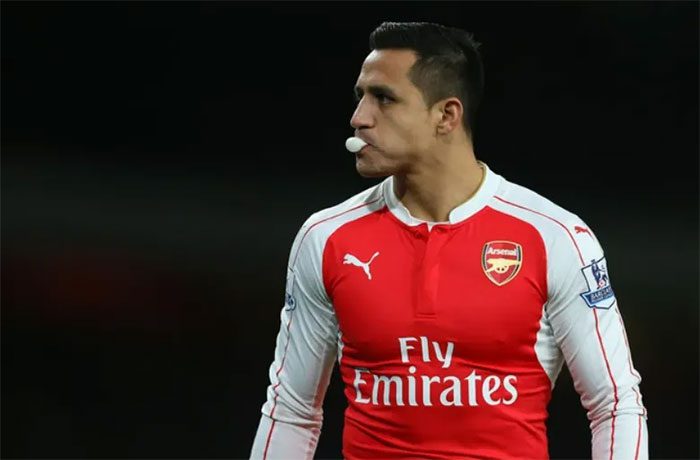 Chewing gum helps improve concentration.
Chewing gum helps improve concentration.
Moreover, increased brain activity means more energy is provided for those cognitive processes, leading to increased blood flow to the brain while chewing. The brain’s higher blood demand causes the heart to beat faster. In summary, chewing activates receptors in our gums to send information to the brain, and as a “reward,” the heart works better, allowing muscles to receive more blood.
Chewing harder gum promotes better concentration than softer gum. Similarly, chewing flavored gum is better for cognitive function because it activates more receptors in the mouth than chewing unflavored gum.
This is why many professional football players and basketball athletes chew gum. They think faster, increase their speed of action, and improve their reflexes.
Chewing gum is also noted for reducing stress and anxiety levels, helping to improve focus. The brain activity triggered by chewing gum occurs in the prefrontal cortex, the area of the brain located just behind our forehead. Once this area is stimulated, it activates our neurons to release serotonin—a neurotransmitter that helps relax the mind.
If you find yourself restless during an exam or facing an important challenge, try chewing gum while taking the test. With lower stress levels and improved focus, athletes will be better able to make decisions in the middle of a game. They can make more accurate passes or move more strategically at crucial moments. Chewing gum also helps them manage their anxiety during major games like finals or title-deciding matches.
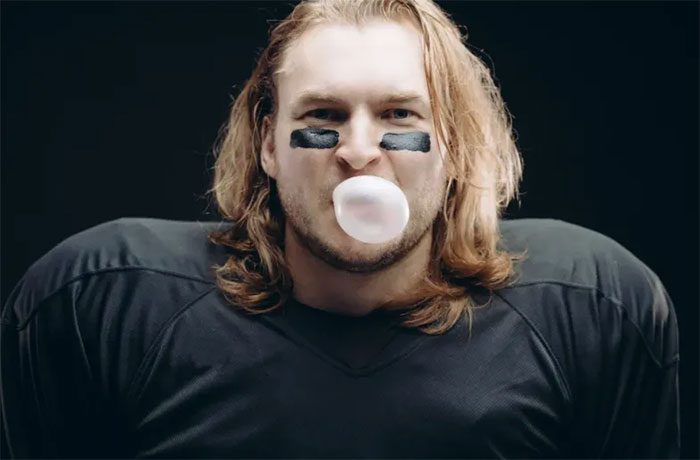 Chewing gum also helps athletes manage anxiety levels.
Chewing gum also helps athletes manage anxiety levels.
Most athletes are constantly active throughout their games. It is estimated that football players run about 6-7 miles per match. Therefore, their mouths can become quite dry if they don’t hydrate frequently due to continuous movement causing dehydration. Even intense matches or daily training sessions can leave you with a dry mouth from fluid loss.
When you chew gum, your mouth continuously produces saliva. This is a natural body response, as saliva contains enzymes that help break down food. Saliva is 99% water, so it helps keep the mouth moist and prevents dryness. This also helps players manage their thirst on the field.
Athletes chew gum to gain competitive advantages. In high-stakes races and long events, even small differences can lead to significant outcomes that help them go the distance. However, scientifically speaking, chewing gum does not double your focus; it merely provides a slight boost to your body.
Additionally, if you have a habit of chewing gum, you should be cautious while exercising or playing sports. In sports like football or rugby, there may be situations where you accidentally swallow the gum, which could cause choking. Stay safe by only chewing one piece of gum to reduce the risk of choking.
Besides gum, another enhancer that athletes often use is caffeine. Athletes utilize the special components of coffee to boost their endurance, alertness, and heart rate. Typically, athletes will drink a caffeine-rich beverage or take a caffeine pill before competing, but gum containing caffeine offers athletes the benefits of both chewing and caffeine. This is believed to be healthier than consuming energy drinks, and the body also absorbs caffeine from gum more easily.
However, you should only consume a moderate amount of gum before exercising or during a major match. Chewing too much gum can make you feel nauseous, as the sugars used in gum can have a laxative effect.