Those unfamiliar with gardening may not know that after harvesting bananas, the entire banana plant is cut down. Why is this the case?
Unlike other fruit trees, despite its large size, the banana is actually a herbaceous plant belonging to the Musa family.
The banana plant has a very unique growth process: although it is a herbaceous plant, it grows vigorously and can reach heights of 3-4 meters. The banana plant is cut down after the fruit is harvested.
Why Banana Plants Are Cut Down Immediately After Harvesting
The reason is quite simple:Each banana plant only bears fruit once in its lifetime. After the fruit is harvested, the mother plant is typically cut down to make room for new shoots to develop.
When the banana plant bears fruit, new shoots or young plants begin to sprout from the base of the mother plant. These young plants will grow into new plants and “compete” for nutrients from the soil with the mother plant. This is why banana plants are cut down immediately after fruit harvesting. It is necessary to create conditions for the young plants to thrive.
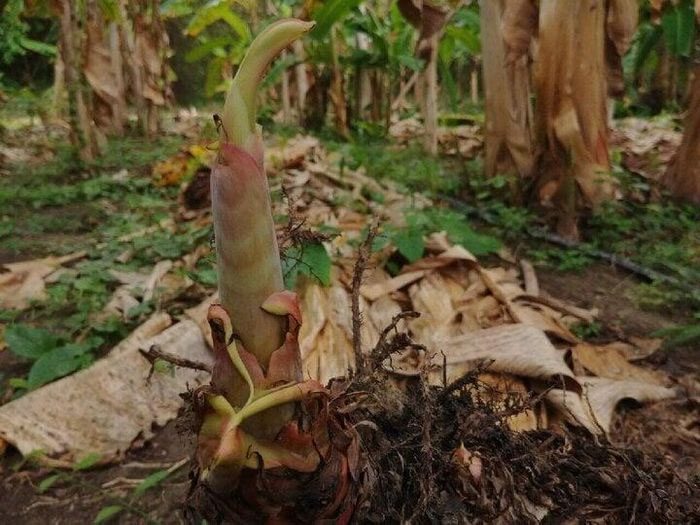

Each banana plant only bears fruit once in its lifetime. (Image: Etsy).
After cutting down the mother banana plant, new banana plants can quickly sprout. If older banana plants are regularly cut down, the quantity and quality of bananas from the subsequent plants will improve.
Trang 163.com explains in more detail why banana plants are cut down right after fruit harvesting:
Due to the nature of the banana plant: Bananas grow larger than typical fruit trees, and their root systems are very developed, capable of absorbing water and nutrients from more than 1 meter below the ground. Additionally, bananas have a strong self-recovery ability and can store a significant amount of water.
After fruiting, the plant begins to age and wither, but if cut down, new shoots can quickly emerge from the base. Farmers can utilize the old banana plants as fertilizer after cutting them down without worrying about them not regrowing.
Cutting the plant promotes regeneration: After the banana plant matures and ages, the nutrients within the plant gradually deplete, leaving behind only dry “hollow shells.” Before the new shoots emerge and the old plant has completely died, the old banana plants become a source of nutrient consumption.
Consuming limited fertilizer is not beneficial for the growth of new plants. At the same time, the surface and interior of old banana plants also serve as an important habitat for pests; if not cut down, the new banana plants may contract diseases and suffer from pest damage, hindering reproduction and renewal of banana plants.
Increasing growth space for new banana plants: As banana plants age, the base begins to rot and lean. When affected by severe weather, such as storms or heavy rain, the plant may topple, posing risks to new banana plants as well as nearby public structures and pedestrians.
Cutting down dead banana plants is a safe measure to protect newly sprouted plants and also creates more space for their development.
Uses of Banana Plants After Being Cut Down
The banana plant is primarily grown for its fruit. However, after harvesting, the plant is often cut down. To avoid waste, the cut banana plants can be reused in the following ways:
Used for Composting
One of the easiest ways to utilize the cut banana plant is as compost material. Banana plants are rich in carbon, potassium, and other essential nutrients, making them ideal for fertilizer. Simply chop the plant into small pieces and add it to the compost pile along with other organic materials. Layer the materials to ensure proper aeration and remember to water frequently.
Used as Animal Feed
Banana plants can also be used as animal feed. The leaves and stems have high protein content and are a great source of nutrition for livestock and goats. It is important to note that the leaves and stems should be thoroughly processed, including cleaning, cutting into small pieces, and fermenting before feeding to animals.
Used for Crafts
The leaves of the banana plant can be used to make baskets and other woven items. They can also be utilized to produce paper or natural dyes. Furthermore, the stems can be used to create furniture and other decorative items.