Diesel and gasoline are both byproducts of crude oil refining, but they have quite different combustion characteristics. This results in each fuel type having its own advantages and disadvantages.
It can be observed that the use of diesel engines is not very common in small car models and usually appears as an option for a few mainstream vehicles. In reality, diesel engines are more frequently found in trucks and heavy-duty vehicles. Why is that?
What are the Advantages of Diesel Engines?
Diesel engines combust fuel through compression, as opposed to the “spark” used in gasoline engines. A higher compression ratio ensures greater thermal efficiency and complete fuel combustion. Diesel-powered vehicles are known for their longer travel ranges, making refueling less frequent. This is particularly essential for heavy vehicles since they often operate for long days and in areas where fuel sources are hard to access.
Although diesel has a thermal value equivalent to gasoline, it is denser in energy, resulting in higher torque.
Moving while carrying heavy loads consumes a lot of energy. The slower combustion process of diesel engines ensures that this energy is delivered as torque to the vehicle, even at low speeds. This makes diesel fuel advantageous for larger vehicles that frequently need to move with heavy loads and sometimes on rough terrain.
Diesel engines are designed to take advantage of these three characteristics. They have larger bore and stroke dimensions and are often turbocharged to maximize the torque provided to the vehicle.
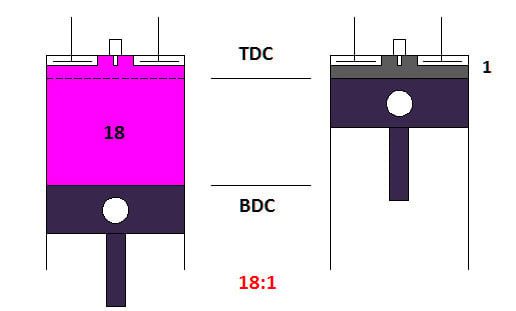
Diesel engines have a higher compression ratio compared to gasoline engines. Diesel engines are typically bulkier and heavier than gasoline engines of the same power output due to their more complex construction and the need for a higher compression ratio. This makes them unsuitable for smaller vehicles that prioritize agility and fuel efficiency in urban settings.
Based on the above reasoning, it is clear that diesel is a very powerful fuel. However, diesel engines also have some disadvantages that make them less favorable for use in smaller cars.
Higher NVH Levels (Noise, Vibration, Harshness)
Due to the higher compression ratio, diesel engines produce louder sounds and more vibrations than gasoline engines. While this does not significantly affect heavy vehicles due to their large size, it can become uncomfortable and even dangerous for smaller vehicles. As a result, many manufacturers have attempted to improve diesel engines for use in some of their models, such as jeeps and SUVs from several brands that offer diesel engine options.

Diesel engines are generally noisier and vibrate more than gasoline engines, especially during startup and acceleration. This affects the comfort of the driving experience, particularly for those using vehicles in urban areas. The production cost of diesel engines is higher than that of gasoline engines due to their more complex design and the use of higher-quality materials. This leads to higher vehicle prices, affecting consumer accessibility.
Higher Maintenance Costs Compared to Gasoline Engines
Machines that endure high vibrations will wear out more quickly and may fail sooner. For diesel engines, their components must be designed to withstand higher NVH levels. This significantly increases maintenance costs compared to gasoline engines. It is important to note that although diesel engines require less frequent maintenance, any benefits gained from this are offset by the costs of each maintenance requirement.
This makes diesel engines less popular among owners of small cars who aim for economical transportation.
Emission-Related Issues
Despite having higher efficiency compared to gasoline engines, diesel engines still emit harmful nitrogen oxides, causing respiratory issues.
Older diesel engines are associated with emitting NOx into the atmosphere at much higher levels than usual. Therefore, many countries around the world have implemented measures to ban diesel engines older than ten years. Consequently, to avoid penalties and taxes related to emissions, diesel engines are often not favored in small cars.

Older diesel engines may emit more NOx and fine particulate matter than gasoline engines, causing environmental pollution. Small cars are typically used primarily in cities for short trips. Gasoline engines, with their quick acceleration and fuel efficiency in congested traffic, are more suitable for these needs. Meanwhile, diesel engines perform better during long-distance operations with heavy loads, making them ideal for trucks, SUVs, and pickups.
However, it is important to note that diesel engine technology is continuously improving, with a focus on reducing size, weight, noise, and emissions. Therefore, in the future, there may be more small cars that use diesel engines, especially those that emphasize performance and fuel efficiency.
Additionally, several other factors may influence the use of diesel engines in small cars, such as fuel prices, tax policies, and emission standards in each country.


















































