In the vast Arctic region, there is a brave group of people known for their unique way of life. This group is the Inuit, and they live in snow houses.
Why Do the Inuit Live in Snow Houses?
Snow houses are a distinctive form of living for the Inuit because they inhabit polar regions with cold and harsh climates. To adapt to this extreme environment, the Inuit invented the snow house, utilizing the thermal properties of ice and snow to maintain a relatively stable internal temperature.
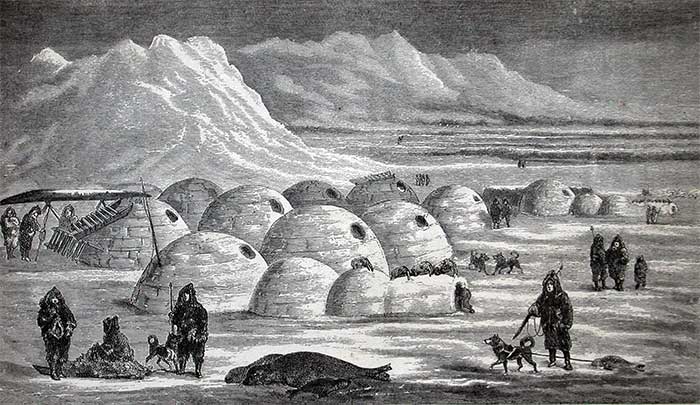

The snow house is a creative housing solution used by the Inuit to address the challenges of the polar climate. It leverages the insulating properties of ice to keep the internal temperature relatively stable and conserve energy. (Photo: ZME).
The main principle of the snow house is to take advantage of the insulating properties of ice and snow. Ice and snow are excellent insulating materials that prevent heat conduction. When blocks of ice are used to construct the walls and roof of the snow house, they can effectively block the intrusion of cold air from the outside and maintain a relatively stable internal temperature. In extremely cold environments, this insulating property is crucial as it helps people fend off the cold and stay warm.
Ice also possesses certain qualities and stability. The Inuit will often gather and store a large amount of ice during the winter to use for building snow houses when needed. The quality and stability of the ice ensure that the structure of the snow house is solid and can withstand the challenges of harsh weather conditions. Although snow houses require regular maintenance and repairs, the durability of ice makes them a reliable choice in the polar environment.
Another advantage of the snow house is its energy-saving capability. Due to the insulating properties of ice, snow houses can retain warmth more effectively than other traditional structures. The equilibrium temperature of a snow house can be significantly higher than the extremely cold temperatures outside, reducing the need for heating. In this way, the Inuit living in snow houses can save considerable energy and decrease their reliance on external energy supplies. This is a very practical and sustainable lifestyle for people living in resource-scarce polar regions.

Despite some challenges, the durability of ice and the sustainability of the snow house make it a unique and viable residential option. The intelligence and creativity of the Inuit are remarkable, and their snow houses are the most exemplary representation of adaptation to the environment. (Photo: ZME).
Although snow houses offer many benefits, they also present some challenges. The ice blocks need regular maintenance to ensure they maintain their insulating properties. The crystallization of water can pose a threat to the stability of the snow house. The Inuit must learn how to handle and utilize ice properly to ensure the reliability and durability of their snow houses.
Regulating the Temperature Inside the Snow House
Snow houses are architectural structures commonly found in the cold northern regions, originating from the adaptations of ancient people to frigid weather. Today, snow houses have become tourist attractions and a temporary shelter chosen by many. However, maintaining an appropriate indoor temperature in such a cold environment is crucial. To address this issue, snow houses utilize various methods to regulate temperature, including stoves, lighting, and body heat.
The stove is considered one of the main ways to control the temperature inside the snow house. The combustion process of the stove generates heat, which can provide effective warmth. Typically, snow houses are designed with a chimney for the stove. When the stove is lit, the temperature inside the snow house rises quickly, creating a comfortable environment for the occupants.

The stove, lighting, and body temperature are the three main factors in regulating the temperature inside the snow house. The stove provides warmth through heat generated from combustion, lighting helps regulate by increasing thermal energy and comfort in the room, and human body temperature becomes a key factor in maintaining warmth. (Photo: Zhihu).
Sunlight is a natural heat source that can penetrate through the doors and windows of the snow house. During the day, sunlight passes through the transparent ice walls of the snow house and transforms into thermal energy, causing the temperature inside to rise.
When people are inside the snow house, their body temperature radiates throughout the space, further increasing the warmth within. Human body temperature is crucial for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures, especially at night when the stove is turned off, and body heat becomes the only source of warmth.

Regulating the temperature inside the snow house is essential for ensuring comfort for its occupants. The stove, lighting, and human body temperature are key factors in temperature control and must be used and maintained properly. (Photo: Zhihu).
The Process of Building a Snow House
A snow house is constructed to take advantage of the freezing properties of ice and snow. It provides temporary shelter against the cold and is a unique and aesthetically pleasing form of architecture. The process of building a snow house requires following certain steps and techniques. Choosing a suitable construction site is essential. The site must be flat and free of any obvious traps or hazards. Additionally, sunny areas are more likely to facilitate freezing effects.

The process of building a snow house requires following certain steps and techniques. (Illustration: ZME).
Ice can be sourced from lakes, rivers, or specialized ice-making equipment. Of course, these ice blocks must be hard enough and not easily breakable. First, a block of ice is placed on the ground to serve as a base. Next, smaller ice blocks are placed on the base, and the gaps between the blocks are filled with snow. This is done layer by layer until the desired height is achieved.
During the stacking process, it is essential to ensure that the connections between the blocks are secure. To enhance structural stability, water can be poured over the ice blocks during the stacking process, and the melting and refreezing properties of ice can be utilized to bond the blocks together. Once the stacking of the blocks is complete, attention must be paid to constructing the roof. To prevent the roof from collapsing, a long pole can be inserted through the ice layer to create an arched structure that increases the roof’s load-bearing capacity.

The process of building a snow house requires choosing the right location. (Illustration: ZME)
Ventilation must also be considered when building a snow house. A small window can be opened on one side of the snow house to allow air circulation and prevent moisture buildup.
The process of building a snow house involves selecting a suitable location, gathering ice, careful stacking, and considering structural stability and ventilation. With proper steps and construction techniques, a snow house can become a unique and aesthetically pleasing architectural form, providing people with a comfortable refuge from the cold.