In the vast universe, as beams of light travel through empty space, occasionally, distortions and bends appear in our view. This magnificent sight, a truth revealed by scientists, is hard to believe: light can actually be attracted and bent!
The Effect of Gravity on Light: The Curvature of Space-Time
Gravity is a term we often hear in everyday life, and its attraction to matter has been known for a long time. However, not everyone realizes that gravity also affects light. Indeed, light undergoes a strange phenomenon when passing through a gravitational field, meaning space and time can be warped.
Gravity also affects light. (Illustrative image).
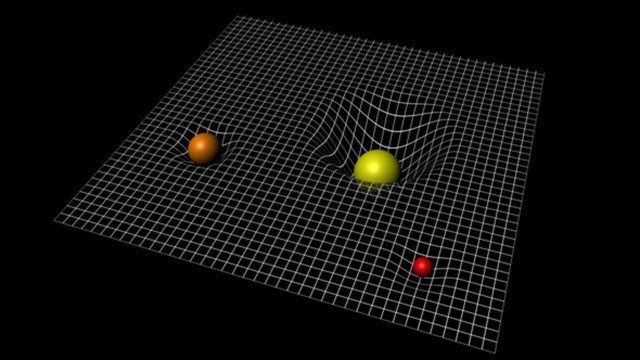
We need to clarify a concept: the effect of gravity on space and time. According to Einstein’s general relativity, gravity is not merely the attractive force of matter but the interaction between matter and space-time. The presence of matter causes space-time to twist and curve, creating a gravitational field. When light travels through this gravitational field, it is affected by the curvature of space and time, thus altering its path.
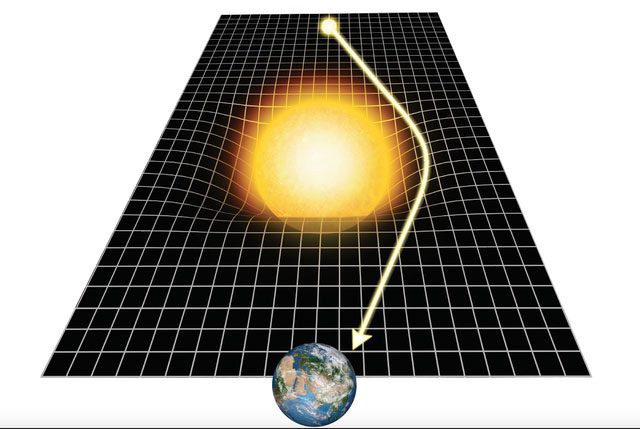
The path of light is usually a straight line, a common phenomenon in our daily lives. When light approaches a gravitational field, it will be influenced by gravity and deviate from its original path. Specifically, the gravitational field acts like a curved mirror, bending the light. This allows light rays emanating from a light source to deviate from a straight line on their way to the destination. This phenomenon has been experimentally confirmed near the Sun.
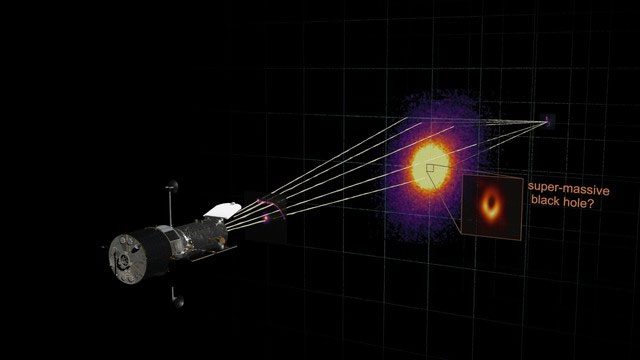
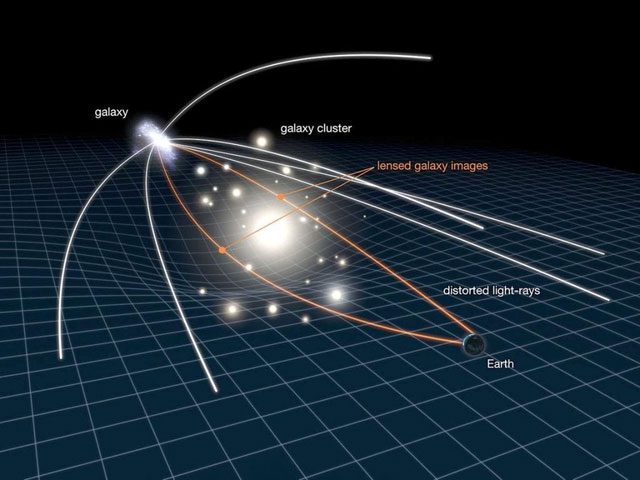
A typical example is when light emitted from a star is bent in its gravitational field. When we observe this light, it seems to come from a completely different direction, known as gravitational lensing. In fact, gravitational lensing has been used to confirm the validity of general relativity. (Illustrative image).
In addition to gravitational lensing, gravity also causes time to slow down. According to relativity, when we are in a stronger gravitational field, time slows down. This is because the gravitational field bends the path of light, and time and space are interrelated. When light travels through a gravitational field, time slows down because the path of light is curved. This is known as the gravitational time dilation effect. Once again, this effect has been experimentally confirmed.
The effect of gravity on light is not just theoretical calculations but can also be verified experimentally. For instance, during the observation of the solar eclipse in 1919, physicists measured the positions of stars near the Sun, confirming the impact of gravity on light. The results of this experiment shocked the entire scientific community and strongly supported the validity of general relativity.
Gravity also causes time to slow down. (Illustrative image).
The effect of gravity on light can be explained by the curvature of space-time. The existence of a gravitational field will deflect the path of light, causing light to bend when passing through a gravitational field. This phenomenon includes gravitational lensing and gravitational time dilation. Through experimental confirmation, scientists have further validated Einstein’s general relativity. The impact of gravity on light not only deepens our understanding of the universe but also provides us with a broader perspective to explore various phenomena in the cosmos.
Relativity and the Deflection of Light: Einstein’s Predictions
When mentioning relativity, most people think of Albert Einstein. He is one of the greatest scientists of the 20th century, renowned for his theory of relativity. One of the most important predictions related to the deflection of light.
Einstein proposed that the transmission of light would not be affected by the state of motion of an object. (Illustrative image).
In 1905, Einstein proposed special relativity, based on two fundamental assumptions: the principle of relativity and the principle of the constancy of the speed of light.
- According to the principle of relativity, there is no specific reference frame that can be called “absolutely fixed,” and all physical laws must be defined relative to the state of motion.
- The principle of the constancy of the speed of light indicates that the value of the speed of light in a vacuum is constant.
Based on these two principles, Einstein concluded that the transmission of light would not be affected by the state of motion of an object. In other words, whether we are stationary or moving, whether we are advancing or retreating, the speed of light remains constant. This conclusion completely overturned the concept of Newtonian mechanics and shocked the scientific community.
Einstein’s predictions did not stop there. In 1915, he published a paper on general relativity. General relativity further developed on the basis of special relativity and included the concept of gravity. According to general relativity, the mass and energy of an object cause space-time to curve, and other objects are affected by the curvature of space-time.
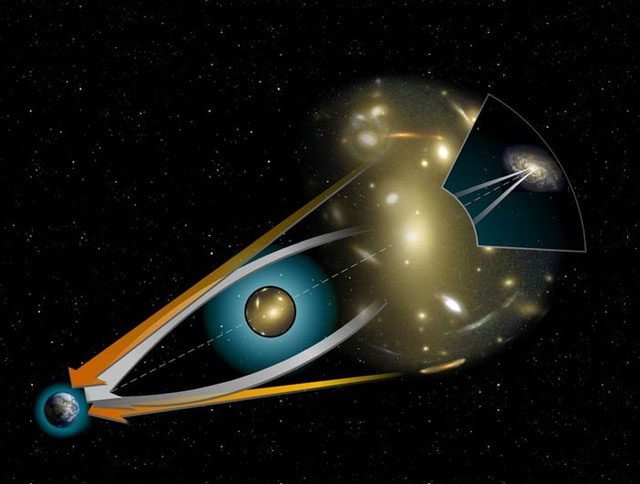
When light passes through a curve in space-time, it is deflected. (Illustrative image).
In this theory, light is also affected by the curvature of space-time. When light travels through a curve in space-time, it is deflected. Simply put, light will be influenced by the gravitational field of an object, causing it to change direction. This phenomenon was confirmed during the total solar eclipse experiment in 1919.
A group of scientists led by Arthur Edenton used the total solar eclipse to observe the path of light from stars near the Sun. According to Einstein’s theory, the Sun’s gravity would bend the light. The results of the experiment confirmed this theory and successfully validated Einstein’s general relativity.
This discovery had a profound impact on the scientific community. It not only demonstrated the correctness of Einstein’s theory of relativity but also provided guidance for further research and experiments.

According to Einstein’s theory, the Sun’s gravity will bend light. (Illustrative image).
The phenomenon of light bending also has many practical applications. For instance, the telescopes and microscopes we use in daily life are designed based on the principle of light deflection. The phenomenon of light bending plays a crucial role in astronomy, providing important clues for us to observe and study the universe.
Einstein’s predictions regarding relativity and the deflection of light are significant milestones in the history of science. His theories have led us to a deeper understanding of the laws of the universe and have had a wide-ranging impact on many fields of study. Relativity and predictions about light deflection will always serve as a vital foundation for scientific research, revealing the mysteries of the universe to us.