In 2024, clocks in many places around the world will be adjusted at 2 AM on March 10 or March 31. So what is the purpose of changing the time?
This year, Daylight Saving Time in the United States will begin at 2 AM on Sunday, March 10, local time. Clocks will be set forward by one hour. Then, on November 3, clocks will be set back by one hour.

If you are in one of the countries that observe seasonal time changes, don’t forget to set your clock forward by one hour this March to start saving daylight. (Photo: Vicat).
In most European countries, Daylight Saving Time will be observed on Sunday, March 31, followed by a return to Standard Time on Sunday, October 27.
Benjamin Franklin, one of the founding fathers of the United States, was the first to propose resetting clocks during the summer months to conserve energy. By moving the clock forward by one hour, people could take advantage of more sunlight in the evenings instead of quickly turning on lights.
At that time, Franklin was the American ambassador in Paris, France, and he sent a letter to the Paris Journal in 1784 presenting his intriguing “discovery.”
However, it wasn’t until more than a century later that Daylight Saving Time was actually implemented. Germany began this practice in May 1916 to save energy during World War I. Other European countries quickly followed suit, and by 1918, the United States did the same.

Former US President Woodrow Wilson signed the Standard Time Act in 1918, establishing time zones and the rules for Daylight Saving Time in the United States starting on March 31, 1918. (Photo: Topical Press Agency/Getty Images).
Since then, the United States has changed its time change regulations multiple times. The last significant change was in 2007, when the Energy Policy Act of 2005 came into effect, establishing the current time change rules that are still in place today.
Why do we have Daylight Saving Time rules?
Currently, less than 40% of countries around the world observe this time change. However, those that do are able to enjoy more sunlight in the evenings during the summer. This is because the daylight hours are longer as the Earth transitions from winter to spring and summer, with the longest day being the summer solstice.
During summer in each hemisphere, the Earth tilts directly toward the Sun.
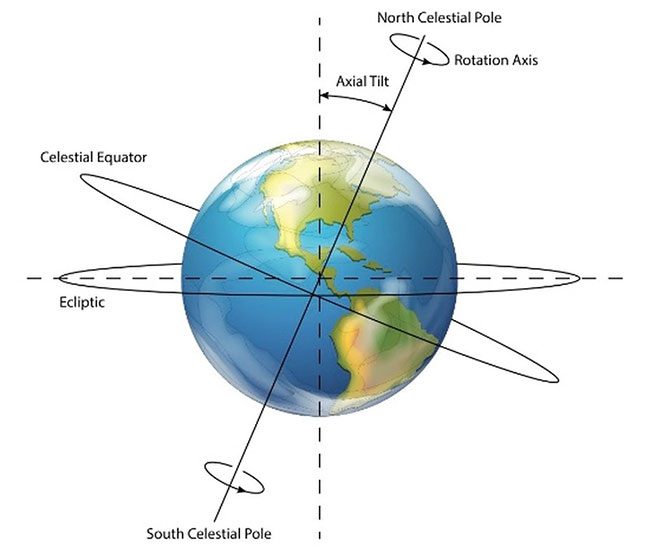
The Earth rotates around the Sun while also spinning on its axis tilted relative to the plane of its orbit, meaning different parts of the Earth receive various amounts of direct sunlight depending on the time of year, which gives us the different seasons. (Photo: BlueRingMedia/Shutterstock).
Regions far from the equator and closer to the poles benefit most from Daylight Saving Time, as the change in direct sunlight between seasons is most pronounced in these areas.
According to researchers, with additional evening sunlight, people experience fewer traffic accidents. More daylight also allows full-time workers the opportunity to exercise outdoors.
However, studies also indicate that there is currently little evidence to support significant energy savings due to seasonal time changes.
Researcher Stanton Hadley at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in the United States states that energy use for lighting is becoming increasingly efficient, meaning modern technologies can help conserve lighting energy. On the other hand, heating and cooling systems are becoming more of a concern. Some regions may require air conditioning for hotter and longer evenings during the summer after the time change.
A 2007 study also showed that temporary time changes in Australia failed to save energy during the 2000 Olympic Games held in that country.
Which places in the world observe Daylight Saving Time?
United States and Canada: Most areas in the US (except Hawaii and Arizona) and Canada (only 1 out of 10 provinces do not observe it) follow the same time change rules. Daylight Saving Time begins at 2 AM on the second Sunday in March, and Standard Time reverts at 2 AM on the first Sunday in November.
Europe: Most European countries (except Russia, Iceland, and Belarus) observe Daylight Saving Time starting from the last Sunday in March and ending on the last Sunday in October. Although the European Union has proposed to discontinue the time change regulation, a recent poll showed that 84% of the 4.6 million participants want to keep it as is.
In the Southern Hemisphere: Countries and regions that observe Daylight Saving Time include Australia, New Zealand, and South Africa. Residents in these areas shift from summer time to winter time between September and November and back from March to April depending on the location.
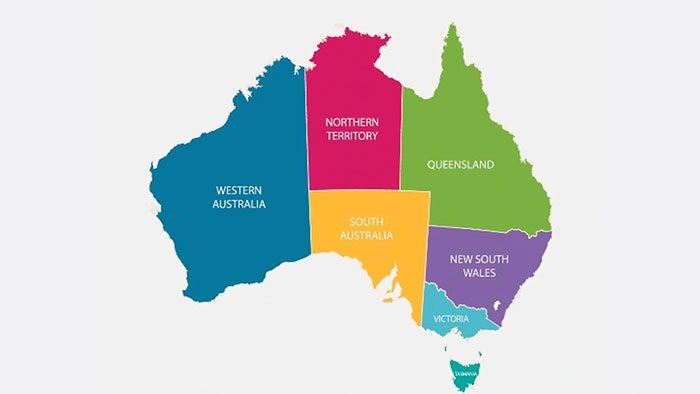
Australian states and territories. New South Wales, Victoria, South Australia, Tasmania, and the Australian Capital Territory observe Daylight Saving Time, while Queensland and the Northern Territory (Western Australia) do not.


















































