Giant squids inhabit all oceans, with an estimated length of 12 to 14 meters and a weight of around 270 kg.
One reason why giant squid (Architeuthis dux) are not commonly consumed is due to their intelligence and emotional capacity. Giant squids are highly developed invertebrates with a sophisticated nervous system and a high IQ. They can learn and remember, and they can establish emotional communication with humans. Therefore, many believe that turning giant squids into food seems disrespectful to their intelligence and emotions.
Giant squids have a long reproductive cycle, and their reproductive capacity is relatively limited. During the breeding season, giant squids build nests and lay eggs, which are protected by the females until they hatch. This process typically takes several months, and only a very small number of larvae develop into mature squids. Consequently, overfishing giant squids can have a negative impact on the oceanic ecosystem.
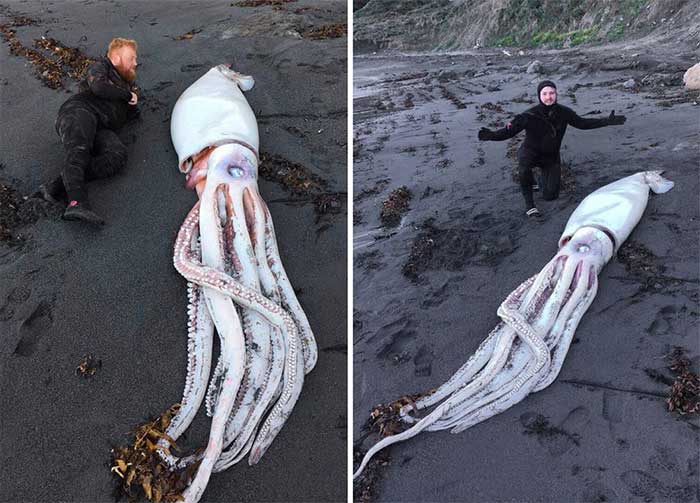

The meat of giant squid has a strong ocean smell and a fishy odor, and is tough and chewy, making it unpleasant. Additionally, the body of giant squid contains a neurotoxin called ‘iridol’ that can cause symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and allergic reactions. Thus, preparing giant squid requires specific skills and knowledge to remove the toxic gland. (Image: Britannica).
The body structure of giant squid makes its meat unsuitable for consumption. Compared to regular squid, giant squids are larger and have thicker bodies. Due to the relatively small meat-to-body weight ratio, their meat is often tough and bland in flavor. This does not align with the taste preferences of most people.
Although giant squid is not a common cooking ingredient among the general population, in some regions, such as certain countries in Asia, it is regarded as a special delicacy and is prepared in various dishes. For instance, giant squid is often featured in Japanese cuisine, where it is made into delicious dishes such as sushi and grilled squid to enhance its flavor.
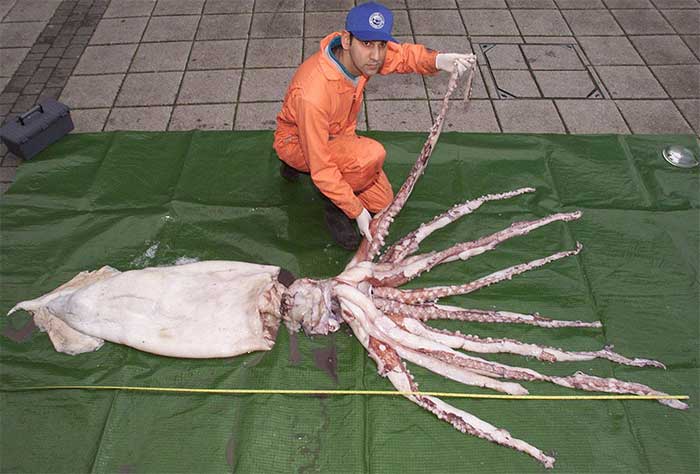

In some places where there is a habit of eating giant squid, they prepare it in many ways. (Image: Britannica).
Giant squid is a deep-sea creature that lives in cold, deep waters. Its appearance is quite different from the seafood we are familiar with, which may be a reason why people are reluctant to eat it. Furthermore, the flavor of giant squid is also unlike that of typical seafood, which increases people’s aversion to the meat of this creature. However, the actual reasons may be more complex and varied.
The appearance of giant squid is indeed distinct from the types of seafood we usually know. It has a massive body with long tentacles and large eyes, characteristics that make it resemble a monster rather than something edible. This unusual appearance can also evoke fear and disgust in humans, inhibiting the desire to eat it.
According to some who have eaten giant squid, its meat is very tough and chewy. In contrast, people tend to prefer softer, juicier seafood like shrimp, crab, and fish.
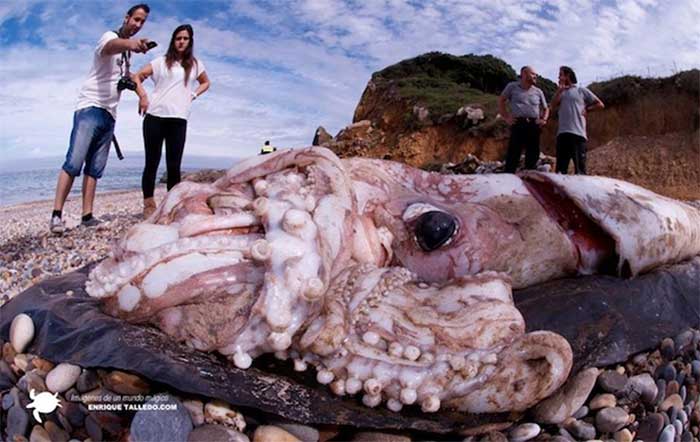

The largest giant squid ever found measured nearly 13 meters, including its tentacles. However, scientists estimate that this species could grow up to 20 meters, based on the size of giant squid beaks found in the stomachs of sperm whales (Physeter macrocephalus), which prey on giant squids. (Image: ZME).
In addition to appearance and flavor, cultural and social backgrounds can also affect people’s acceptance of giant squid. In some areas, giant squid is considered a rare delicacy, enjoyed only on special occasions. Such cultural restrictions can render the idea of eating giant squid unfamiliar. Conversely, in some regions, giant squid is prized for its unique flavor and rich nutritional value.
Although people may feel disgusted by the appearance of giant squid, its meat is actually very nutritious. It is rich in protein, vitamin B12, minerals, and various antioxidants. Studies have also found that giant squid is high in polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health. Thus, giant squid can be a good choice for those pursuing a healthy diet.

The beak of the giant squid is made from hard chitin, a material similar to the exoskeleton of insects, with sharp edges suitable for slicing prey into bite-sized pieces. (Image: Britannica).

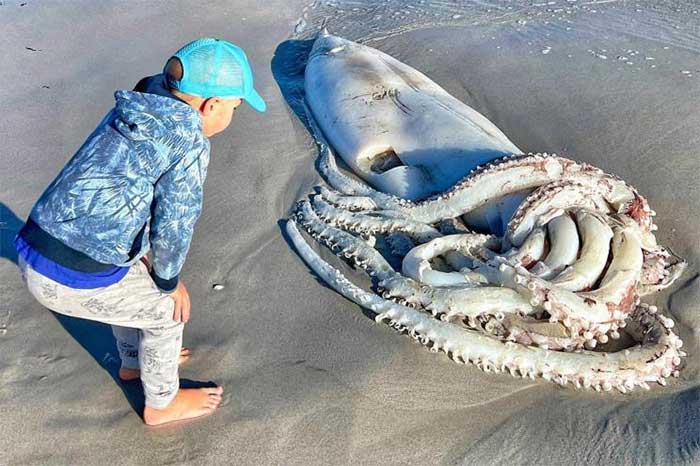
Giant squid has 8 small tentacles and 2 long tentacles for capturing prey. However, their tentacles lack any muscle to control the prey. Therefore, when faced with a sperm whale, they can only flee. (Image: Britannica).