The sunset sky turns red and orange due to the phenomenon of light scattering in the atmosphere.
>>> Why are there “moon halos” and “moon rays”?
The Earth’s atmosphere contains many tiny particles such as dust, ash, pollen, gases, and water vapor. These components in the atmosphere reflect and scatter sunlight in different directions before reaching the human eye.
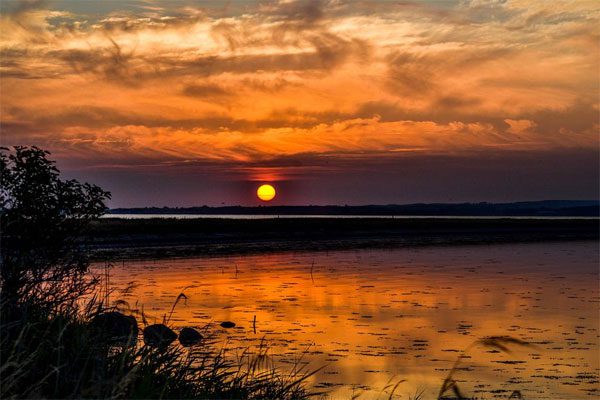

The sky turns red and orange at sunset. (Photo: Timm Jensen)
When the sun is low on the horizon, the distance that sunlight must travel through the atmosphere is over 30% longer than during the day. Short-wavelength light, such as violet and blue, is scattered more, while longer-wavelength light like yellow, orange, and red is less scattered and reaches the observer’s eyes (red is the color with the longest wavelength in the visible spectrum). Therefore, during sunrise and sunset, the sky appears red and orange, according to MNN.
Sunlight is a mixture of many monochromatic lights. During rain, the water vapor in the air acts like a prism, separating sunlight into different monochromatic wavelengths, which is why people see rainbows.
“We often think that everything has a specific color. However, the colors we see depend on the reflection of light from the object and the path of the light,” said Stephen Corfidi, a meteorologist from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).