Gorillas have always been regarded as having a common ancestry with humans, both differing from ancient apes. However, natural selection has led both to follow different evolutionary paths.
In the minds of many, gorillas are considered a rather aggressive species. They are the largest living primates. Typically, wild male gorillas can reach heights of over 1.7 meters and weigh more than 300 kg.
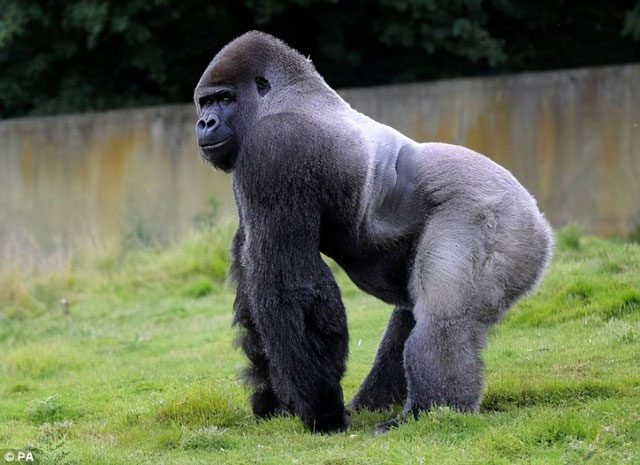

The natural habitat of gorillas also plays an important role. Gorillas live in tropical rainforests, where they must climb and move through branches to find food and territory. This activity is akin to a form of natural exercise, helping their muscles develop and maintain endurance.
In fact, the massive size of gorillas is certainly not for show but is a true symbol of strength. Although the combat effectiveness of gorillas is difficult to compare with lions, tigers, and leopards, they can outmatch many wild animals with bare hands and possess a certain degree of self-defense against lions and tigers.
However, it is noteworthy that despite their bulging muscles, their primary food is plant-based. Why can gorillas maintain their muscles on a vegetarian diet without exercising, while humans cannot?

Gorillas have a higher ratio of type I muscle fibers (slow-twitch, endurance) compared to humans. This type of muscle fiber allows gorillas to maintain strength over long periods without expending much energy. Humans, with a higher proportion of type II fibers (fast-twitch, powerful), are more susceptible to muscle fatigue and loss if they do not exercise regularly.
In reality, many people have certain misconceptions about gorillas, believing them to be herbivorous. The truth is that gorillas are omnivores. Although the majority of their diet is plant-based, they also consume some protein-rich foods from insects, including ants and termites. While not as protein-rich as meat, the foods that gorillas eat are high in fiber and contain plant-based proteins that can support muscle development.
Adult gorillas can consume 25 to 30 kg of food each day. This means that gorillas consume a significant amount of protein daily. Anyone who has ever engaged in physical training knows that to have healthy muscles, you not only need to exercise hard but also to provide enough protein, and this adequate protein intake lays a solid foundation for gorilla muscle development.
More importantly, compared to humans, gorillas possess a very powerful body part, their digestive system is larger and longer and can absorb more nutrients than humans in the same time frame.
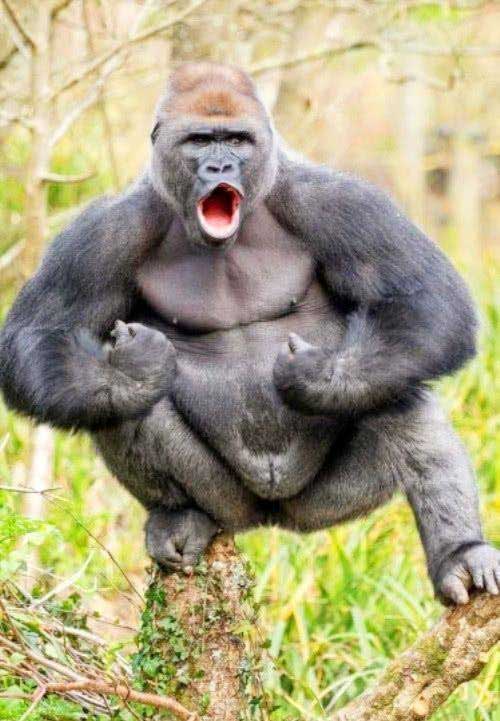

Gorillas have a higher muscle density than humans, meaning that in a given volume of muscle, gorillas have more muscle fibers. This helps gorillas generate more force compared to humans with the same muscle size. Gorillas spend most of their time moving in dense forest environments, climbing, and foraging for food. These activities require significant strength and endurance, helping gorillas maintain muscle without needing to train in traditional human ways.
Additionally, the plant cellulose that humans cannot absorb is an important energy source for gorillas. The bacteria in their intestines that digest cellulose provide a vital protein source for gorillas.
According to research, human muscle development is not only related to training methods but also to myostatin in our bodies. Therefore, if humans want stronger muscles, they must persistently fight against inherent genetic limitations.
In fact, when considering muscle alone, there are many herbivorous animals in nature that surpass humans in muscle mass and circumference—humans cannot have as much muscle as elephants or large creatures like rhinoceroses. Despite the hard work of bodybuilders, human muscles still struggle to catch up with large mammals like gorillas.

Moreover, we cannot deny that the bodies of gorillas and humans respond differently to physical activity. Gorillas have a higher muscle-to-body weight ratio than humans, which helps them maintain muscle even without engaging in deliberately high-intensity physical activities.
In contrast, humans have a different biological system and energy requirements. Our bodies have evolved to adapt to a life that no longer relies heavily on physical strength as our ancient ancestors did. This means we need to stimulate our muscles through specialized training and a high-protein diet to maintain or enhance muscle mass.
Additionally, the need for humans to maintain muscle through training is also related to today’s sedentary lifestyle and unbalanced diet. Low physical activity levels combined with the consumption of processed, energy-rich foods can lead to muscle decline if not balanced with regular training.