Hormones, diet, clogged pores, excessive sweating, or certain medical conditions can lead to an unpleasant body odor even after bathing.
Reasons Your Body May Smell Even After Showering
Typically, body odor stems from personal hygiene issues. However, for some individuals, body odor can persist naturally and does not dissipate even after bathing. This situation can be challenging to manage, leading to feelings of self-consciousness despite maintaining a relatively clean lifestyle. Experts have identified several reasons why many people may still have body odor immediately after showering.
Hormones
According to Dr. Pramod Kumar, a dermatologist at KMC Hospital in the U.S., excessive sweating and body odor are linked to hormonal changes. This is often more noticeable during puberty, pregnancy, premenopause, and menopause due to increased activity of hormones and sweat glands. During these periods, women may experience hot flashes and night sweats, which can lead to increased sweating and body odor.
Eating Strong-Smelling Foods
Regular bathing, exfoliating, or washing your hair may not be sufficient to eliminate body odor if it originates from foods you have consumed. Mark Lewis, a health expert based in California, notes that certain foods like garlic, onions, and spicy dishes can contribute to persistent body odor even after showering.
Hot showers may also cause certain odors to diffuse more, according to Justin Neubrander, a physician at the Fredheim Lifestyle Center. “Consuming a large amount of garlic can cause the scent to be released through the pores in your skin. Therefore, hot showers can help these compounds excrete,” he explains.
In addition to garlic and onions, other foods like broccoli, cabbage, and cauliflower produce gases that can affect body odor. Some individuals experience a rare condition called trimethylaminuria, causing them to emit a fishy odor after eating seafood. Processed foods, alcohol, and certain grains can also contribute to body odor.
Clogged Pores
According to Dr. Neubrander, clogged pores can be a major cause of body odor. While exfoliating the surface of the skin with soap can remove compounds and microorganisms on the skin’s surface, pores are not easily cleaned.
Dr. Neubrander recommends using warm water to open the pores and employing a washcloth to increase friction, effectively cleaning debris and dead skin cells.
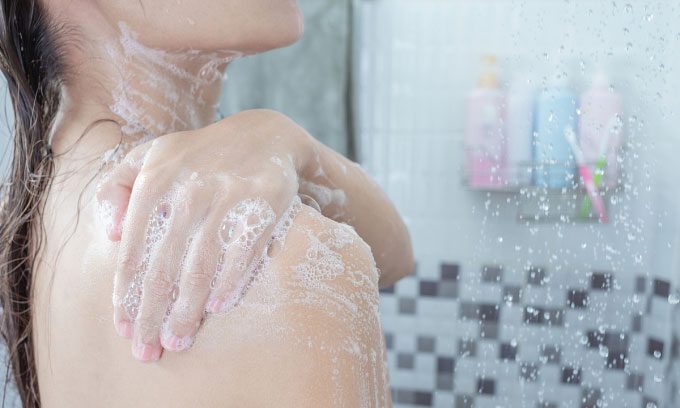

Not cleaning pores deeply can lead to unpleasant body odor. (Image: Freepik).
Excessive Sweating
Everyday activities like jogging or riding public transport can lead to body odor, no matter how thoroughly you shower. Experts state that sweat itself is odorless; however, when it comes into contact with air, the natural bacteria on the skin break down the sweat into thioalcohol. Body odor arises from this interaction between bacteria and sweat. Warm, moist, and dark areas of the body are most likely to retain odors, as they provide ideal conditions for bacteria to thrive.
Medical Conditions
For some individuals, body odor is not related to personal hygiene. They may have certain medical conditions that cause their bodies to emit natural odors, such as tonsillitis, gum disease, and sinus infections, which can lead to worse breath.
Diabetes or infections can also result in stronger breath and body odors. Typically, infections can create foul odors in unusual areas, such as the navel.
According to Michael Kummer, a health expert and former professional athlete, conditions that can affect body odor include gout, hyperthyroidism, liver disease, and kidney issues.
Smoking Habits
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), smoking increases the risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease, stroke, lung disease, diabetes, emphysema, and chronic bronchitis. Additionally, smoking contributes to unpleasant breath and body odor, regardless of how hard you try to mask the scent.
The use of nicotine also causes individuals to sweat more, and the sweat produced tends to have a stronger odor.