Solar panels are one of humanity’s greatest inventions, and their history is more fascinating than you might think.
Solar energy, one of the most popular and rapidly developing renewable energy sources today, has undergone an incredible journey of development. From early experiments to technological breakthroughs, solar energy has demonstrated its potential to meet the increasing energy demands of humanity.
The history of solar energy began in 1884.
Initial Steps and Ambitious Experiments
The history of solar energy began in 1884, when Charles Fritts, a pioneering scientist, installed the first photovoltaic solar panel on a rooftop in New York City. Although it only achieved an efficiency of less than 1% in converting sunlight into electricity, Fritts’s project marked a significant milestone in the development of solar energy technology. He used selenium coated with a thin layer of gold to generate electricity, which he described as “continuous, stable, and having significant force.” However, due to the high cost of materials, this project could not advance further and failed to become a competitive commercial product.
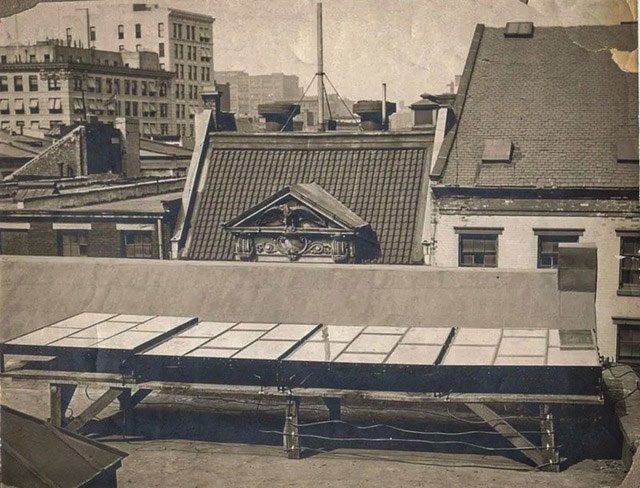

Early solar panels.
Twenty years later, George Cove, a Canadian inventor, continued Fritts’s work and developed a “solar power generator,” using semiconductor materials with a bandgap similar to silicon, the material primarily used in today’s solar panels. Cove made significant progress by developing batteries to store and release energy, attracting the interest of many investors when he introduced this technology in Halifax, Nova Scotia, in 1909. However, Cove’s story took a strange turn when he claimed to have been kidnapped and was offered a large sum of money to abandon his work. Although this incident was never verified, it led to a rapid decline in Cove’s career, and solar energy technology was forgotten for the next 40 years due to the rise of coal and oil.

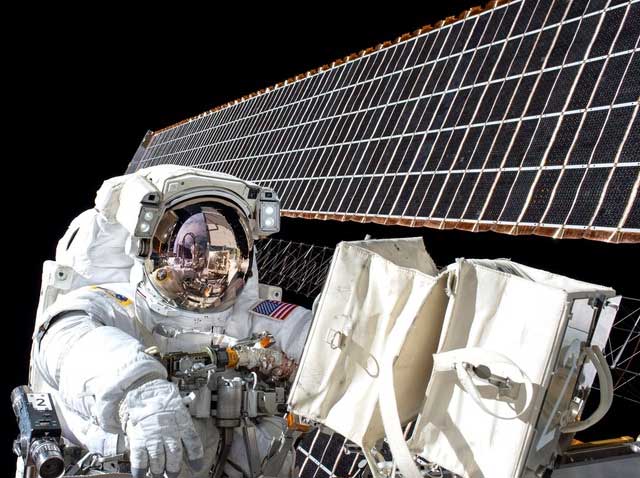
The first application of solar panels appeared in 1958.
Technological Breakthroughs and the Resurgence of Solar Energy
While solar energy was forgotten, other key technologies were developed, laying the groundwork for its resurgence. In 1918, Jan Czochralski, a Polish chemist, inadvertently discovered the method for growing single crystals (monocrystalline), which later became the backbone of 90% of today’s electronic devices, including solar panels. This discovery significantly contributed to the development of silicon solar cells, achieved by scientists at Bell Labs in 1954. With a conversion efficiency of 6%, this represented a breakthrough compared to previous experiments and marked a strong comeback for solar energy technology.

From the 1960s to the 1980s, solar energy began to be more widely used.
The first application of solar panels appeared in 1958 with the launch of the Vanguard I satellite, becoming the first solar-powered object in space. This demonstrated that solar energy technology had potential not only on Earth but also in outer space. From the 1960s to the 1980s, solar energy began to be adopted more widely, especially in remote areas where electricity lines were impractical or too costly.
Modern Development and Future Potential of Solar Energy
In the 1980s, solar panels were improved with the advent of multi-junction cells, which increased the efficiency of energy capture from the sun. By 2006, researchers achieved an efficiency of 46% with multi-junction cells, nearly double that of traditional silicon cells. Although these cells remained expensive, they were widely used in aerospace applications such as the International Space Station.
With the introduction of perovskite materials, solar panel technology continued to improve with superior efficiency. Bifacial solar panels, capable of capturing sunlight from both sides, have also become popular in the past decade, especially in large-scale solar power plants.

With the introduction of perovskite materials, solar technology continues to improve.
One of the biggest breakthroughs in modern solar energy technology is energy storage capability. With the development of batteries such as lithium-ion, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), and other energy storage technologies, solar energy is increasingly becoming viable for providing stable and reliable power even at night. This plays a crucial role in transforming solar energy into a sustainable power source capable of meeting the growing electricity demands of humanity.
From Charles Fritts’s initial experiments to modern technological breakthroughs, solar energy has undergone an incredible journey of development. Today, it has become one of the cleanest, economically viable energy sources with the greatest potential for growth globally. As the world moves towards a carbon-neutral goal by 2050, solar energy will continue to play a vital role in ensuring sustainable energy for the future.




















































