An imbalanced diet can lead to overweight, accumulation of visceral fat, and high blood lipids. However, there are numerous foods that can help improve this condition, though not everyone is aware of them.
Besides subcutaneous fat, the body also contains visceral fat. This type of fat is stored in the abdominal cavity, near several vital organs including the liver, stomach, and intestines. Blood lipids are important components of blood, consisting of both “good” and “bad” fats. When blood lipid levels are too high, it can lead to high blood lipid disease.
However, while ordinary fat can be easily reduced through exercise and dieting, visceral fat and blood lipids are much more difficult to decrease and can pose a serious threat to life.
Specifically, high blood lipids can easily lead to cardiovascular diseases, increase the risk of stroke, high blood pressure, and fatty liver disease… Visceral fat not only causes weight gain and abdominal obesity but also harbors many serious health issues, such as increased risks of inflammation, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, stroke, dementia, gout, and joint diseases…
According to experts, diet is both a cause and a solution to combat high blood lipids and visceral fat. In addition to increasing physical activity and adjusting lifestyle habits like when trying to reduce ordinary fat, utilizing certain foods can also be very beneficial.
Here are 6 foods that help “suck out” oil from the blood and effectively reduce visceral fat, compiled from the votes of 27 medical experts and announced in a recent health program on NHK Japan:
1. Mackerel and Sardines

Mackerel and sardines are considered the best for reducing blood lipids and visceral fat.
Renowned Japanese nutritionist Katamura Yumi states that deep-sea fatty fish are beneficial for blood vessels and overall health. They are especially regarded as “golden protein” for those with blood lipids. Among them, mackerel and sardines are deemed the best for reducing blood lipids and visceral fat.
They provide essential nutrients while containing high-quality fats that help reduce bad fats. For example, the high-quality fats in mackerel can prevent the formation of internal fat and promote better blood circulation. Sardines are very rich in EPA and DHA, which help inhibit the increase of cholesterol levels.
Both types of fish are rich in Omega-3, which can improve insulin sensitivity and combat inflammation caused by visceral fat. Additionally, fatty fish provide a significant amount of vitamin D, which helps improve the immune system, regulate bone density, and reduce overall visceral fat in the body.
2. Green Tea
Green tea consistently ranks among the top healthy foods, particularly for cardiovascular health. A study involving 40,530 Japanese adults found that those who drank more than 5 cups of green tea daily had a 36% lower risk of death from heart attacks or strokes and a 16% lower risk of death from all causes compared to those who drank less than one cup a day.
Japanese cardiologist Toshiro Iketani explains that the powerful antioxidants in green tea, especially Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), can help prevent atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque in arteries, and reduce bad blood lipids.
Green tea also contains tannins, which can improve fat metabolism, reduce fat, while caffeine contributes to fat burning. The phenols in green tea can effectively inhibit the increase in blood pressure and blood sugar levels, accelerating metabolism. This leads to better reduction of excess fat in the blood and visceral fat.
3. Peas
Peas have a unique benefit that few people know about: they effectively help with weight loss, particularly in reducing waist circumference—where visceral fat is concentrated. Dr. Toshiro Iketani also emphasizes that peas are good for cardiovascular health and help prevent and reduce blood lipids.
Studies show that after consuming peas, the levels of cholesterol—bad blood lipids—can drop by about 15%. They are also rich in plant protein and soluble fiber, making them very effective for burning excess fat.
This food is low in calories and contains many components beneficial for digestion. Consequently, consuming peas not only provides a feeling of fullness quickly and keeps hunger at bay but also accelerates detoxification, reduces visceral fat, and prevents the accumulation of excess fat.
4. Oatmeal

Oatmeal is one of the best foods for blood vessels, especially in preventing and supporting the treatment of blood lipids. Oatmeal is very rich in β-glucan and soluble fiber, which can inhibit the body’s absorption of cholesterol and effectively regulate blood lipids.
Oatmeal also protects the cardiovascular system and helps prevent heart disease by reducing triacylglycerol levels in the liver. Additionally, the potassium in this food can help excrete sodium and lower blood pressure, which is very good for blood health.
For those looking to lose weight, especially stubborn visceral fat, oatmeal is a must-have. This food is high in fiber and low in calories, helping to “burn” excess fat while keeping you full for longer. The best time to consume oatmeal for weight loss and reducing visceral fat is at breakfast.
5. Natto
There are at least 17 studies worldwide on the benefits of natto for dissolving blood clots and preventing strokes. This dish originates from Japan and is made from fermented soybeans using beneficial bacteria Bacillus, fermented at 40 degrees Celsius for 24 hours.
Nattokinase in natto has the ability to break down fibrin (the protein that causes blood clotting) effectively, four times more than plasmin (the enzyme that dissolves blood clots). Combined with vitamin K2 and many antioxidants, it helps purify the blood, improve blood circulation, reduce blood lipids, and prevent arterial stiffness.
Dr. Katamura Yumi further notes that natto is high in fiber and vitamins while being very low in calories, making it a favorite among those looking to lose weight, especially abdominal fat. It also has excellent effects on gut regulation, being rich in beneficial bacteria that accelerate metabolism and support the reduction of visceral fat while reducing inflammation caused by visceral fat.
6. Tomatoes
When looking for foods to combat stubborn blood lipids and visceral fat, tomatoes cannot be overlooked. Scientific studies show that tomatoes and tomato products contain the carotenoid pigment lycopene, which helps reduce inflammation, lower total cholesterol, increase good cholesterol (HDL), and decrease the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis. Especially when cooked with olive oil, tomatoes can improve arterial blockages and effectively prevent cardiovascular diseases and blood lipids.
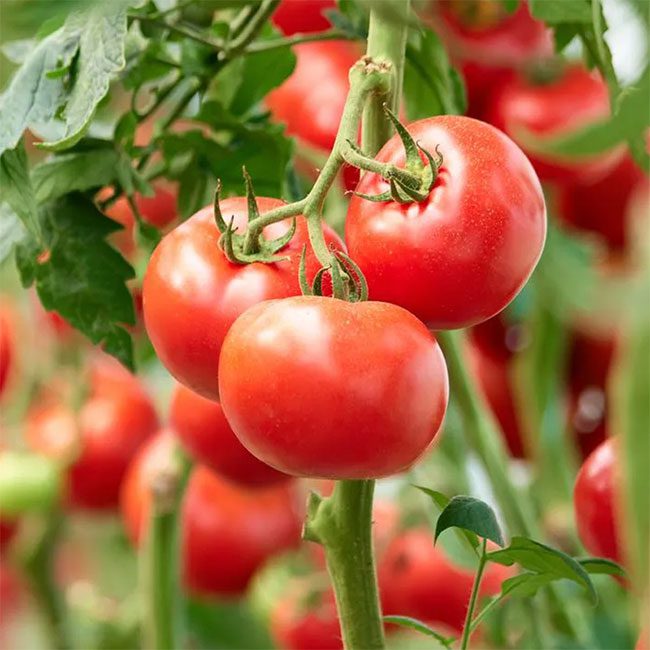

Tomatoes not only help reduce bad fats in the blood but also “melt” visceral fat, helping you achieve a better body shape (Illustrative photo)
A vitamin called rutin in tomatoes can enhance the body’s antioxidant capabilities, effectively cleaning out “waste” in the blood and reducing visceral fat. Similarly, pectin in tomatoes significantly reduces cholesterol in the bloodstream and decreases blood viscosity. The very act of lowering blood lipids also positively supports the process of reducing visceral fat.
Tomatoes have the ability to “suck up fat” while being high in fiber, promoting digestion, which is excellent for absorbing excess fat in the intestines and expelling fat and toxins from the body. Moreover, although low in calories, this food is rich in vitamin C—a powerful antioxidant that aids in burning excess fat.