Everything on Earth is constantly changing; the fact is that tectonic plates are expanding and contracting, albeit at a very slow pace.
Why is this happening?
Before we delve into the reasons behind the changing sizes of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, it’s essential to understand the basic principles of plate tectonics.
The size of the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans is changing due to the processes of seafloor spreading and subduction. (Image source: Science ABC).
The lithosphere is the solid outer layer of the Earth, comprising the Earth’s crust and the uppermost part of the mantle, divided into large and small plates.
These plates move on the asthenosphere (the soft layer), which is as pliable as plastic in the mantle. Convection currents in the mantle are responsible for the movement of these plates.
There are three types of plate boundaries: divergent, convergent, and transform. At divergent boundaries, two plates move apart, creating new crust that spreads under the ocean. At convergent boundaries, two plates move toward each other, and one plate may eventually slide beneath the other, forming a subduction zone.
At transform boundaries, two plates slide past each other in parallel directions.
The Atlantic Ocean is expanding
The Atlantic Ocean on our planet is a natural wonder. It is a vast body of water that occupies over 20% (equivalent to 106.5 million km2) of the Earth’s surface area and is the second-largest ocean in the world.
However, this number is changing, primarily due to the mid-Atlantic ridge, which is a long chain of underwater mountains separating two tectonic plates: the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate.
This movement causes magma from the Earth’s mantle to rise to the surface, leading to the formation of new crust. This process is known as seafloor spreading.
The Pacific Ocean is contracting
The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean in the world, covering 46% of the Earth’s total surface area, equivalent to about 63.8 million square miles.
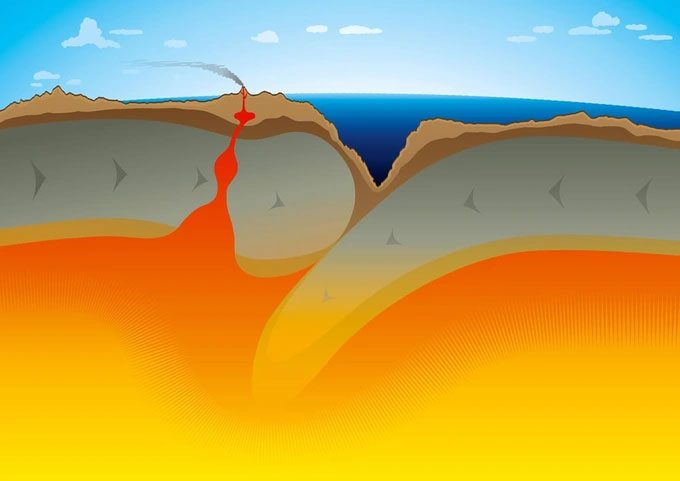 The process of subduction of the seafloor. (Image source: Science ABC).
The process of subduction of the seafloor. (Image source: Science ABC).
If we consider the Pacific Ocean as a gigantic swimming pool and fill it with all the water from rivers, lakes, and streams around the world, it would take humanity over 500 years, assuming there was no evaporation or leakage.
Despite its immense size, the Pacific Ocean is actually shrinking. This is due to the Pacific Plate, the largest tectonic plate on Earth, being pushed under other plates, a process known as subduction.
To better understand subduction, we can visualize it as a sandwich-making machine, with the two plates resembling slices of bread and the subduction zone being the filling.
The two slices of bread come together when the machine heats up, and the filling is pushed out. In the subduction zone, a similar process occurs; instead of filling the two plates, magma rises to the surface, forming volcanoes.
In summary, the movement of tectonic plates is the reason why the sizes of our oceans are gradually changing.
The Atlantic Ocean is expanding due to the formation of new oceanic crust at the mid-Atlantic ridge, while the Pacific Ocean is contracting due to the subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath surrounding plates.
These geological processes are ongoing and have shaped the world as we know it for millions of years. So, when we look at a world map, remember that it is just a snapshot of a continuously changing and dynamic planet.
The oceans are not just vast bodies of water; they are the result of tectonic interactions that continue to shape the foundation of our world, much like an endless dance.
In this dance, the movement of one plate affects others, leading to a spectacular and ever-changing planetary masterpiece.


















































