In addition to the environment, the Tiangong Station can withstand temperatures of 150 degrees Celsius on the sun-facing side, while the rear side drops to -100 degrees Celsius.
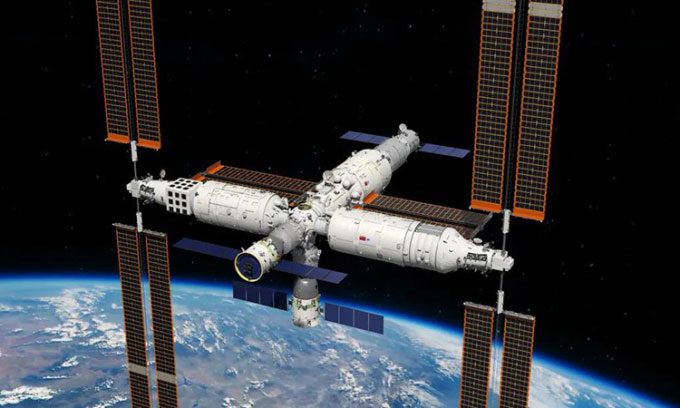

Simulation of the three basic modules of the Chinese space station. (Photo: CMG).
Orbiting Earth at an altitude of 400 km, the Chinese Tiangong Space Station must endure direct sunlight in space due to the lack of atmospheric protection. This necessitates the station to be equipped with advanced thermal management technologies, as reported by CGTN on September 9.
The surface of Tiangong can experience heat rays up to 150 degrees Celsius when facing the sun, while temperatures on the rear side can drop to -100 degrees Celsius. Therefore, the thermal control system plays a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable environment inside the cabin.
This system ensures that all parts of the space station remain within suitable temperature ranges for operation while creating a pleasant environment for astronauts to live in. Unlike previous short-term crew missions, the space station is designed for long-term use, which comes with higher and stricter temperature control standards.
The fluid circuit is a vital component of the thermal control system as it surrounds the main modules, including the core module and the laboratory module. By providing balanced heat distribution, the system helps cool overheated areas and warm up excessively cold spots. With fluid circulating through pipes, excess heat generated by equipment and astronauts is transferred to other devices or components.
The laboratory module, Wen Tian, which houses numerous experiments and is currently the heaviest and largest part of the space station, requires special care. A team of experts has developed three sets of cooling systems to absorb heat generated by various devices and dissipate it into space. These systems can release thousands of kilowatts of heat, ensuring that the sophisticated equipment in the laboratory operates smoothly.

The Tianzhou 4 spacecraft covered with gray thermal insulation material on the left and white on the right. (Photo: China Media Group)
In addition to the thermal control system, other passive measures are also implemented. These have advantages such as low cost, small volume, lightweight, and low risk. One such measure is the use of thermal coatings. The Shenzhou spacecraft series began using silver thermal coatings starting from Shenzhou-12. The coating material absorbs less sunlight and helps reduce heat.
Another passive measure is the use of insulation materials. The Tiangong Station employs various types of insulation for different spacecraft. The Tianzhou 4 uses multilayer insulation materials consisting of high-reflectivity film layers and polyester mesh to prevent heat loss. The crew cabin of the spacecraft is coated with gray insulation, absorbing more sunlight to create a higher temperature for human activities. Meanwhile, the propulsion section, which primarily contains equipment, is covered with white insulation to reflect sunlight, maintaining a cooler temperature.