These genes can be considered prototypes of “superpower” genes. While they won’t allow a person to become a superhero like in science fiction movies, they can make a person “better” than an average individual in certain aspects.
Individuals with Super Short Sleep
The common belief is that adults should sleep around 8 hours. Insufficient sleep can lead to not only mental fatigue and reduced immunity but also impaired judgment and memory.
However, some people seem to need significantly less time to maintain their energy and can even work all day without feeling sleepy.
You might think they are just pushing through, but in reality, they may have been born with a rare gene mutation. A research team led by Fu Yinghui, a professor of neurology at the University of California, discovered that there is a gene called “DEC2” in the human body. This gene significantly affects sleep behavior. When this gene mutates, a person only needs about 6.25 hours of sleep each night to feel fully rested, effectively clearing waste from the body and replenishing energy.

Individuals with this gene mutation are extremely rare. (Illustrative photo).
After Professor Fu Yinghui announced the experimental results, he received emails from around the world with claims of the ability to sleep less than average. He later found a father and son who only sleep an average of 4-5 hours each day, nearly half of what is normal, yet they seem to suffer no negative effects from sleep deprivation.
After sequencing the genes of the father and son, the research team discovered they had a rarer gene mutation called “npsr1” compared to the “DEC2” mutation. Individuals with this gene mutation are extremely rare, with only about 1 in 250,000 people possessing it. This group only needs to sleep 4-5 hours each day to recharge their bodies. Moreover, those with the “npsr1” mutation can not only recover physically after short sleep periods but it may also prevent memory loss due to lack of sleep.
Individuals with Super Strong Bones
Most people are familiar with Wolverine from the “X-Men” series, as he is a quintessential character in the franchise. Besides his extraordinary healing abilities, Wolverine’s strength comes from the adamantium alloy embedded in his bones, making them nearly indestructible.
But can humans actually possess such abilities? To answer this question, we must start with the hardness of human bones. The hardness of human bones is controlled by a gene called LRP5. This gene regulates the density and strength of human bones.
This gene is crucial for human health as it is associated with osteoporosis, a common bone disease. Osteoporosis occurs due to mutations in the LRP5 gene, causing bones to become weak and brittle. But what if the LRP5 gene mutated in a different direction?
This gene mutation makes bones much harder than those of average individuals. (Illustrative photo).
Scientists discovered this rare gene mutation in a family in Connecticut, USA. Members of this family exhibited greatly increased bone mass and remarkable bone density due to the LRP5 gene mutation.
Their bones are significantly harder than those of average individuals, making fractures nearly impossible. Moreover, their skin appears younger than their actual age, and scientists believe that family members have no risk of fractures even in severe car accidents.
It sounds incredible, but possessing such superpowers is not entirely beneficial as it also brings some side effects and risks. Individuals with the LRP5 gene mutation may experience excessive bone growth, putting pressure on surrounding nerves, leading to serious consequences. In the worst-case scenario, they could even suffer from hearing loss.
Additionally, as these individuals age, they will face some issues that ordinary people do not encounter. For instance, if they need joint replacement surgery, doctors may find their bones too dense to accommodate artificial joints, affecting their mobility. This is reminiscent of Wolverine in the films; despite possessing superpowers, there is a steep price to pay as they age.
Individuals with Blood More Precious than Gold
Most people can probably name the four common blood types: A, B, AB, and O. Some may have heard of RH-negative blood. However, you might not know that scientists have discovered over 30 blood types in humans, one of which is extremely rare and referred to as “golden blood.”
This blood type is RH null, characterized by the absence of any RH antigens on red blood cell membranes, allowing it to be safely transfused to all RH-negative individuals. According to statistics, only 43 people have been identified with this blood type worldwide in the past 50 years.
If your blood type is RH null and type O, then your blood is the best kind of golden blood. This is because RH null type O can be transfused not only to all RH-negative individuals but also to everyone with RH-positive blood, meaning it can be given to anyone in the world without causing immune rejection. Currently, there are only nine people in the world with such universal blood.
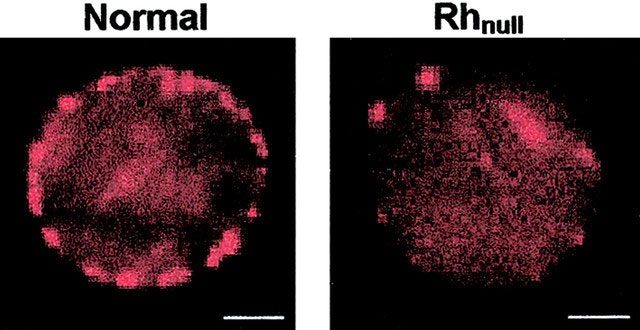
In the past 50 years, only 43 people have been identified with this blood type. (Illustrative photo).
However, for those with golden blood, this is not a blessing but a terrifying nightmare. When they themselves need a blood transfusion, only “like blood” can help them, and with only 43 people sharing the same golden blood type scattered across different countries and regions, this becomes a significant issue.
Thus, to prepare for emergencies, golden blood holders regularly draw their own blood each year and store it in blood banks to safeguard their own health.
Due to the rarity and mystique of this blood type, many individuals with golden blood choose to keep their identities hidden and do not wish to disclose their identities to avoid unnecessary troubles. They worry they might become targets for scientists or malicious criminals or be forced to become “living blood banks” for others.


















































