Researchers are developing a new solar sail design that enables spacecraft to travel through space without fuel.
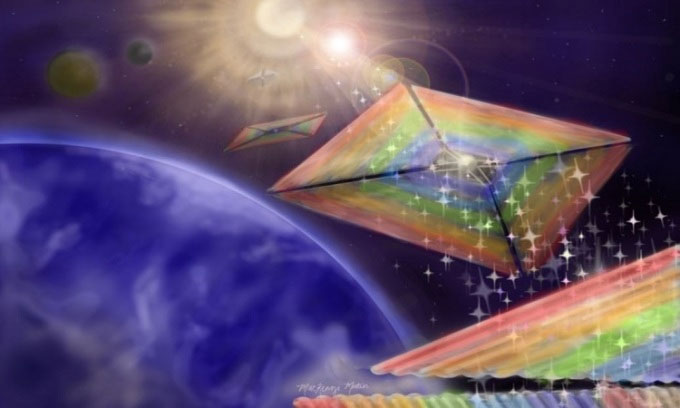

Simulation of a diffractive solar sail. (Photo: MacKenzi Martin).
A project aimed at developing an advanced solar sail has entered the final phase of NASA’s research program. Phase 3 of the NASA Innovative Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program will allow researchers to continue exploring and developing diffractive solar sails over the next two years with a budget of $2 million. This funding will help promote the solar sail design for broader applications.
“As we venture further into space than ever before, we need superior and advanced technology to carry out our missions,” said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson. “NASA’s Innovative Advanced Concepts program helps bring ideas like solar sails closer to reality.”
Similar to traditional sails on boats that harness wind power to create movement, solar sails operate by using the pressure generated by sunlight to move through space. When photons bounce off a mirror-like surface, their momentum pushes the sail forward without the need for fuel. The current design of diffractive solar sails is quite large, thin, and often limited in directional movement. However, a diffractive solar sail with small squares on a thin film could be smaller, more flexible, and easier to steer.
The idea of a diffractive solar sail was first selected for phases 1 and 2 of NIAC in 2019. Throughout these two phases and testing, a research team examined several materials for constructing the sail while also developing positioning and control methods for missions orbiting the Sun’s poles. Both phases included weather experiments to test durability when exposed to ultraviolet rays. In phase 3, researchers will optimize the construction materials and conduct ground tests to prepare for a mission to the Sun.
The Indian government previously launched solar sail missions to support communication satellites in 1992 and 2003. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) successfully launched the new spacecraft IKAROS equipped with a solar sail in 2010 to study Venus and the Sun. Since then, both NASA and the nonprofit research organization Planetary Society have successfully launched spacecraft equipped with solar sails into low Earth orbit.