With a distance of 2,600 km from the nearest land, Point Nemo is the “resting place” for hundreds of spacecraft at the end of their missions.
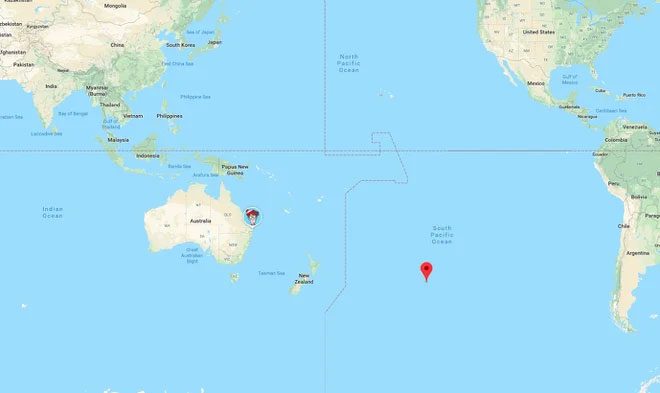
Point Nemo in Latin means “no man’s land”. This invisible point is located in the Pacific Ocean, surrounded by Australia, South America, and New Zealand. The islands near Point Nemo include Ducie to the north, Motu Nui of Easter Island to the northeast, and Maher to the south. (Image: The Sun).
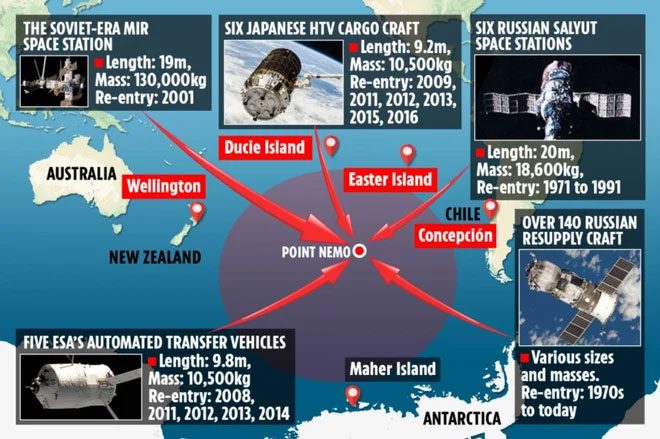
With a distance of over 2,600 km to the nearest land, Point Nemo is the ideal place for spacecraft to crash after mission completion. Since it was first used in 1971, Point Nemo has become the “resting place” for over 270 spacecraft from NASA and various space organizations. (Image: The Sun).

The first person to locate Point Nemo was Hrvoje Lukatela, a Croatian-Canadian geodesist. He used software to calculate the coordinates that are the farthest from three equidistant points, thus finding the location of Point Nemo in 1992 without needing a physical site. The image shows Motu Nui, one of the islands closest to Point Nemo. (Image: Flickr).
Point Nemo is the safest place for spacecraft to fall because the risk of collision with populated areas or human structures is virtually zero. Due to ocean currents, this area is devoid of marine life and lacks fishing vessels due to low nutrient levels. This is why Point Nemo is nicknamed “the spacecraft graveyard” or “the loneliest place on Earth.” (Image: Auto Evolution).

The largest structure ever to fall at Point Nemo is the Russian Space Station (MIR), weighing about 120 tons, which fell in 2001 after 15 years of operation. Many other spacecraft have also “rested” at Point Nemo, including cargo ships from the European Space Agency, Japan’s HTV cargo spacecraft, and over 140 supply vessels from Russia… (Image: ABC News).

The International Space Station (ISS) is expected to fall at Point Nemo in 2031. Due to its large size, the ISS will not completely burn up upon re-entering Earth’s atmosphere. The people “living” closest to this area are the scientists on the ISS. When flying over Point Nemo, the distance from the ISS to Earth is 360 km, closer than any island on the planet’s surface. (Image: Getty Images).
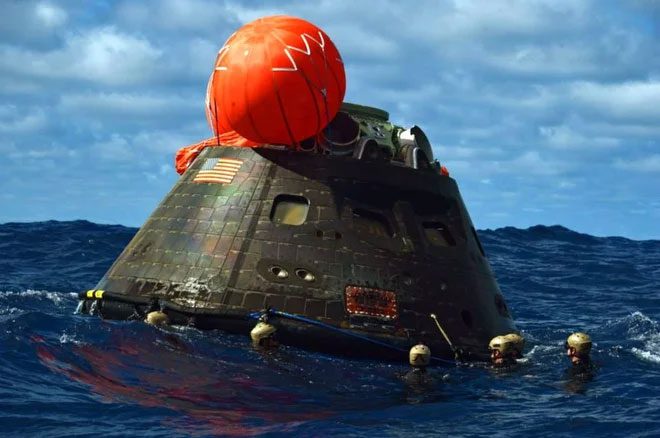

Engineers must time the descent of spacecraft to fall at Point Nemo. Upon re-entering Earth’s atmosphere, spacecraft will break into many small pieces. For large objects like China’s Tiangong-1 space station, debris can scatter across a 1,600 km stretch of ocean. However, it is impossible to pinpoint the exact location of the debris fall. (Image: Getty Images).
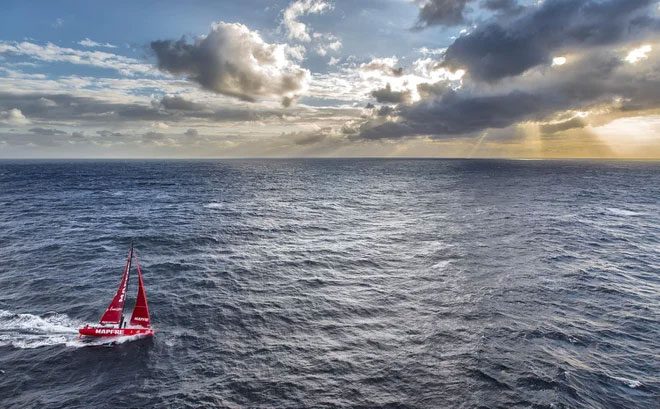

In 1997, a loud noise was detected about 2,000 km east of Point Nemo, known as “The Bloop.” Science fiction enthusiasts believed this was the sound of a sea monster. However, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) concluded that it was merely the sound of ice breaking in Antarctica. During the 2017-18 Volvo Ocean Race, boats passing through Point Nemo collected microplastics for ocean waste research. (Image: The Ocean Race).




















































