Urban populations are set to triple, half of the world’s population may lack access to clean water, and millions could face starvation… these are some of the daunting challenges that Earth may encounter in the next four decades.
With advancements in science and technology, we now have self-driving cars and semi-intelligent robots. However, alongside these technological improvements, humanity is facing countless difficulties arising from pandemics, poverty, and natural disasters…
Experts indicate that significant issues await us in the coming decades. Science and technology must focus on finding solutions to improve our future as these challenges are rapidly approaching.
Let’s review the alarming scenarios that Earth will face by 2050, as summarized by Business Insider.
1. Urban Population to Triple
Statistics show that in 1950, the population living in major cities was 750 million. This number has surged to 4 billion today and is expected to continue increasing.
The latest estimates from the United Nations indicate that 7.6 billion people currently inhabit Earth, and this figure is expected to reach 9.8 billion by 2050. By the end of the century, around 11.2 billion people are predicted to inhabit our planet.
Each of these individuals will need a place to live, a job, water, and energy for daily activities. As a result, there will be a tendency for increased consumption of products such as meat, eggs, and dairy, which will further pressure global food supplies.

Along with the overpopulation issue, the likelihood of spreading infectious diseases, viruses, tuberculosis, and flu will rise dramatically. This is partly due to depleting water sources and healthcare systems struggling to meet the needs of everyone.

Compared to rural areas, cities will consume about three-quarters of the world’s energy and emit a significant amount of carbon dioxide. According to the WHO, air pollution caused 3.7 million deaths in 2012. This number is expected to rise as urban populations grow and pollution worsens.
2. Air Pollution Deaths to Reach 6 Million
A recent report from the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) stated that by 2050, air pollution-related deaths could reach 6 million.

Experts attribute this increase to warming weather, which will enhance chemical reactions that produce more pollutants.
One of these toxins is ground-level ozone or “bad” ozone, created by chemical reactions between nitrogen oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the presence of sunlight.
Emissions from industrial facilities, vehicle engines, and chemical solvents are the primary sources of NOx and VOCs. These substances will cause respiratory issues, leading to coughing and, over time, asthma.
3. Half of the World’s Population Lacks Access to Water
Believe it or not, currently, 1.1 billion people (1/6 of the global population) lack access to clean water, and this number is expected to rise.

According to the International Water Management Institute, by 2050, this number could rise to nearly 2 billion, primarily concentrated in the Middle East and North Africa. Not only clean water but also significant amounts of water for irrigation are under threat.
Currently, one-third of groundwater is gradually disappearing. With the rapid population growth and global warming, this situation will worsen. Alongside water scarcity, the world will also face droughts and wildfires at alarming levels.
4. Many Fish Species We Consume Will Become Extinct
A report from the United Nations Environment Program indicates that global fishing levels are at 87% of maximum sustainable yield. If fishing practices continue at the current rate, countless fish species will face extinction by 2050.

The decline in fish populations will also lead to job losses for those dependent on fishing and aquaculture, causing significant damage to the global seafood export industry. This loss could reach up to 129 billion USD.
5. Millions of People Worldwide May Face Starvation
Global temperatures are gradually rising, raising alarms about severe food shortages in Africa and Asia, which will have catastrophic consequences for the impoverished in these regions.

Currently, the global food supply has decreased by about 2%, and if this trend continues, over the next decade, we could lose 4,440,000 tons of food.
A report from the world’s largest agricultural research organization asserts that by 2050, food production will need to increase by 60% to keep pace with climate change and the growing global population.
6. Rainforests Will Disappear Forever
Did you know that we lose a significant amount of rainforest each year due to rampant deforestation?

Although the exact area lost is not fully determined, it is estimated that at least 32,300 hectares of forest disappear from the Earth each day, with another 32,300 hectares being degraded.
Along with the disappearance of tropical rainforests, hundreds of species are at risk of extinction. Furthermore, when forests are destroyed, a significant amount of carbon is released into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change.
7. Superbugs Could Cause 10 Million Deaths Annually
The world has recently been warned about the rise of antibiotic-resistant superbugs, referred to as “bacterial nightmares” or “deadly superbugs.”
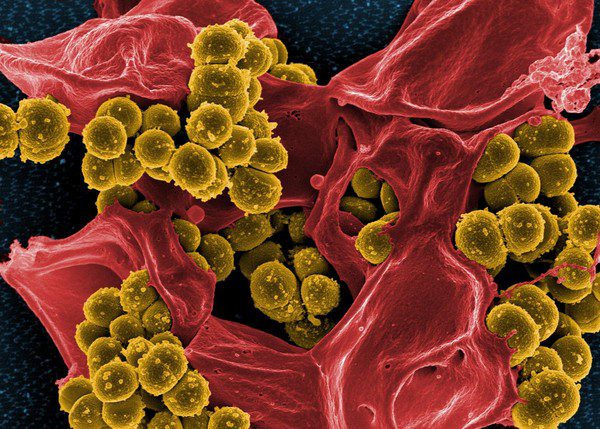
This issue currently claims 700,000 lives annually, and a scientific report from the United States projects that by 2050, infectious diseases could kill 10 million people worldwide – more than all forms of cancer combined.
Like any living organism, bacteria can reproduce and mutate to survive. Some species will adapt to increase their resistance to the antibiotics designed to eliminate them.
8. Diseases Spread Easily
Rising temperatures, combined with floods and droughts, pose a significant threat to global health. These conditions create an ideal environment for mosquitoes, parasites, rodents, and many other disease-carrying organisms to thrive.

According to estimates by the World Health Organization (WHO), by 2030, an additional 60,000 people will die from malaria. By 2050, 4.6 billion people will be at risk of contracting dengue fever, and cholera will also become more prevalent, potentially leading to 130,000 deaths each year. With a weakened immune system due to unpredictable climate changes, it is likely that the actual figures will far exceed these estimates.
9. Storms Become More Frequent and Severe
The National Climate Assessment in the United States reports that the number of Category 4 and 5 storms (the strongest types) has been increasing since 1980. Experts predict that this trend will continue to escalate in an uncontrollable manner.

Specifically, climate change causes increased sea levels and higher temperatures. As the Earth warms and more water vapor is released, storms could become up to 300% stronger by 2100.
Therefore, scientists believe that the Earth is facing significant challenges, and changing habits while educating the public about the importance of environmental protection is essential to prevent the planet from confronting a terrifying future by 2050.
10. Rising Sea Levels Flood Major Cities Worldwide, Power Outages Become Common
Experts suggest that with uncontrolled carbon emissions, global warming will result in sea levels rising by approximately 35 cm, submerging many cities.

One report indicates that if global temperatures rise by 1 degree Celsius, over 40 of the 700 UNESCO World Heritage sites will be submerged within the next 2,000 years. If temperatures rise by 3 degrees Celsius, that number will increase to 136 sites.

Additionally, widespread power outages are expected. By 2050, more than 50% of the population may live in darkness. This impact will worsen, particularly in densely populated areas like the Northeastern United States, including New York and Philadelphia.
11. Oil Becomes a Luxury Item
Experts note that with a rising population, ensuring energy consumption needs will be a significant concern in the future.

If global energy consumption continues at its current rate, by 2050, oil demand will increase by 110% – equating to 190 million barrels of oil consumed daily. Additionally, carbon emissions will double.

The exploration of new energy sources, such as coal, to replace oil is also a focus. However, this is one of the most environmentally polluting energy sources in the world. As a result, scientists are struggling to develop a viable solution.




















































