In the vast journey of exploring energy, nuclear fusion reactions shine like a new star, attracting the attention of scientists worldwide due to their enormous energy potential and clean, environmentally friendly characteristics.
When scientists assert that “0.6 tons of nuclear fusion fuel is equivalent to 2 million tons of high-quality coal,” we cannot help but be astonished by this incredible energy conversion efficiency. So, what else is captivating about nuclear fusion? How will it change our future?
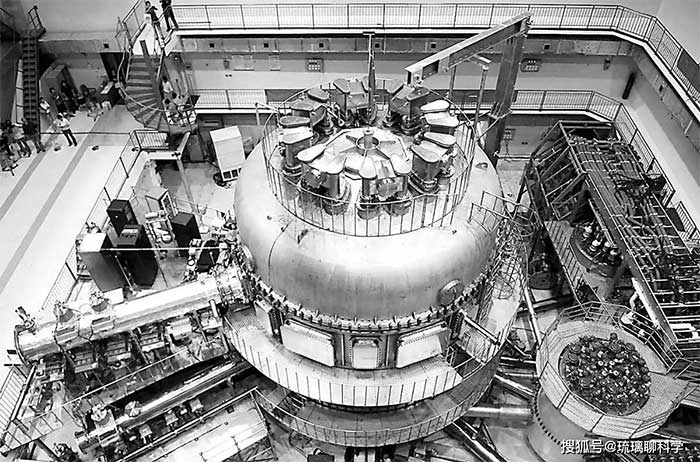

Nuclear reactor.
Nuclear fusion can be considered the most fundamental way to release energy in nature, operating on principles similar to the energy production mechanisms inside the Sun—two lighter nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus in a high-temperature and high-pressure environment, simultaneously releasing a large amount of energy. Through calculations, scientists have found that only 0.6 tons of nuclear fusion fuel can generate a power equivalent to burning 2 million tons of high-quality coal. This energy density far surpasses that of traditional fossil fuels, highlighting the immense potential of nuclear fusion in the energy sector.
Taking the Sun as an example, it has continuously produced heat and light for over 5 billion years based on the nuclear fusion of hydrogen, and this process is predicted to continue for billions of years to come. If humanity can master controllable nuclear fusion technology, it would be equivalent to creating an “artificial sun” with a nearly limitless clean energy source. This not only holds the promise of fundamentally addressing the energy crisis but also propels human society into a new phase of development.

Nuclear fusion can be considered the most fundamental way to release energy in nature.
The allure of nuclear fusion also lies in its abundance of raw materials and the cleanliness of the production process. Currently, the most efficient isotope for achieving nuclear fusion is hydrogen, which is extremely abundant on Earth. Although the hydrogen content in the atmosphere is not high, the oceans serve as a vast reservoir of hydrogen. Scientists estimate that each liter of seawater contains 0.03 grams of deuterium (a hydrogen isotope). The energy released by these deuterium atoms through nuclear fusion is equivalent to burning 300 liters of gasoline. The global ocean reserves amount to 1.38 billion cubic kilometers, containing enough fusion fuel for human civilization to use for tens of thousands of years.
Moreover, no radioactive waste is produced in this type of nuclear fusion reaction. Its primary product is helium, a gas that is harmless to the human body and widely used in industry. In contrast, although current nuclear fission technology can also provide a significant amount of energy, its uranium raw material reserves are very limited, and handling nuclear waste is both challenging and costly. Therefore, from the perspective of cleanliness and environmental protection, nuclear fusion is undoubtedly a better energy option for the future.
In recent years, research on nuclear fusion has made significant advancements worldwide. As a groundbreaking project in the field of controllable nuclear fusion, the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) gathers leading scientists and technical forces from various countries and regions, including China. The goal of ITER is to verify the scientific and technical feasibility of using nuclear fusion energy for peaceful purposes and to lay the groundwork for the construction of commercial fusion reactors in the future.
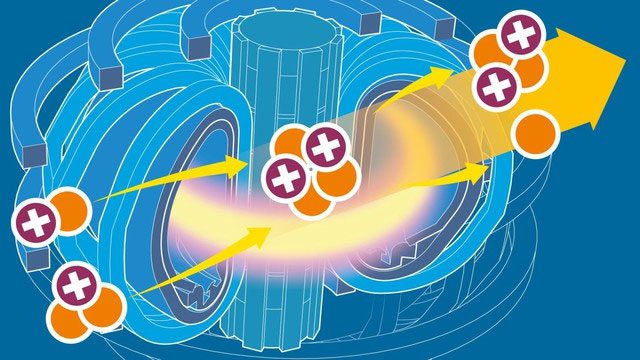
No radioactive waste is produced in this type of nuclear fusion reaction.
In addition to the ITER project, the United States, Europe, Japan, and other countries are also actively promoting their own nuclear fusion research plans. For instance, the National Ignition Facility (NIF) in the United States is committed to achieving nuclear fusion ignition using laser technology; the European Joint European Torus (JET) is exploring high-temperature plasma heating and confinement technologies; these are significant breakthroughs made in the field of laser fusion.
The progress of these scientific research projects not only helps humanity gain a deeper understanding of the principles of nuclear fusion but also brings the potential for commercial applications of nuclear fusion. In the future, as technology continues to advance and costs gradually decrease, nuclear fusion is expected to become the new dominant energy generation after wind and solar power, providing a strong impetus for the sustainable development of human society.

Nuclear fusion is expected to become the new dominant energy generation.
Nuclear fusion demonstrates an attractive development prospect with its enormous energy potential, abundant raw materials, and clean production processes. It is expected not only to address the energy crisis and environmental pollution issues that humanity faces but also to promote scientific and technological progress and industrial upgrades. Although nuclear fusion technology is still in the experimental stage and is far from commercial application, we believe that with the joint efforts of all humanity, this dream will eventually become a reality. Let us look forward to that day and welcome a future world illuminated by nuclear fusion.


















































