The European Southern Observatory (ESO) has released stunning updated images of the NGC 2024 nebula in the constellation Orion.
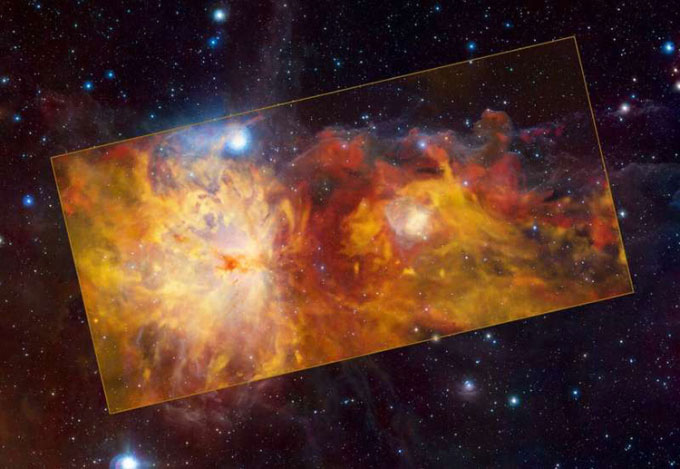
Latest image of the NGC 2024 nebula released on January 4. (Image: ESO)
The processed infrared and radio wave images, captured by the APEX telescope operated by ESO in the Atacama Desert of Chile, reveal the giant clouds of gas and dust in NGC 2024 glowing red like a raging fire.
“The nebula contains a young star cluster at its center emitting high-energy radiation, causing the surrounding gas and dust to shine brightly,” ESO explains.
Despite being nicknamed “the flame nebula”, the clouds of NGC 2024 are actually very cold, with temperatures just slightly above the threshold of “absolute zero”, or 0 Kelvin (approximately -273.15°C). Most of the brightness results from the recombination of ionized electrons and hydrogen.
The new images also reveal the speed at which gas flows within NGC 2024, with the red clouds moving away from us faster than the yellow clouds.
Located 1,300 to 1,600 light-years from Earth, NGC 2024 is one of the most active “star nurseries” in the vicinity of the Solar System. X-ray and infrared observations show that the nebula contains hundreds of young stars, with the youngest objects situated near the center.


















































