During the process of setting up camera traps to collect additional data on wildlife for the purpose of enhancing documentation and improving the chances of biodiversity conservation in the designated forest area, the Management Board of Hòn Bà Nature Reserve captured images of the Java Mouse-deer.
At Hòn Bà, the Java Mouse-deer is commonly found in forests planted with species such as rubber trees and eucalyptus, as well as in areas of forest recovering after logging at altitudes ranging from 50 to 300 meters, particularly in ecological restoration zones. They can be seen both day and night.
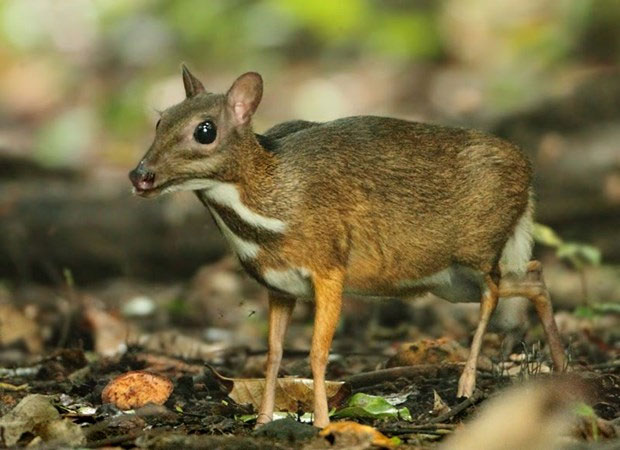

Java Mouse-deer. (Photo: Ydvn).
Previously, the staff of the reserve had seen them many times but were unable to capture images due to the species’ shy nature.
According to the Department of Environmental Education and Forest Environmental Services, the Management Board of Hòn Bà Nature Reserve states that the Java Mouse-deer is scientifically named Tragulus javanicus. This mammal belongs to the mouse-deer family and the even-toed ungulate order, making it the oldest hoofed mammal species, which is rare and only survives in the tropical forests of Southeast Asia.
In Vietnam, the Java Mouse-deer has been recorded from Lạng Sơn to Tây Ninh. However, in the northern provinces, they are nearly extinct.
In the southern provinces, the population of Java Mouse-deer has significantly decreased due to the shrinking forest area.
In the Vietnam Red Book (2007), they are classified as VU (Vulnerable), and there is currently no government document for their protection.
When fully grown, each Java Mouse-deer has a body length of about 40-50 cm, an average weight of 1.3-2.3 kg, lacks preorbital glands, has elongated canine teeth (with males having longer canines than females), and is missing upper incisors; their legs are very slender, with digits 3 and 4 being well-developed.
Their fur is short and fine, with a reddish-brown color on the upper side fading to the sides, a dark stripe along the back, black fur along the nape, and two white stripes at the chin and throat, with one vertical stripe in the middle being free and bushy tail fur.
The Hòn Bà Nature Reserve is located about 40 km southwest of Nha Trang city, covering four districts: Cam Lâm, Diên Khánh, Khánh Sơn, and Khánh Vĩnh (Khánh Hòa Province).
The Hòn Bà ecosystem is rich, with many areas still relatively pristine; it boasts a diverse range of flora and fauna, including many rare and endemic species.
According to incomplete statistics, Hòn Bà Nature Reserve has 321 species from 90 families across 27 orders, including 56 rare animal species. Specifically, it is home to 70 species of mammals from 23 families in 9 orders.
Compared to the national mammal resources of 252 species, 41 families, and 14 orders, the resources in this reserve account for 27% of the species, 56% of the families, and 64% of the orders.
Notable mammal species in this reserve include the Black-shanked Douc (Nomascus gabriellae), the Black-footed Gray Langur (Pygathrix nigripes), the Rhesus Macaque (Macaca mulatta), and the Assamese Macaque (Macaca arctoides)…