The startup MagicLab introduces humanoid robots at a factory to train for various tasks.
MagicBots collaborating in the factory. (Video: MagicLab).
MagicBot by MagicLab performs various tasks such as production monitoring, material handling, component picking and sorting, inventory checking, and management. The humanoid robots also demonstrate effective collaborative operation on a small scale, proving that they can work efficiently together, reported Interesting Engineering on December 9.
In January, MagicLab unveiled their third-generation humanoid robot named MagicBot, designed to compete with Boston Dynamics’ Atlas robot. In February, they shared a video showing the robot making marshmallows, performing magic tricks, and dancing. MagicLab has joined the wave of companies deploying robots in an industrial context as China aims for mass production of humanoid robots by 2025 and seeks to dominate the market by 2027. Founded in December 2023, MagicLab (Magic Atom Robotics Technology) focuses on revolutionizing research and rescue, logistics, and manufacturing with humanoid robots.
In the new video, several MagicBot humanoid robots work together. One robot transfers a material tray to another robot at a workstation after lifting it from an assembly point. Their effective collaboration is showcased as the second robot retrieves objects from a box and passes them to processing machinery.
“Compared to traditional composite robots, humanoid robots are more adaptable to complex environments due to their human-like features and can be adjusted for different tasks and production line layouts. They are particularly suited for fields such as computing, communications, consumer electronics, household appliances, and many other factories that frequently change production lines,” said Wu Changzheng, director of Magic Atom.
Currently, the MagicBot humanoid robots used in the factory can rotate freely up to 42 degrees. Its arms can lift loads weighing up to 20 kg, while the entire body can transport 40 kg of goods. Made from ultra-lightweight, high-strength materials to enhance efficiency, MagicBot has a battery life of up to 5 hours during continuous movement and operation. Besides making marshmallows on trays, folding children’s clothes and placing them in baskets, the remote-controlled robot can also water plants and dance to lively music. It also demonstrates impressive dexterity when handling small objects and performing various tasks with smooth agility.
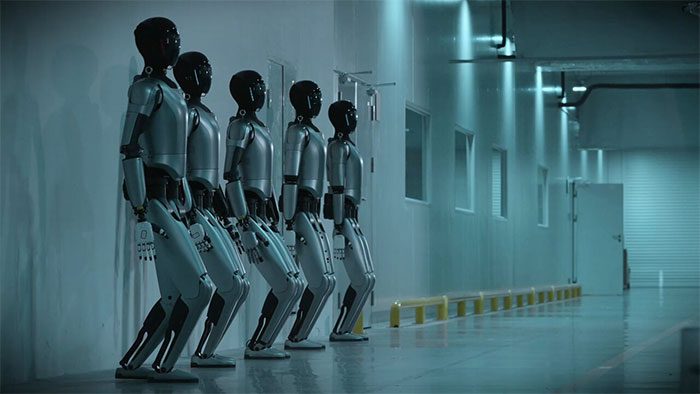
MagicBot humanoid robot in the factory can rotate freely up to 42 degrees.
MagicBot achieves these advanced skills by using high-torque miniature servo actuators combined with ultra-sensitive multi-dimensional pressure sensors, allowing for exceptionally smooth hand movements. The developers emphasize that six servo actuators play a key role in enabling it to manipulate objects flexibly, ensuring users can control precision and intuitiveness. The robot’s hands excel at grasping objects of various shapes, sizes, weights, and materials, including soft, slippery, or flexible items.
According to the manufacturers, MagicBot can mimic about 70% of human hand movements, meeting the demands for a wide range of applications, from household tasks and public services to specialized industrial operations and hazardous material handling. MagicBot is also equipped with multiple sensors. Data from the sensors is processed by an algorithm to create super-cognitive sensing, allowing the robot to perceive its environment in 360 degrees and recognize semantics.
According to Sango Automation, the cognitive capabilities allow MagicBot to plan safe pathways, avoid obstacles, and reach operational points effectively using self-developed orientation algorithms. Through reinforcement learning, MagicBot continuously improves its ability to recognize environments, make decisions, and perform tasks. MagicBot utilizes four types of training data: synthetic data, remote operation data, imitation learning data, and real-time field data. To optimize data usage, the MagicData AI engine team is focused on data labeling, processing, and training simulations.
The new MagicBot robot, expected to launch in early 2025, will enter small-scale production and can be deployed in various industries and commercial sectors.


















































