There are many bizarre natural phenomena on Earth that you may never have seen, such as fire rainbows, red tides, or lightning strikes on volcanoes. However, when it comes to the most incredible natural phenomena, we must consider what is happening in the vast universe, which holds many mysteries that we have yet to explore.
1. Glass Rainstorms
HD 189733b, located 63 light-years away from Earth, is known as a counterpart to Jupiter, but it has far more extreme weather conditions. The surface temperature of this planet can reach up to 980 degrees Celsius, with winds consistently blowing at 6,400 km/h. Under such harsh weather conditions, it seems unlikely that any object could exist on its surface.
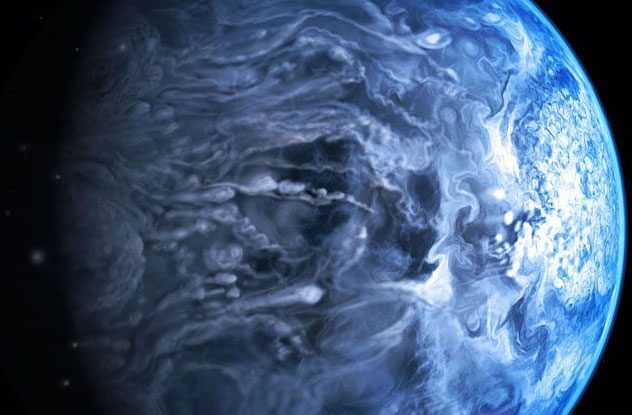

Even the rocks on this planet vaporize every second, causing it to lose about 600 million kilograms of mass each second. Although this planet is not too far from Earth, its extreme conditions prevent scientists from clearly observing what is happening on its surface.
Scientists had to use indirect observation methods by tracking the light reflected from the planet onto its stars, discovering that this planet also has a blue atmosphere similar to our Earth. However, what makes it unique is that this atmosphere is a massive storm continuously moving, primarily composed of silicate glass particles. This composition reflects sunlight, giving it a color similar to Earth’s.
2. Crystal Rain
You may have heard of hail or meteor showers, but crystal rain is a more bizarre phenomenon that can only be seen in space. Star HOPS-68, located 1,350 light-years from Earth, is a star that closely resembles the Sun in its early formation. Surrounding this star is a cloud of gas and dust, primarily composed of green olivine crystals (a type of gemstone on Earth made mainly of iron and magnesium).
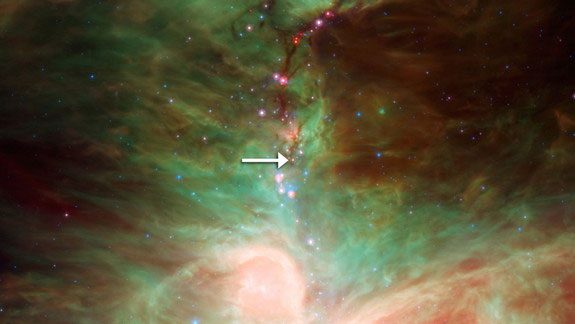
What makes this phenomenon special is that due to the relatively cold temperature of these gas clouds (around -170 degrees Celsius), olivine crystals condense into small particles and fall like a spectacular blue crystal rain.
This extraordinary phenomenon has been observed by NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope. Similar crystals have also been found in comets in the outer regions of Earth. Scientists believe that these gemstones may have formed in the early stages of the solar system when comets bombarded the planets during the cooling process.
3. Mercury Clouds
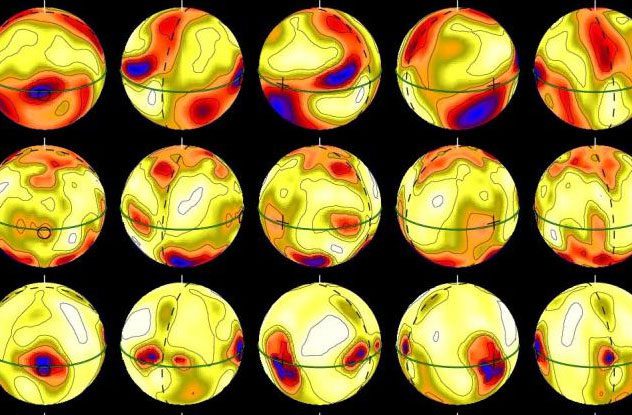
Alpha Andromedae, also known as Alpheratz, is the brightest star in the Andromeda constellation. Additionally, this star has a unique feature: it is the only star discovered to have a weather system similar to that of Earth. Scientists have observed changes in the concentration of mercury on the surface of this star.
Researchers continued to monitor it over the past seven years and found that this change is a temporal movement. This process resembles the movement of the atmosphere and clouds on Earth. They believe that this star has very special mercury clouds that exhibit a temporal movement. However, they have yet to explain how these mercury clouds form or why they move so consistently. Scientists only know that there is no magnetic field on this star, a necessary condition for such phenomena to occur.
4. Superheated Waves
HD 80606b is another “hot Jupiter” that is four times larger than the original we know. With a flattened elliptical orbit, the planet takes 111.4 days to orbit its star and is located 0.88 times the distance from Earth to the Sun. While observing this planet, scientists discovered significant changes in thermal radiation on its surface.
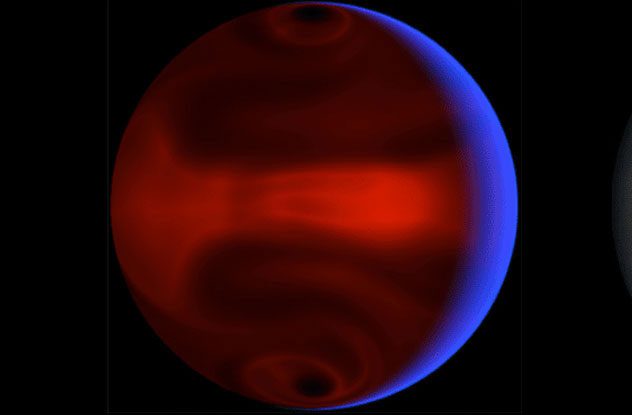
The sudden change in radiation over just a few hours causes the surface temperature of the planet to double from 500 degrees Celsius to over 1,000 degrees Celsius. This temperature fluctuation phenomenon is the largest compared to all other planets that scientists have observed.
However, it doesn’t stop at temperature changes; this special phenomenon causes unexpected radiation explosions. Such an explosion can generate winds on the surface reaching up to 17,000 km/h and create superheated waves engulfing the entire planet. At that moment, the planet is surrounded by a wall of wind and fire, making it impossible for any object to approach.
5. Rain of Sand and Molten Iron
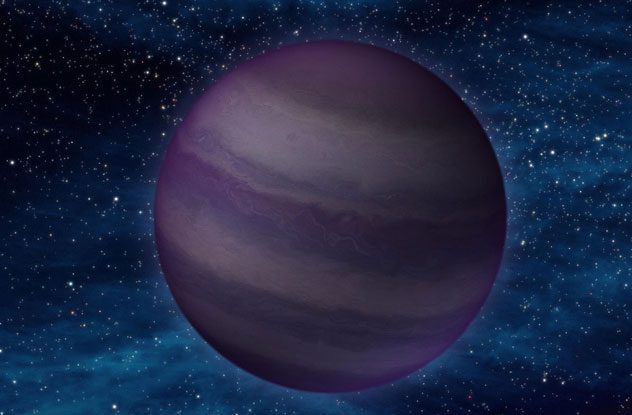

Brown dwarfs form from stars that lack the necessary mass and material to ignite. Therefore, they are relatively cold, and some brown dwarfs can even be colder than the human body. Low temperatures mean they cannot emit light detectable by telescopes. Among them is brown dwarf 2M2228, located 39.1 light-years away, with light changes on its surface occurring every 90 minutes.
This variation results from clouds moving on the surface of the brown dwarf in storms the size of Earth. The surface temperature of the star is about 600-700 degrees Celsius, so the clouds consist of strange materials, including sand and droplets of molten iron.





















































