Surprisingly, the “ghost” species of a mysterious 50,000-year-old girl has not disappeared. They still exist, lurking in our very bloodline.
According to Science Alert, a team of scientists from Pompeu Fabra University (Spain) and the University of Tartu in Estonia utilized AI (artificial intelligence) to analyze a “tangled mess” in the prehistoric bloodlines of humanity, uncovering a previously unknown “ghost ancestor.”
This refers to an ancient human species represented by a famous fossil – a teenage girl discovered in the Denisova Cave in Siberia, Russia, in 2018. Upon her discovery, the well-preserved skeleton of this young girl astonished scientists as it exhibited traits resembling both Neanderthals and Denisovans.
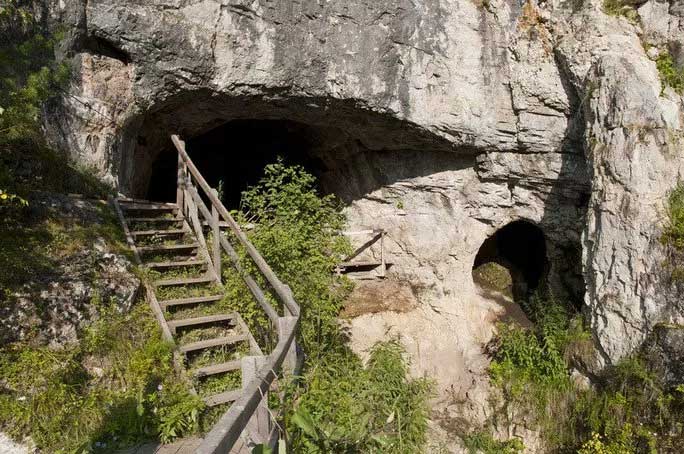

Denisova Cave in Siberia, Russia – (Photo: Discover Magazine)
Neanderthals and Denisovans are two extinct human species that vanished around 30,000 to 40,000 years ago and belong to the genus Homo alongside Homo sapiens (modern humans). The hybrid girl in Russia was once speculated to be a direct offspring of a mixed-race union between Neanderthals and Denisovans.
However, new findings suggest she likely belonged to a ghost species – literally ghosts, as they no longer exist directly but have left traces in the DNA of present-day Eurasians.
In the new study, scientists employed a technique known as Bayesian inference, discovering evidence of “third-party admixture” in our Homo sapiens lineage. Many modern Europeans and Asians are indeed descendants of these hybrids with the ghost species.
As is known, our bloodlines are not purely homogenous but have mixed with two ancient species, Neanderthals and Denisovans, through a series of interspecies marriages. However, thanks to complex algorithms designed to sift through a complicated genetic tapestry of ancient and modern humans, a “third partner” has emerged.
This ghost species has never been documented in the fossil record – evolutionary anthropology. “They are related to the Neanderthal and Denisovan branches or may have diverged early from the Denisovan lineage,” the researchers stated, also not ruling out the possibility that hybrids of the two species could have separated and formed a new species.
All findings inadvertently align with the unusual genetic traces of the mysterious hybrid girl from Denisova Cave, Russia, suggesting that she may be the only representative of this ghost species ever found through tangible evidence.
It is certainly a distinct species that has separated and evolved in its own way. “When we remove parts of the Neanderthal and Denisovan genes, something very different remains in the genome,” asserted evolutionary biologist Jaume Bertranpetit from Pompeu Fabra University.
The study has just been published in the scientific journal Nature Communications.