The driving force behind the development of this species of chimpanzee is even built on sexual behavior, occurring among all individuals in the group.
Most notably in sexual activities is the bonobo (scientific name: Pan paniscus), which is related to the common chimpanzee and is often referred to as pygmy chimpanzee.
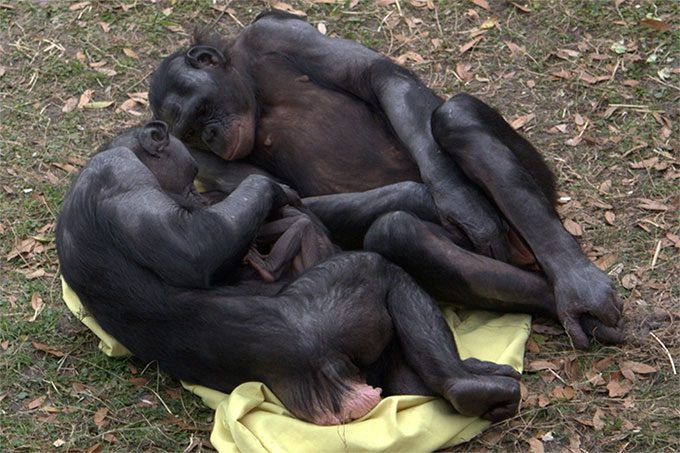

Along with the common chimpanzee, the bonobo is the species most closely related to humans. (Image: Wikipedia).
These chimpanzees are referred to by scientists as a “sex-crazed species”, as every individual is willing to engage in mating behaviors that last throughout the day and night. They do this not only to meet reproductive needs but also to build bonds between individuals in the group.
“It is not an exaggeration to say that the driving force behind the development of this group of chimpanzees is built on sexuality,” stated IFLscience.
What is particularly interesting about bonobos is that they are not limited to heterosexual sexual behaviors. Researchers have observed many individuals engaging in sexual behaviors regardless of gender.
Specifically, female bonobos engage in genital rubbing with one another, while males are often seen performing oral sex on other males and frequently embracing.
Researchers believe that such homosexual behavior seems to mark an important social function in many mammal species.
Along with maintaining strong social relationships, it also alleviates sexual tension, reducing the risk of aggression and conflict among competing males.
The positive impact of homosexual behavior appears to explain why there is so much independent evolution in nature, which may be a classic example of convergent evolution.
“The characteristics of the repeated evolutionary transitions to the same state may be indicative of the convergent evolution process,” the researchers stated.
“Although it may arise from random evolutionary processes, the association with natural selective environments indicates new evidence occurring in adaptive evolution.”