Images from the International Space Station (ISS) reveal mysterious blue spots glowing in Earth’s atmosphere. What are they?
Recently, an astronaut aboard the International Space Station (ISS) captured a strange image of Earth from space. The photo features two unusual blue spots, shimmering and floating in the atmosphere.

Two unusual blue spots glowing in Earth’s atmosphere. (Photo: NASA).
After being shared, many conspiracy theorists immediately suggested that these could be supernatural phenomena or even spacecraft from extraterrestrial beings approaching Earth.
However, scientists at NASA’s Earth Observatory have a different perspective. According to their analysis, while these may appear to be supernatural phenomena, they are actually the result of two unrelated natural occurrences happening simultaneously.
Specifically, the bright streak at the bottom of the image is actually a large lightning bolt located in the Gulf of Thailand, although such lightning is often difficult to see from the ISS due to being obscured by clouds.
Nasa explains that this lightning bolt seems particularly large, occurring in an open area, and appears to be directed towards the top of a cloud. This causes the lightning to illuminate the “cloud walls,” creating a prominent glow when observed from space.
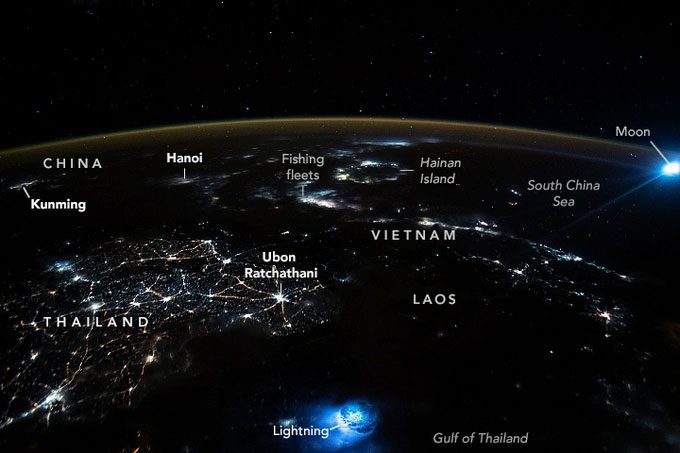
NASA identifies the source of the two unusual glowing spots.
The second bright spot visible in the upper right corner of the image is the result of distorted light from the Moon.
Observers explain that in the image, the Moon is positioned at an angle where its reflected light travels directly through Earth’s atmosphere, transforming into a blue glowing spot with a slightly hazy halo.
This effect typically occurs when some rays of light from the Moon scatter off small particles in Earth’s atmosphere. They appear blue because this light has the shortest wavelength and the highest scattering potential.
A similar effect explains why the sky appears blue during the day. This is due to the blue wavelengths of sunlight scattering more and becoming more visible to the human eye, according to NASA.




















































