Sterilization is a contraceptive method that offers a reliable, long-term solution and is utilized by many countries around the world. In Vietnam, due to various misconceptions, people still hold a cautious view towards this method. The following article will provide basic information about sterilization procedures for both men and women.
Understanding Sterilization in Men and Women
1. What is Sterilization?
Sterilization is a safe contraceptive method that provides a permanent solution, with a relatively simple procedure. For women, the method is tubal ligation and for men, it is vasectomy. Both procedures do not adversely affect health, sexual relationships, or the psychological well-being of either gender.
2. Female Sterilization – Tubal Ligation
2.1. What is Tubal Ligation?
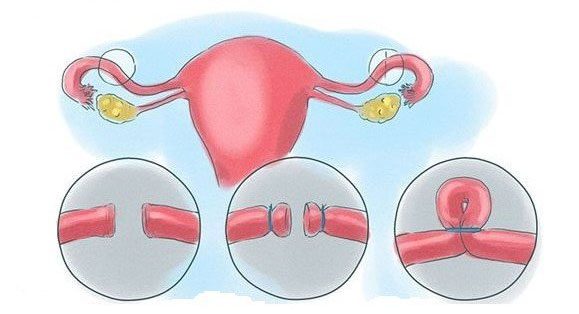
Tubal ligation prevents the egg from moving into the uterus.
Tubal ligation is a method that provides permanent contraception for women, typically performed on those over 30 years old who have two or more children and do not wish to have more. Essentially, tubal ligation involves blocking the fallopian tubes, preventing the egg from moving into the uterus, thereby stopping it from meeting sperm. There are several techniques for performing tubal ligation, including tying, cutting, clamping, and knotting.
Tubal ligation is a safe and effective contraceptive method but is not completely foolproof. The pregnancy rate after this procedure within one year is less than 1 in 100 women. After 10 years, the pregnancy rate varies from fewer than 1 to under 4 in 100 women, depending on the type of method used. Tubal ligation does not protect against sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea, syphilis, genital warts, or HIV. Therefore, it is advisable to use condoms during sexual intercourse to prevent the spread of these diseases.
2.2. The Best Time to Undergo Tubal Ligation
According to Dr. Pooja Shah from Banner Medical Center in Chandler, Arizona, the best time to perform tubal ligation is immediately after a cesarean section (C-section) or within the first 24-36 hours after a vaginal delivery. It is important not to delay beyond 48 hours post-delivery. This is recommended as it reduces the risk of bleeding and prevents the mother from undergoing multiple painful procedures. Furthermore, sterilization through tubal ligation is most effective when performed before the uterus returns to its normal position, usually within a few hours or days after birth.
However, if there are abnormal conditions during delivery such as premature rupture of membranes, fever during labor, or if uterine exploration is required and there are risk factors for infection, the procedure should be postponed. Specifically, it can be performed six weeks postpartum.
Typically, the best time for the procedure is 3-5 days after the menstrual cycle has ended, when the couple is abstaining from intercourse. This not only enhances the effectiveness of tubal ligation but also avoids early and difficult-to-detect pregnancies.
2.3. Does Tubal Ligation Affect Health?
Tubal ligation is an effective and safe contraceptive method. It only affects the fallopian tubes and has no impact on the ovaries. The ovaries are responsible for hormone secretion and regulating the menstrual cycle. Therefore, tubal ligation does not affect hormonal balance, menstrual cycles, or sexual activity.
After undergoing tubal ligation, women may experience abdominal pain, nausea, dizziness, irregular menstrual cycles, and heavier menstrual bleeding than usual. Notably, there is a risk that the fallopian tubes may reconnect, leading to an ectopic pregnancy. However, this risk is quite low, approximately 0.01% – 1%.
3. Male Sterilization – Vasectomy
3.1. What is Vasectomy?
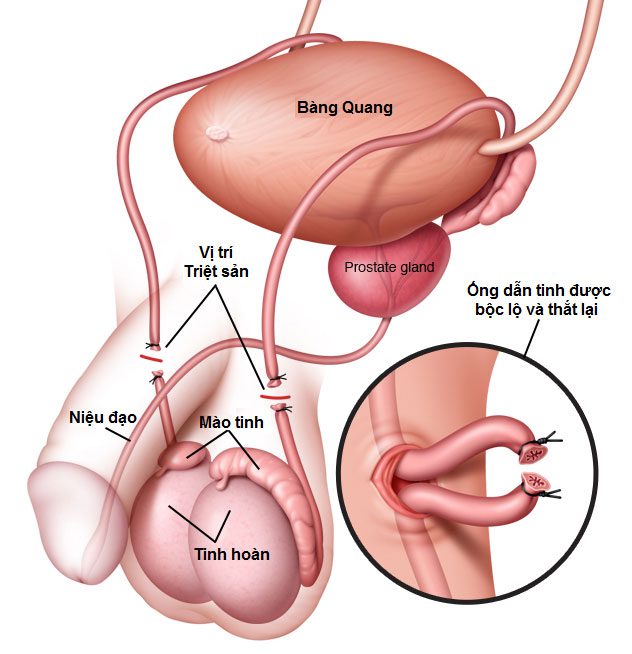
Vasectomy prevents sperm from being released.
Vasectomy is a method of male sterilization, performed by cutting or tying the vas deferens to prevent sperm from being released. It takes about 2-4 months for the semen to be completely sperm-free. It is advisable to use another contraceptive method or abstain from sexual intercourse until sperm-free status is confirmed.
Vasectomy is performed by creating one or two small openings in the scrotum, pulling the vas deferens through the opening, then cutting a small section of the vas deferens and sealing both ends with laser or electrocautery. This method is contraindicated for individuals with bleeding disorders, abnormalities in the scrotum such as inguinal hernia, varicocele, and other complications in the spermatic cord.
3.2. Does Vasectomy Have Any Effects?
Vasectomy is generally considered safer than female sterilization and only requires local anesthesia. Risks associated with vasectomy may include bleeding or infection. Similar to female tubal ligation, vasectomy does not prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases.
Vasectomy is a straightforward procedure that causes minimal discomfort and does not affect the sexual activities of the patient. To alleviate the burden of childbearing on women, husbands should consider permanent sterilization.
Patients can resume sexual activity about a week after the vasectomy procedure.
3.3. Who Should Consider Vasectomy?
Individuals who should consider using this method include:
- When both partners feel they have enough children and do not wish to have more.
- When either partner has a hereditary condition that may result in unhealthy offspring.
Some contraindications for vasectomy include:
- Bleeding disorders
- Sexual dysfunction
- Abnormalities in the scrotum such as inguinal hernia, varicocele, hydrocele, chronic infections, and other complications in the spermatic cord.
Disability and death caused by deep-sea lobster
Strange anglerfish with bright white eyes caught off the coast of Australia




















































