 |
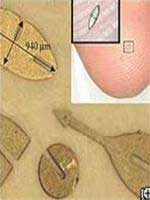
| The magnetic frequency will stretch the robot, making it no larger than a fingerprint. A frequency of 2 kilohertz can move the robot, stretching it small enough to be inserted into blood vessels. |
A miniature robot that can be injected into the body via a syringe will be used by doctors to analyze health conditions, deliver medication, or perform surgeries in extremely small areas.
This ultra-miniature biomedical robot system has been developed by a team of scientists at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology in Zurich, Switzerland. It is the smallest device in its category and has been successfully tested in the laboratory.
This minimally invasive robot is specifically designed to navigate through blood vessels of the heart or fluids located behind the eyes and in the ears, allowing for diagnosis and treatment of diseases while reducing patient discomfort and accelerating recovery time.
“Another application we are actively considering is using this device for eye surgery, where it would be inserted into the eye, reaching the retina to deliver medication to the small retinal veins that are as thin as human hair,” said Brad Nelson, a professor specializing in robotics and intelligent systems, and the head of the research team.
Unlike most conventional mobile robots, which either use batteries or are connected to an electric cable for control, this robot operates using a magnetic field generated by a machine. For example, a frequency of 2 kilohertz can activate the robot, stretching it small enough to enter blood vessels. A frequency of 3 kilohertz can adjust a pump to deliver medication into the bloodstream…
This invention will be presented for the first time at the 8th International Conference on Computer Imaging and Computer-Assisted Medicine next October.


















































