In the following article, we will explore the phenomena of solar and lunar eclipses. Why are these events so captivating for astronomy enthusiasts?
Essential Facts About Solar and Lunar Eclipses
What is a Solar Eclipse?
A solar eclipse is a phenomenon where the Sun is obscured by the Moon as viewed from Earth.
When Does a Solar Eclipse Occur?
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes directly between Earth and the Sun, causing the Moon to completely or partially cover the Sun.
For a solar eclipse to happen, the Sun, Moon, and Earth must be aligned in a straight line or very close to it. This alignment is referred to by astronomers as syzygy. This can only occur during a new moon.
Although a new moon is necessary for a solar eclipse to happen, not every new moon results in an eclipse. This is because the plane of the Moon’s orbit around Earth is tilted about 5° relative to the plane of Earth’s orbit around the Sun (the ecliptic plane). The locations where these two orbital planes intersect are known as the lunar nodes. A solar eclipse can only occur when a new moon happens near these nodes.
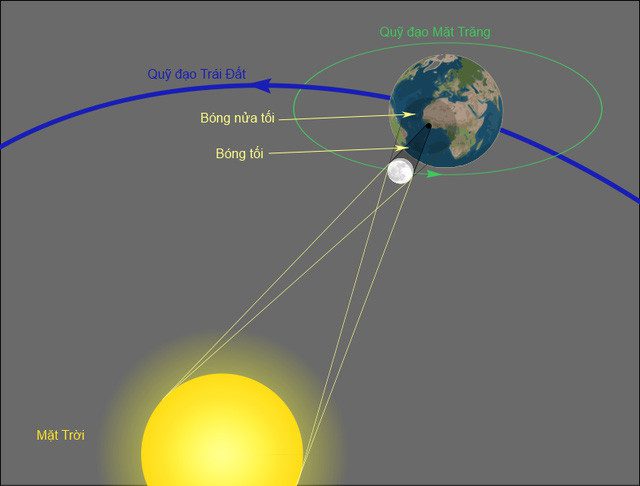
3D illustration of a solar eclipse.
Types of Solar Eclipses
There are four types of solar eclipses, defined by the shadow regions of the Moon on Earth’s surface.
- Total Solar Eclipse: A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon completely covers the Sun, creating regions of total darkness and partial darkness on Earth’s surface. A total solar eclipse can only happen when the Moon is near its perigee. You can observe a total solar eclipse if you are located on the path of the Moon’s umbra. Those not in the umbra but in the penumbra can view a partial eclipse.
- Partial Solar Eclipse: A partial solar eclipse occurs when the Moon does not completely cover the Sun’s disk, resulting in a penumbral shadow on Earth’s surface.
- Annular Solar Eclipse: An annular solar eclipse happens when the antumbra of the Moon’s shadow appears on Earth. The Moon’s disk obscures the central part of the Sun’s disk, leaving the outer edge of the Sun visible, resembling a ring. An annular eclipse can only occur when the Moon is near its apogee.
- Hybrid Solar Eclipse: Hybrid solar eclipses are extremely rare. They occur when an annular eclipse transitions into a total eclipse.
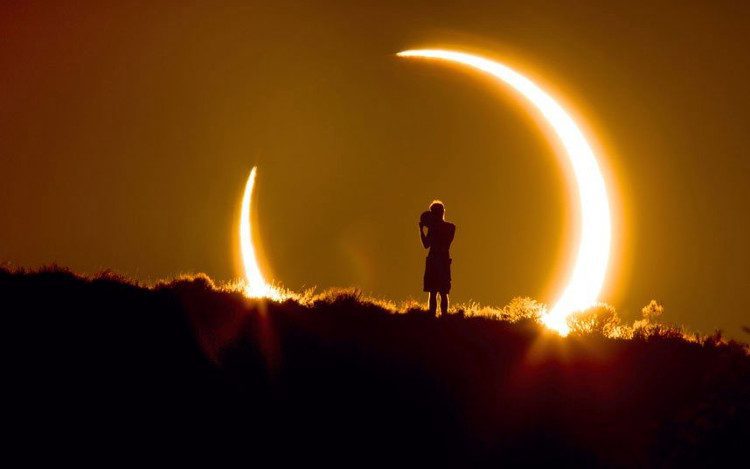

Annular solar eclipse.
How to Observe a Solar Eclipse
Observing a solar eclipse directly with the naked eye can cause permanent damage to your eyesight, so observers must exercise extreme caution. Here are some guidelines for safely observing a solar eclipse:
- Observing a solar eclipse with regular sunglasses, X-ray film, floppy disk material, or video tape is not safe, as these only reduce brightness and do not block harmful radiation.
- Indirect observation or using specialized filters such as welding glasses (shade 14) or solar filters from astronomy clubs is recommended.
- Observers can also use a piece of cardboard to project an image of the Sun through a small telescope or binoculars, or by creating a small hole in the cardboard and observing the image of the Sun projected on the ground through that hole.
What is a Lunar Eclipse?
A lunar eclipse is the phenomenon where the Moon is obscured by Earth’s shadow from sunlight, commonly referred to as a blood moon. It occurs when the Moon enters the umbra of Earth’s shadow while being opposite to the Sun.
Since the Moon does not emit its own light, we see it because sunlight reflects off the Moon’s surface. However, when the Moon, Earth, and Sun are aligned, Earth blocks sunlight from reaching the Moon, causing the Moon to gradually darken as it is hidden behind Earth’s shadow. This moment and phenomenon is known as a lunar eclipse.
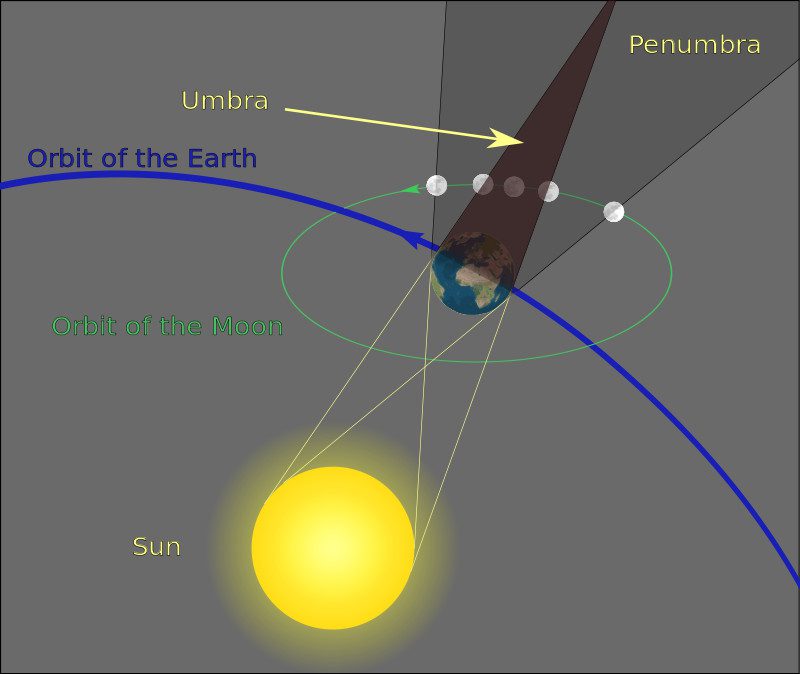
3D illustration of a lunar eclipse.
Types of Lunar Eclipses
- Total Lunar Eclipse: Occurs when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are aligned in a straight line, and the Moon enters Earth’s umbra. The Moon will appear dimmer and take on a reddish or dark orange hue. During a total lunar eclipse, sunlight entering the Moon’s shadow is refracted by Earth’s atmosphere, allowing only longer wavelengths (red, orange) to pass through, which is why the Moon often appears reddish. The maximum duration of a total lunar eclipse is 104 minutes (common occurrence).
- Partial Lunar Eclipse: Occurs when the Sun, Earth, and Moon are nearly aligned, causing part of the Moon to be obscured. The shadow of the Earth (black or dark red) can be seen covering part of the Moon. Partial eclipses can appear before and after total lunar eclipses and can last up to 6 hours.
- Penumbral Lunar Eclipse: Occurs when the Moon passes through Earth’s penumbral shadow. The Moon will appear dimmer and more obscure. Penumbral eclipses can be hard to see with the naked eye due to reduced sunlight.
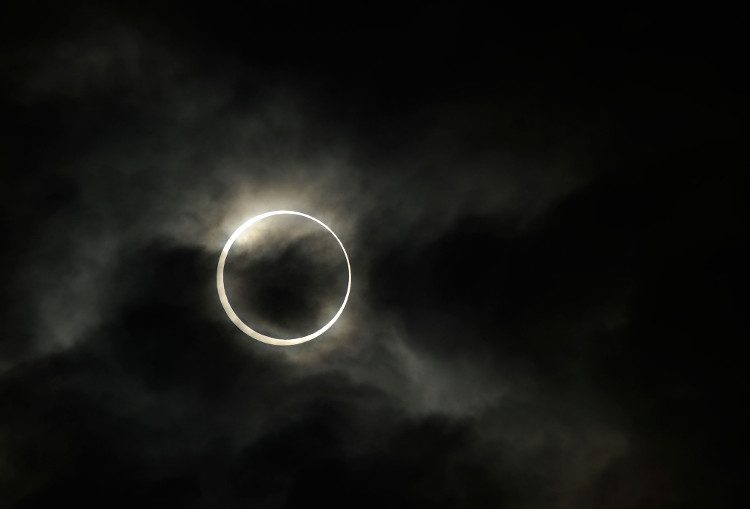

Lunar eclipse is one of the easiest astronomical events to observe.
How to Observe a Lunar Eclipse
A lunar eclipse is one of the easiest astronomical events to view. Just go outside and enjoy the spectacle. You do not need a telescope or any additional equipment. However, using binoculars or a small telescope can provide detailed images of the Moon’s surface.
How Many Solar and Lunar Eclipses Occur Each Year?
Typically, there are about four solar and lunar eclipses each year, which is the minimum number of eclipses that can occur in a year. Two of these four events must be solar eclipses. A maximum of seven eclipses can occur in one year, although this is very rare (five solar and two lunar, or two solar and five lunar).
There can be at least two and a maximum of five solar eclipses in a year. Beyond this, no more than two of the solar eclipses can be total. It is very rare to have five solar eclipses in a single year.
According to NASA, only about 25 instances in the past 5,000 years have had five solar eclipses in one year. The last occurrence was in 1935, and the next will be in 2206, when two total solar eclipses will occur in December.