For a long time, we have known that some bird species can mimic sounds, with parrots being perhaps the most famous example. In fact, the English language uses the verb “parrot” to mean “to repeat someone else’s words without understanding or thinking.” However, have you ever wondered why parrots possess this skill?
Reasons Parrots Like to Mimic Human Voices
It turns out that the ability to mimic sounds is not exclusive to parrots but has developed in all songbird species.
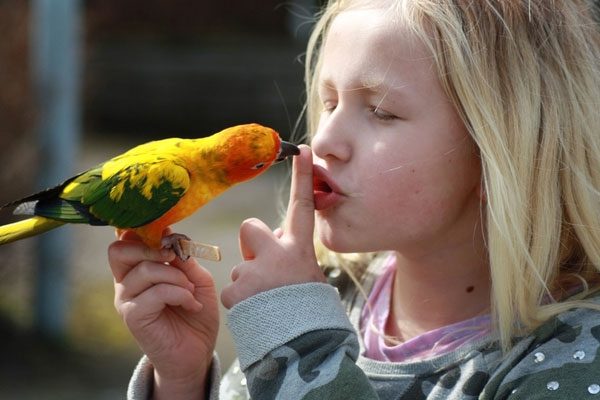

Parrots are known for their ability to mimic human voices.
Songbirds and Their Mimicking Ability
Some animal and bird species not only produce sounds characteristic of their species but can also replicate sounds from other species! Such animals are referred to as vocal mimics.
The majority of vocal mimics are songbirds. Other birds, known as “suboscines”, do not exhibit the ability to mimic sounds, except for a few species like parrots and hummingbirds.
About half of the bird species worldwide are songbirds. Research on zebra finches has shown that young birds learn and remember their species’ sounds by mimicking the songs of their fathers or nearby males, starting as early as one week after hatching and continuing until they reach maturity.
If isolated from their fathers during this critical learning period, young birds may develop abnormal calls. This highlights the importance of modeling in the song-learning process of birds.

A bird singing to call its kind.
Thanks to their innate song-learning ability, songbirds are very proficient in improving their pronunciation across various types of voices.
Purpose of Mimicking
In the 1930s, scientists observed that male parrots mimic better than female parrots. From this, they inferred that the ability to mimic sounds was a result of song learning to attract mates in male birds. Furthermore, male songbirds mostly mimic during mating season, confirming that the ability to mimic sounds evolved as a byproduct of song practice.
It has also been noted that some songbird species create sounds to distract predators.
Singing Skills and Evolution in Birds
Typically, a singer with a wide vocal range is more successful than one with a narrower range. Similarly, male larks with a broader vocal range to learn various songs will have higher chances of successful mating.
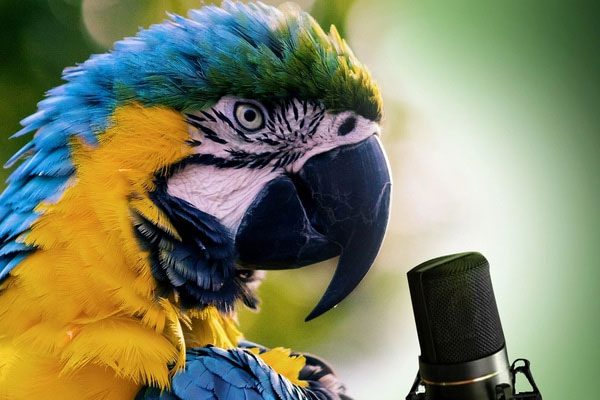

A parrot mimicking human speech.
Through evolution, birds with limited singing abilities were eliminated. Ultimately, songbirds developed such extensive vocal skills that they could not only mimic the voices of their own species but also those of other species.
Thus, the ability to mimic sounds emerged in songbirds as a byproduct of song learning.
Voice Mimicking in Parrots
Parrots are not classified as songbirds but are the most famous for their voice mimicking abilities. They can imitate complex pronunciations in human speech, learned from their caregivers.
The reason for this is not to attract mates or to ward off predators, as scientists previously thought. Pet parrots often mimic humans to establish social bonds, and they mimic other species in the wild for similar reasons.
Parrots Mimicking Human Speech and Language Learning in Humans
In a study involving an African Grey parrot, scientists observed that it not only mimicked human speech but could also learn hundreds of words, understand their meanings, recognize objects by name, and even count! This research has led scientists to believe that parrots do not merely mimic; their pronunciation is very similar to human speech.
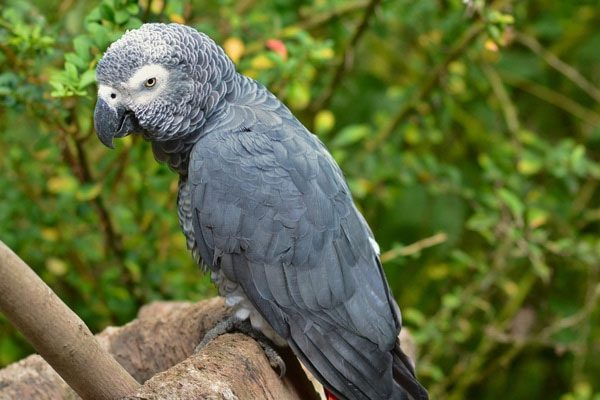

The African Grey parrot is famous for its ability to speak and has been studied.
This is a significant discovery, as humans are the only known species capable of using “language” until now, but this research indicates that parrots possess many abilities seen in humans, such as the capacity to recognize rhythm and count.
Thus, many studies suggest that parrots mimic human speech to enhance their social bond with their caregivers. However, scientists have yet to determine the reasons and methods behind voice mimicry in parrots and some other suboscine species, and whether this skill has evolved similarly to songbirds.
Why Can Parrots Mimic Human Voices So Well?
Parrots have a unique ability to replicate sounds they hear, whether in the wild or domesticated. Language is a product that developed solely within human society. In addition to the necessity of phonation (through the coordinated movements of the throat, tongue, teeth, and lips) to articulate sounds, a combination of vocabulary and language rules is required to effectively express thoughts.
For a parrot, sounds originate from an organ called the syrinx, located at the base of its trachea. Typically, many bird species have two vocal membranes within this organ, but parrots have only one. When sounds escape from the respiratory tract, parrots use their tongues and beaks to modulate them. Parrots can do this because they possess a uniquely flexible and powerful tongue.

The parrot’s brain contains many interconnected regions, allowing it to hear, remember, and speak.
Like other animals capable of learning sounds, a parrot’s brain contains interconnected regions that enable them to hear, remember, modify, and produce complex sounds. While songbirds have only one system in their brains, most parrots have an additional system.
According to scientists, this may help parrots be more flexible in learning the calls of their species and human speech. With this specialized anatomical feature, parrots can bark, shout, and memorize bits of information.