What are the impacts of this?
Everything around us is constantly changing, and although it may be happening more slowly than usual, it is still occurring right before our eyes. Did you know that the Pacific Ocean (which includes the South China Sea) is gradually shrinking while the Atlantic Ocean is expanding? The answer lies in the fascinating science of plate tectonics.
Before we explore why the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans are changing in size, let’s review the basic principles of plate tectonics.
The lithosphere is the outermost solid layer of the Earth. It includes the crust and the uppermost part of the mantle; this layer is divided into large and small plates. These plates move on the asthenosphere — a semi-fluid part of the mantle. Convection currents in the mantle are responsible for the movement of the plates.
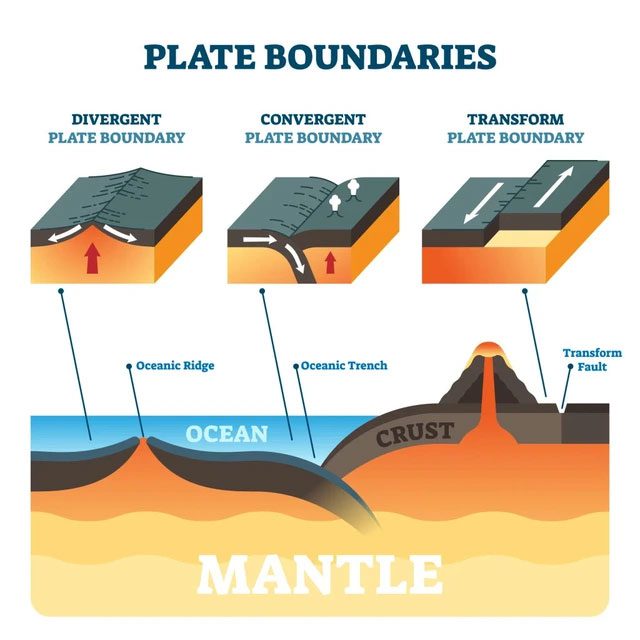
In plate tectonics, there are three types of plate boundaries: Divergent, Convergent, and Transform. (Source: VectorMine/Shutterstock).
Divergent, convergent, and transform are the three types of plate boundaries. Two plates move away from each other at a differgent boundary, creating new crust and causing the ocean floor to widen. Meanwhile, two plates move toward each other at a convergent boundary, where one plate may slide beneath the other, forming a subduction zone. At a transform boundary, two plates slide past each other parallel to one another.
This knowledge will explain why the Atlantic Ocean is expanding while the Pacific Ocean is shrinking.
Why is the Atlantic Ocean “expanding”?
The Atlantic Ocean on our planet is a natural wonder. It is a vast body of water that covers over 20% of the Earth’s surface. The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest ocean in the world, spanning an astonishing area of 106.5 million square kilometers. However, as scientists have pointed out, this number is changing.
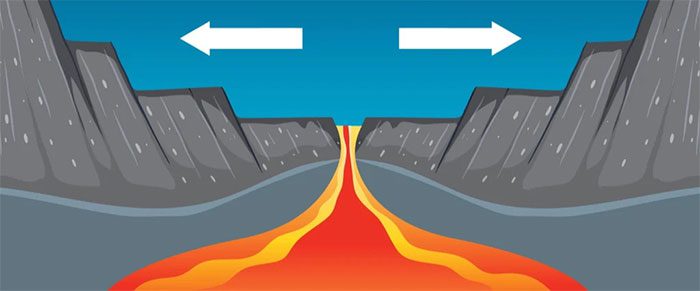
Divergent plate boundaries are responsible for adding new oceanic crust, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. (Image Source: BlueRingMedia/Shutterstock).
So why does the Atlantic continue to expand? The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a long chain of underwater mountains separating two tectonic plates: the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate. This movement causes magma from the Earth’s mantle to rise to the surface, leading to the formation of new crust. This process is known as seafloor spreading.
This seafloor spreading can create a new valley filled with water, resulting in the formation of a new ocean basin beneath the Atlantic Ocean.
Why is the Pacific Ocean shrinking?
The Pacific Ocean is the largest ocean in the world, covering an area greater than 165 million square kilometers, which accounts for 46% of the total surface area of the Earth.
To answer the above question, think of the Pacific Ocean as a gigantic swimming pool (without water). Now, imagine trying to fill that pool with all the water from all the rivers, lakes, and streams on Earth. It would take over 500 years to fill that pool — of course, not accounting for evaporation or leaks.
Despite its massive size, the Pacific Ocean is actually shrinking. This is due to the Pacific Plate — the largest tectonic plate on Earth — being pushed down beneath other plates in a process known as subduction.
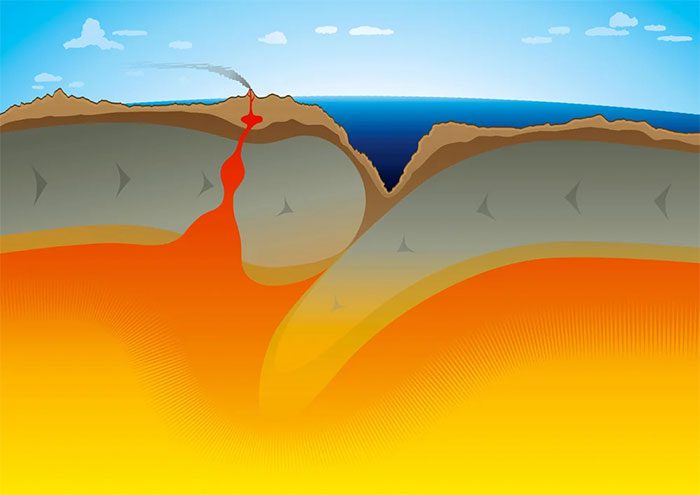

Subduction is the reason the Pacific Ocean and the Ring of Fire volcanic chain are shrinking. (Image Source: daulon/Shutterstock).
The Pacific Plate shrinks as it moves deeper into the Earth’s mantle, causing the ocean above it to contract.
Thus, the movement of tectonic plates is the reason our ocean sizes are changing, though the process occurs slowly. The Atlantic Ocean is expanding due to the formation of new oceanic crust at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, while the Pacific Ocean is shrinking as the Pacific Plate subducts beneath surrounding plates. These geological processes are ongoing and have shaped the world as we know it for millions of years.
Oceans are not just vast bodies of water; they are the result of tectonic interactions that continue to shape the geology of our world.




















































